RTN4和 TG2在增生期血管瘤组织中高表达及其临床意义
唐 甜 葛 伟
(武汉大学人民医院肿瘤Ⅱ科,武汉 430060)
RTN4和 TG2在增生期血管瘤组织中高表达及其临床意义
唐 甜 葛 伟
(武汉大学人民医院肿瘤Ⅱ科,武汉 430060)
目的 探讨 RTN4和 TG2在人皮肤血管瘤组织中的表达及其临床意义。方法 收集武汉大学人民医院病理科2008年 -2011年皮肤毛细血管瘤存档蜡块40例,其中男性15例,女性25例。采用免疫组织化学S-P法检测40例皮肤血管瘤增生期、退化期及正常皮肤组织RTN4和 TG2表达水平,采用图像分析系统对 RTN4和 TG2的表达进行定量分析,并用 SPSS13.0软件对各组免疫组织化学反应阳性颗粒的平均光密度、阳性面积率做单因素方差分析和 SNK(q)检验。结果 增生期组 RTN4的表达明显高于退化期组和正常皮肤组,而后两组比较差异无统计学意义;增生期组 TG2的表达明显高于退化期组和正常皮肤组,而后两组比较差异无统计学意义。结论 RTN4和 TG2在增生期血管瘤组织中的表达明显高于正常皮肤组及退化组,提示RTN4和TG2在增生期血管瘤组织中表达上调,可能与瘤细胞的过度增殖,抗凋亡增强等有关。
血管瘤;RTN4;TG2;免疫组织化学
皮肤血管瘤是婴幼儿最常见的良性血管肿瘤,是由血管形成异常而引起的疾病,血管瘤的自然病程经历增生期、退化期和退化完成期三个阶段。血管瘤是通过未成熟的内皮细胞弥散增殖而快速生长,之后自发消退。一般认为毛细血管内皮细胞的增生与消退是血管瘤生长和消退的关键原因[l-2]。血管瘤虽然是一个良性肿瘤,本身对人体危害不大,一般不会发生生命危险,但是血管瘤生长的部位不同对人体的造成的危害的影响也不一样,如:面部血管瘤会影响容貌、头部血管瘤会影响头发生长、生殖部位血管瘤会影响生育、肝血管瘤会影响肝功能等。往往给患者及其家人带来极大痛苦,但关于血管瘤的发病机制,目前还未明了,因此对于皮肤血管瘤的临床治疗也是目前急待解决的关键问题。
RTN4又名 Nogo(Neurite Outgrowth Inhibitor ASY/RTN-X),RTN4是网状蛋白家族的成员之一,包含三个剪切变体:RTN4A,RTN4B,RTN4C,每个剪切变体在不同的细胞中发挥不同的生物学功能,广泛地参与了细胞分化成熟,增殖,凋亡,迁移,粘附,侵袭等各项功能的调控[3-4]。组织型转谷氨酰胺酶2(tissue transglutaminase 2,TG2)蛋白在人体分布较为广泛(如血管内皮细胞、平滑肌细胞以及成纤维细胞等),在不同的细胞环境中发挥截然不同的生理功能,与组织纤维化、神经退行性疾病、动脉粥样硬化和癌症等疾病的发生发展密切相关。近年来,大量研究表明 TG2在多数肿瘤细胞中上调表达,包括乳腺癌、卵巢癌、胰腺癌、结肠癌等[5-7]。但RTN4和 TG2在皮肤血管瘤组织中的表达尚未见报道。
本文应用免疫组织化学方法和图像分析技术检测了血管瘤增生期、退化期以及正常皮肤组织中RTN4和TG2的表达水平,探讨RTN4和TG2在血管瘤发生、发展过程中的作用机制,为临床上治疗血管瘤提供实验依据。
材料和方法
1.材料
1.1 材料来源
收集武汉大学人民医院病理科2008年-2011年皮肤毛细血管瘤存档蜡块 40例,其中男性 15例,女性25例。这些血管瘤所在的部位有头皮、前额、眼睑、耳背、颈部、背部、上臂、大腿、手和足的皮肤等。患者术前均未做任何辅助性治疗。
1.2 材料分组
将所有标本进行免疫组织化学 S-P法检测增殖细胞核抗原(proliferating cell nuclear antigen,PCNA),按 Mulliken分类标准并结合 PCNA的表达进行分组:石蜡标本中增生期血管瘤 22例,退化期血管瘤18例。另取距癌组织 5cm外的周围正常皮肤组织5例作对照。
