层间接触状态和横向力大小对车辙贡献率的影响
仲甡,李杰,黄敏*
1.云南建工集团有限公司,云南 昆明 650000;2.武汉工程大学资源与土木工程学院,湖北 武汉 430074
层间接触状态和横向力大小对车辙贡献率的影响
仲甡1,李杰2,黄敏2*
1.云南建工集团有限公司,云南 昆明 650000;2.武汉工程大学资源与土木工程学院,湖北 武汉 430074
车辙贡献率是反映沥青路面各结构层车辙病害程度的一个主要参数,可用于指导沥青路面的设计和施工.利用三维有限元计算软件建立三维有限元模型用于理论分析,将有限元计算结果与理论解进行对比,验证了该三维有限元模型的可靠性.采用实测的轮胎接地压力,考虑不同层间接触状态和横向力大小,结合有限元计算的数据,分析了沥青路面结构层的车辙贡献率.结果表明:在层间完全连续状态下,横向力大小的选取不能简单地选取最大垂直轮胎接地压力的一定比例,而是要根据所研究的具体情况具体分析.在对沥青路面车辙贡献率的研究中,可以忽略层间接触状态,即假定层间完全连续.
沥青路面;车辙贡献率;层间接触状态;横向力大小
0 引言
很多学者对沥青路面车辙贡献率的问题进行过研究,也采取了很多方法,例如室内车辙试验和现场钻芯实测并结合统计学原理、圆形均布荷载理论分析、以及实测轮载有限元理论分析等[1-6].本文采用实测轮载并考虑不同层间接触状态和横向力大小,通过有限元分析来研究有关沥青路面车辙贡献率的问题.
1 三维有限元计算模型的建立
计算用路面结构及其参数见表1,文中所采用模量均为动态模量.标准轴载BZZ-100的轮载P=25 kN,p=700 kPa,当量直径d=0.213 m(双圆荷载);层间接触条件考虑完全连续.由于车辙是在压应变和横向剪应变共同作用下引起的[7],故本文在建立三维有限元计算模型时,考虑的对比计算指标为压应变εz和横向剪应变γxz.
沥青路面车辙贡献率有限元计算模型根据经验[7]初定为:单元类型:plane82,solid45;尺寸:4 m×4 m×8 m;边界条件:沿行车方向的前后侧没有Y方向的位移,左右侧没有X方向的位移,底部没有Z方向的位移.有限元的计算模型见图1.
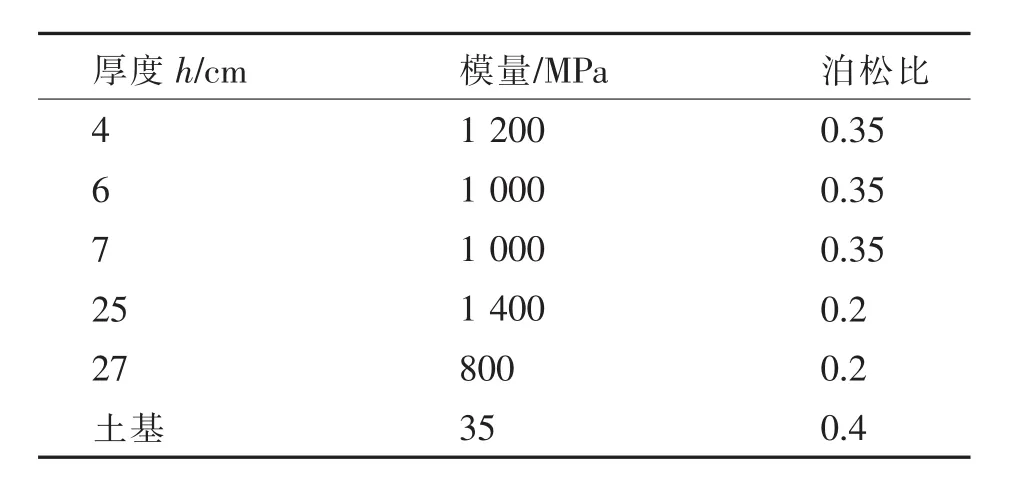
表1 路面结构计算参数Table 1 Pavement structure calculations
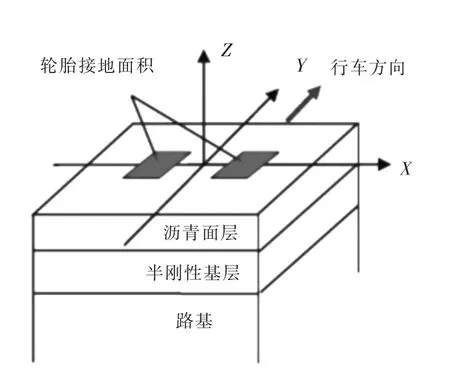
图1 三维有限元计算模型Fig.1 Three-dimensional finite element calculation model
为保证所建立的计算模型的可靠性,本文将三维有限元计算模型与多层弹性体系理论解按上述指标进行对比,结果如图2所示.

图2 有限元计算模型和多层弹性理论的剪/压应变响应Fig.2 Finite element model and the shear/compressive strain response of the multi-layer elastic theory
通过图2有限元计算模型和多层弹性体系理论的压应变和剪应变响应趋势对比分析,可验证该计算模型的可靠性.
2 数据处理方法的确定
沥青路面车辙贡献率是指沥青路面面层各层的车辙量占总车辙量的比例.车辙是一种累积变形量;而应变则是具有一定尺寸(长度、角度)的物体在该尺寸方向发生的变形与该物体原有尺寸的比值.每一层的应变乘以该层的厚度就是车辙量,这样就能建立应变与车辙量的关系.假设不考虑回弹恢复等,即每个量都是绝对量.
压/剪应变车辙贡献率,如图3所示.图3中,A1ε/A1γ分别表示上面层压/剪应变与上面层厚度的乘积A2ε/A2γ表示中面层压/剪应变与中面层厚度的乘积,A3ε/A3γ表示下面层压/剪应变与下面层厚度的乘积,则有:
SA1ε=A1ε/(A1ε+A2ε+A3ε)表示上面层压应变车辙贡献率,%;
ZA2ε=A2ε/(A1ε+A2ε+A3ε)表示中面层压应变车辙贡献率,%;
XA3ε=A3ε/(A1ε+A2ε+A3ε)表示下面层压应变车辙贡献率,%;
SA1γ=A1γ/(A1γ+A2γ+A3γ)表示上面层剪应变车辙贡献率,%;
ZA2γ=A2ε/(A1γ+A2γ+A3γ)表示中面层剪应变车辙贡献率,%;
XA3γ=A3γ/(A1γ+A2γ+A3γ)表示下面层剪应变车辙贡献率,%.