1.3 主要试剂
即用型鼠抗人 PCNA单克隆抗体、兔抗人RTN4多克隆抗体、兔抗人 TG2单克隆抗体(购于北京中杉生物技术有限公司);超敏即用型SP通用型免疫组织化学试剂盒(购于福州迈新公司);DAB显色试剂盒及多聚赖氨酸(购于北京中杉生物技术有限公司)。
2.方法
2.1 免疫组织化学 SP法染色
组织切片常规脱蜡入水;抗原修复(柠檬酸缓冲液微波抗原修复法);滴加 3%过氧化氢,37℃湿盒孵育10min以抑制内源性过氧化物酶活性;正常羊血清37℃湿盒孵育 10min以减少非特异性背景;分别滴加一抗;滴加链霉素抗生物素蛋白-过氧化物复合物37℃湿盒孵育;滴加新鲜配置的 DAB显色液显色;苏木素复染;梯度酒精脱水,二甲苯透明,中性树胶封片并镜检;用 PBS代替一抗作为阴性对照组,购买的阳性片作为RTN4及TG2的阳性对照组,人正常皮肤表皮作为 PCNA的阳性对照组。
2.2 免疫组织化学结果判断
RTN4及TG2都是以胞浆出现棕黄色颗粒为阳性反应,PCNA以细胞核出现棕黄色颗粒为阳性反应。阴性对照组除细胞核染成蓝色外,应无棕黄色反应物。
2.3 统计学处理
采用 HPIAS-1000高清晰度彩色病理图文报告管理系统(同济千屏影像公司)对RTN4及TG2的表达进行定量分析,每张切片随机选取 5个完整而不重叠的高倍镜视野(400×),测定每个视野下阳性反应的平均光密度、阳性反应面积和所有细胞总面积,计算阳性面积率。以每例 5个视野的平均光密度、阳性面积率的平均值作为该例的测量值。(阳性面积率 =单位面积中阳性反应的总面积/单位面积中细胞的总面积 ×100%)
数据以均数 ±标准差表示,用 SPSS11.5软件对各组免疫组织化学反应阳性颗粒的平均光密度、阳性面积率做单因素方差分析和 SNK(q)检验,检验水准α为0.05。
结 果
1.增生期血管瘤内皮细胞 PCNA的表达强
增生期血管瘤内皮细胞核肥大,核内弥漫分布棕黄色颗粒,PCNA表达强(图1);退化期血管瘤内皮细胞核扁平,胞核内有少量棕黄色颗粒,PCNA表达弱(图2)。
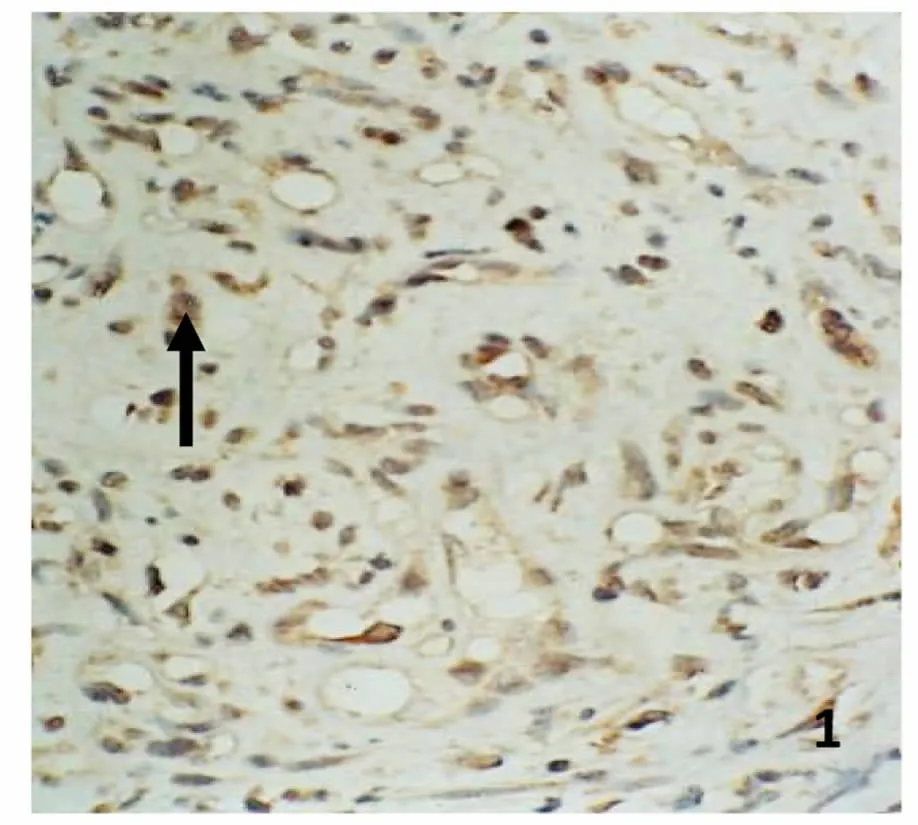
图 1 增生期血管瘤PCNA的表达。增生的内皮细胞核内弥漫分布棕黄色颗粒(→),PCNA表达强,S-P 400×Fig.1 PCNA expression in proliferating hemangioma.There were plenty of brown particles in the nucleus of proliferating endothelial cells,which showed PCNA expressed strongly(→).S-P 400×
2.增生期血管瘤内皮细胞 RTN4的表达强
增生期血管瘤内皮细胞胞浆内有较多棕黄色颗粒,RTN4表达强(图3);退化期血管瘤内皮细胞胞浆内有较少的棕黄色颗粒,RTN4表达弱(图4);正常皮肤组织内皮细胞胞浆内有少量的棕黄色颗粒,RTN4表达弱(图5)。图像分析结果见表1。增生期血管瘤内皮细胞 RTN4的表达显著高于退化期血管瘤内皮细胞和正常组织(P<0.05),而后两组比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)(表1)。

图3 增生期血管瘤RTN4的表达。内皮细胞胞浆内有较多棕黄色颗粒,RTN4表达强,S-P 400×Fig.3 RTN4 expression in proliferating hemangioma.There were plenty brown particles in cytoplasm the of proliferating endothelial cells,RTN4 expressed strongly(→).S-P 400×
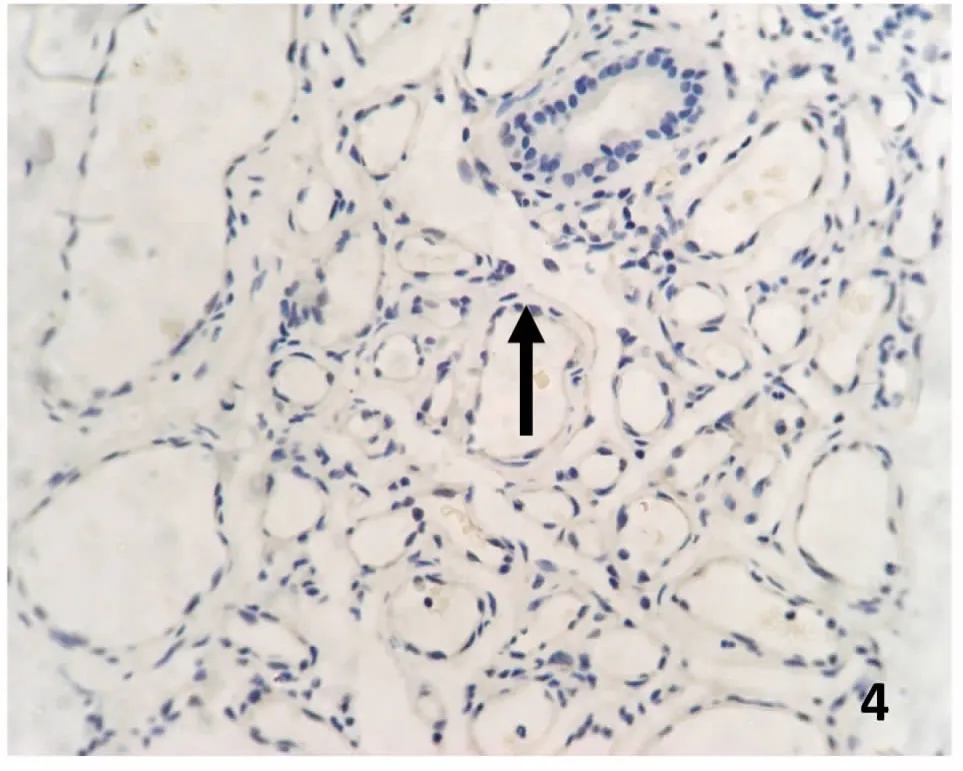
图 4 退化期血管瘤RTN4的表达。内皮细胞胞浆内有少量棕黄色颗粒(→),RTN4表达弱(→)S-P 400×Fig.4 RTN4 expression in involuting hemangioma.There were few of brown particles in cytoplasm the of involuting endothelial cell,RTN4 expressed weakly(→).S-P 400×
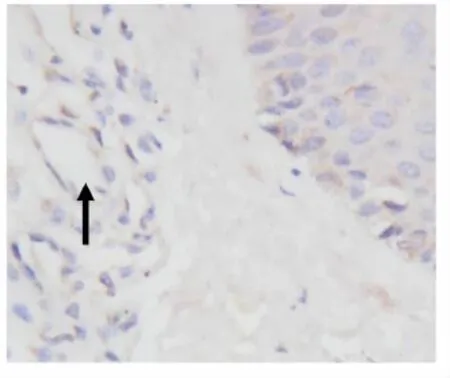
图5 正常对照组 RTN4的表达。内皮细胞胞浆内有少量的棕黄色颗粒(→),RTN4表达弱,S-P 400×Fig.5 RTN4 expression in normal skin Group.There were few of brown particles in cytoplasm the of in normal skin endothelial cells,RTN4 expressed weakly(→).S-P 400×
表1 血管瘤不同时期 RTN4表达的平均光密度和阳性面积率((±s))Table 1 the average optical density and the rate of RTN4 positive area of in differ period of human dermal hemangiomas((±s))
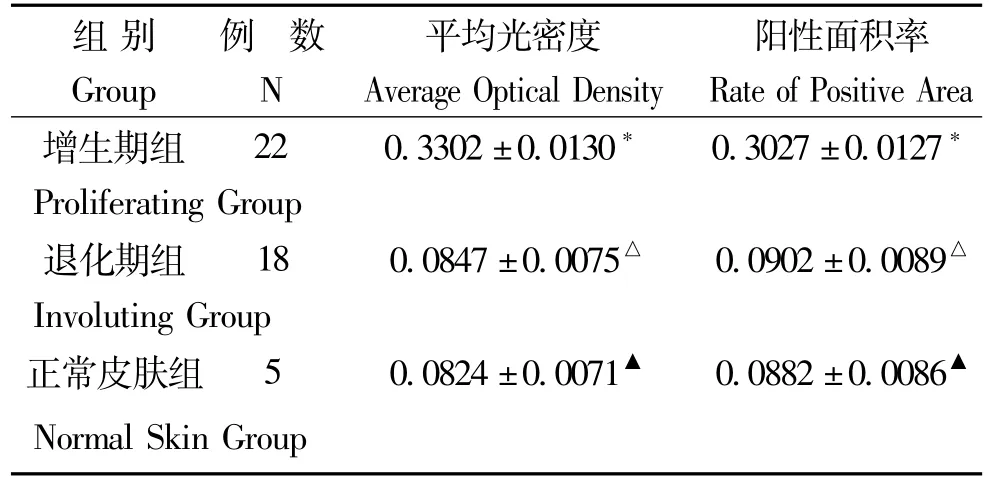
表1 血管瘤不同时期 RTN4表达的平均光密度和阳性面积率((±s))Table 1 the average optical density and the rate of RTN4 positive area of in differ period of human dermal hemangiomas((±s))
与退化期组比较*P<0.05;与正常皮肤组比较△P >0.05;与增生期组比较▲P<0.05*P<0.05,comparison between proliferating hemangiomas and involuting hemangiomas;△P>0.05,comparison between involuting hemangiomas and normal skin tissue;,▲P<0.05,comparison between proliferating hemangiomas and normal skin tissue
数 平均光密度 阳性面积率Group N Average Optical Density Rate of Positive Area增生期组 22 0.3302±0.0130* 0.3027±0.0127组别 例* Proliferating Group退化期组 18 0.0847±0.0075△ 0.0902±0.0089△Involuting Group正常皮肤组 5 0.0824±0.0071▲ 0.0882±0.0086▲Normal Skin Group
3.增生期血管瘤内皮细胞 TG2的表达强
增生期血管瘤内皮细胞胞浆内有较多棕黄色颗粒,TG2表达强(图6);退化期血管瘤内皮细胞胞浆内有较少的棕黄色颗粒,TG2表达弱(图7);正常皮肤组织内皮细胞胞浆内有少量的棕黄色颗粒,TG2表达弱(图8)。图像分析结果见表2。增生期血管瘤内皮细胞 TG2的表达显著高于退化期血管瘤内皮细胞和正常组织 (P<0.05),而后两组比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)(表2)。
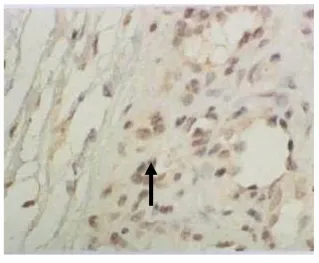
图6 增生期血管瘤 TG2的表达。血管瘤内皮细胞胞浆内有较多棕黄色颗粒(→),TG2表达强,S-P 400×Fig.6 TG2 expression in proliferating hemangioma.There were plenty of brown particles in cytoplasm the of proliferating endothelial cells,TG2 expressed strongly(→).S-P 400×
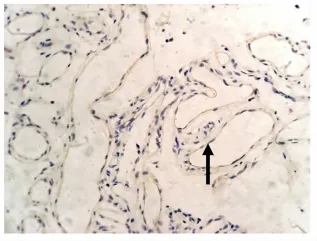
图7 退化期血管瘤 TG2的表达。血管瘤内皮细胞胞核或胞质内有较少棕黄色颗粒,TG2表达弱或无表达(→),S-P 400×Fig.7 TG2 expression in involuting hemangioma.There were few brown particles in cytoplasm the of involuting endothelial cells,TG2 expressed weakly(→).S-P 400×
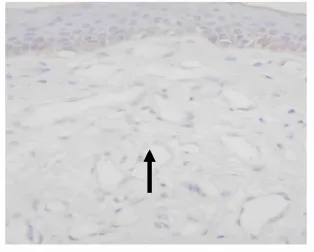
图8 正常组TG2的表达。血管内皮细胞胞核或胞质内有较少棕黄色颗粒,TG2表达弱或无表达(→),S-P 400×Fig.8 TG2 expression in normal skin Group.There were few brown particles in cytoplasm the of in normal skin endothelial cells,TG2 expressed weakly(→).S-P 400×
表2 血管瘤不同时期 TG2表达的平均光密度和阳性面积率((±s))Table 2 The average optical density and the rate of TG2 positive area of in differ period of human dermal hemangiomas((±s))
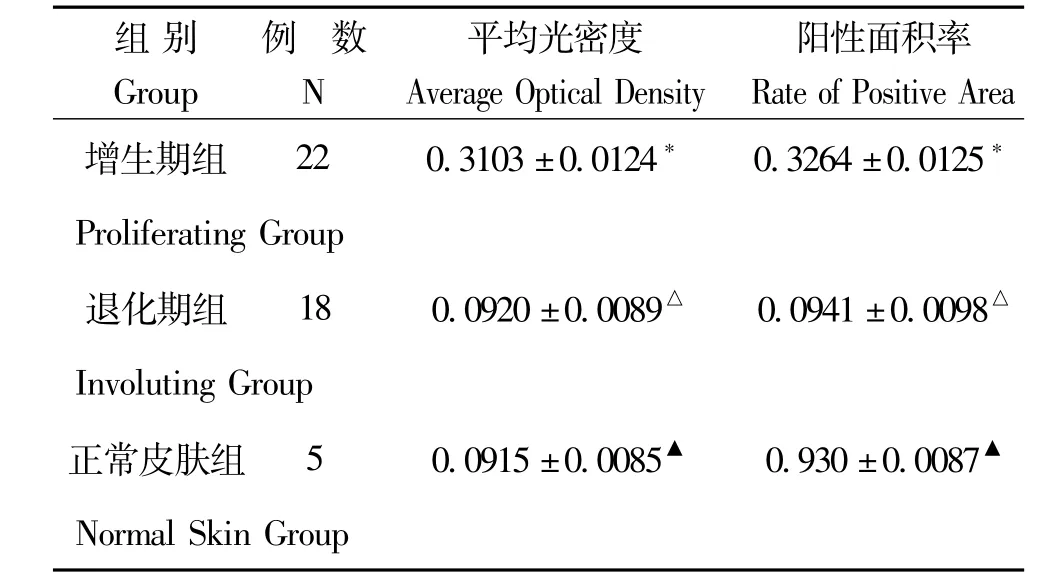
表2 血管瘤不同时期 TG2表达的平均光密度和阳性面积率((±s))Table 2 The average optical density and the rate of TG2 positive area of in differ period of human dermal hemangiomas((±s))
*P<0.05,与退化期组比较;△P >0.05,与正常皮肤组比较;▲P<0.05,与增生期组比较*P<0.05,comparison between proliferating hemangiomas and involuting hemangiomas;△P>0.05,comparison between involuting hemangiomas and normal skin tissue;▲P<0.05,comparison between proliferating hemangiomas and normal skin tissue
数 平均光密度 阳性面积率Group N Average Optical Density Rate of Positive Area组别 例增生期组 22 0.3103±0.0124* 0.3264±0.0125*Proliferating Group退化期组 18 0.0920±0.0089△ 0.0941±0.0098△Involuting Group正常皮肤组 5 0.0915±0.0085▲ 0.930±0.0087▲Normal Skin Group
讨 论
皮肤血管瘤是一种常见的良性肿瘤,在婴幼儿中发病率较高,新生儿的患病率为1.1%-3.8%,至1岁时可高达10%。皮肤血管瘤的自然病程经历增生期、退化期和退化完成期三个阶段。该良性肿瘤通过未成熟的内皮细胞弥散增殖而快速生长,之后自发消退。一般认为毛细血管内皮细胞的增生与消退是血管瘤生长和消退的关键原因。肿瘤发生发展的机制亦涉及到血管内皮细胞的变化[8-9]。目前关于治疗血管瘤方法的成效并不十分显著,一些治疗模式的副作用也限制了其应用。因此探讨皮肤血管瘤的发病机制对临床上治疗血管瘤有着重要的意义。
RTN4属于髓鞘相关的内质网蛋白成员,广泛存在于高等真核生物中,有三个主要的异构体,即RTN4-A、B、C。它们具有不同的N-末端序列和一个共同的C-末端,其中 C-末端约 190个氨基酸残基组成,包括两个跨膜区、Nogo-66亲水环,以及一段亲水尾,统称为RHD区。根据RHD跨膜区节段数的不同又提出了两种特殊的拓扑结构,即马蹄状和 ω-形,也因此赋予了 RTN4蛋白不同的生物学功能[10]。因为是内质网的定位膜蛋白,而内质网的功能又与蛋白质的分泌密切相关,所以推测 RTN4的功能涉及蛋白的分泌加工过程,最早被作为神经内分泌特异性蛋白的标记[11]。近年来,关于 RTN4与瘤细胞凋亡之间的关系存在很大争议。Tagami等[12]报道,RTN4B在肿瘤细胞中具有一定的促凋亡倾向,他们发现过量表达的 RTN4B能够干扰凋亡抑制因子Bcl-2、Bcl-xL的活性,诱导肿瘤细胞的凋亡。最近,又有研究认为 RTN4通过介导 Drs基因诱导凋亡,但研究仅证实了 RTN4可与 Drs蛋白产生交联反应,并没有进一步证实 RTN4是 Drs凋亡中必不可少的凋亡分子[13-14]。
TG2为一类结构功能复杂的蛋白质,由四个结构域组成,行使功能的主要为α/β催化核心区,通过转氨基作用来实现蛋白质分子间的共价交联反应,对蛋白质进行翻译后修饰,从而改变它们的结构,功能及稳定性。TG2除了催化钙依赖性的蛋白质翻译后修饰,还可以结合并水解 GTP/ATP,同时也具有蛋白质二硫键异构酶活性,甚至在细胞信号传导过程中充当 G-蛋白的功能[15]。TG2蛋白在人体分布较为广泛(如血管内皮细胞、平滑肌细胞以及成纤维细胞等),主要为细胞内蛋白质,定位在细胞质、细胞核、细胞膜等,部分还能分泌到胞外基质中,在不同的细胞环境中发挥截然不同的生理功能,与组织纤维化、神经退行性疾病、动脉粥样硬化和癌症等疾病密切相关[16]。由此可见,TG2的功能取决于它在细胞的定位及其与其它蛋白、辅助因子之间的相互作用所决定。尽管 TG2与肿瘤的关系较为复杂,在不同组织和细胞中的功能也不尽相同,但随着对 TG2研究的深入,其各种生物学机制也不断被揭示,将可能为肿瘤的诊断、疗效及预后提供新的线索。
本研究发现,RTN4和 TG2蛋白在增生期血管瘤组织中的表达明显高于正常皮肤组及退化组,推测 RTN4和TG2蛋白在增生期血管瘤组织中呈高表达,导致增生期血管瘤组织内皮细胞不断增殖,使血管瘤不断发展,而 RTN4和 TG2蛋白在退化期血管瘤组织中呈低表达,推测 RTN4和 TG2蛋白在退化期血管瘤组织中抗凋亡作用变化有关。这些结果预示RTN4和 TG2蛋白与血管瘤的发生存在一定关联,将为进一步探讨 RTN4和 TG2蛋白在血管瘤发生和发展分子机制的研究提供有力的实验依据。
[1]Jinnin M,Ishihara T,Boye E,et al.Recent progress in studies of infantile hemangioma.The Journal of Dermatology.2010,37(4):283-298
[2]Shan G,Tang T,Zhang D.Expression of HLA-G in hemangioma and its clinical significance.J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci.2012;32(5):713-718
[3]Gao L,Utsumi T,Tashiro K,et al.Reticulon 4B(Nogo-B)facilitates hepatocyte proliferation and liver regeneration regeneration in mice.Hepatology.2013,57(5):1992-2003
[4]Acevedo L,Yu J.Erdjument-Bromage H,et al.A new role for Nogo as a regulatorof vascular remodeling.Nat Med.2004,10:382-388
[5]Kapil Mehta,Aupam Kumar,Hong Im Kim,et al.Transglutaminase 2:A multi-tasking protein in the complex circuitry ofinflammation and cancer.BiochemicalPharmacology. 2010,80:1921-1929
[6]Stiles JM,Rowntree RK,Amaya C,et al.Gene expression analysis reveals marked differences in the transcriptome of infantile hemangioma endothelial cells compared to normal dermal microvascular endothelial cells.Vasc Cell.2013;25;5(1):6
[7]Kotsakis P,Wang Z,Collighan RJ,et al.The role of tissue transglutaminase(TG2)in regulating the tumor progression of mousecolon carcinoma CT26.Amino Acid 2011,41:909-921
[8]Deng C,Shan G,Zhang D.Angiogenic Effect of Intercellular Adhesion Molecule-1.Huazhong Univ Sci Technol(Med Sci).2007,27(1):9-12
[9]Shan S,Shan G,Zhang D.Treatment of hemangioma by transfection of antisense VEGF gene.J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog,2009;29(3)335-339
[10]Yicun Chen,Xiaojun Tang,Xiran Zhang,et al.New mutations of Nogo-C in hepatocellular carcinoma.Mol Biol Rep.2009,36:377-380
[11]Mi YJ,Hou B,Liao QM et al.Amino-Nogo-A antagonizes reactive oxygen species generation and protects immature primary cortical neurons from oxidative toxicity.Cell Death Differ.2012,19:1175-1186
[12]Tagami,S,Eguchi Y,Kinoshita M,et al.A novel protein,RTN-XS,interacts with both Bcl-XL and Bcl-2 on endoplasmic reticulum and reduces their anti-apoptoticactivity.Oncogene.2000,19:5736-5746
[13]Nadalutti C,Viiri KM,Kaukinen K,et al.Extracellular transglutaminase 2 has a role in cell adhesion,whereas intracellular transglutaminase 2 is involved in regulation of endothelial cell proliferation and apoptosis.Cell Prolif. 2011,44:49-58
[14]Shi S,Zhou B,Wang Y,et al.Genetic variation in RTN4 3′-UTR and susc eptibility to cervical squamous cell carcinoma.DNA Cell Biol.2012,31(6):1088-1094
[15]Wang Y,Ande SR,Mishra S,et al.Overexpression of phospho mutant forms of transglutaminase 2 downregulates epidermal growth factor receptor.Biochem Biophys Res Commun.2012,417:251-255
[16]Wang Z,Griffin M.TG2,a novel extracellular protein with multiple functions.Amino Acids.2012,42:939-949
High expression and significance of RTN4 and TG2 in human dermal hemangiomas
Tang Tian,Ge Wei
(Department of Oncology,Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University,Wuhan 430060,China)
Objective To study the expression and clinical significance of RTN4 and TG2 in human dermal hemangiomas. Methods Specimens from 40 cases(15 males and 25 females)of hemangioma were collected from the Department of Pathology in Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University from 2008 to 2011.We examined the expression of RTN4 and TG2 in proliferative,involuting derml hemangiomas and normal skin tissues by using immunohistochemical technique.Average optical density and positive area rates of expression of RTN4 and TG2 were measured by image analysis(HPIAS-1000).The single factor analysis of variance and SNK test(q)of average optical density and positive area rates were conducted by SPSS13.0 software.Results The expression of RTN4 was obviously higher in the proliferative phase than in involuting hemangioma and normal skin.No significant difference was found in the expression of RTN4 between involuting hemangioma and normal skin.The expression of TG2 was obviously higher in the proliferative phase than in involuting hemangioma and normal skin.No significant difference was found in the expression of TG2 between involuting hemangioma and normal skin.Conclusion The expressions of RTN4 and TG2 are obviously higher in proliferative hemangioma than in involuting hemangioma and normal skin,which suggests that RTN4 and TG2 are closely correlated with cells apoptosis and proliferation.
Hemangiomas;RTN4;TG2;Immunohistochemical
R735.1
A
10.16705/j.cnki.1004-1850.2015.05.009
2015-06-06
2015-09-10
〔项目来源〕国家自然科学基金(青年基金)资助项目(81402242);湖北省自然科学基金(青年基金)(2014CFB419)
唐甜,女(1981年),汉族 ,主治医师

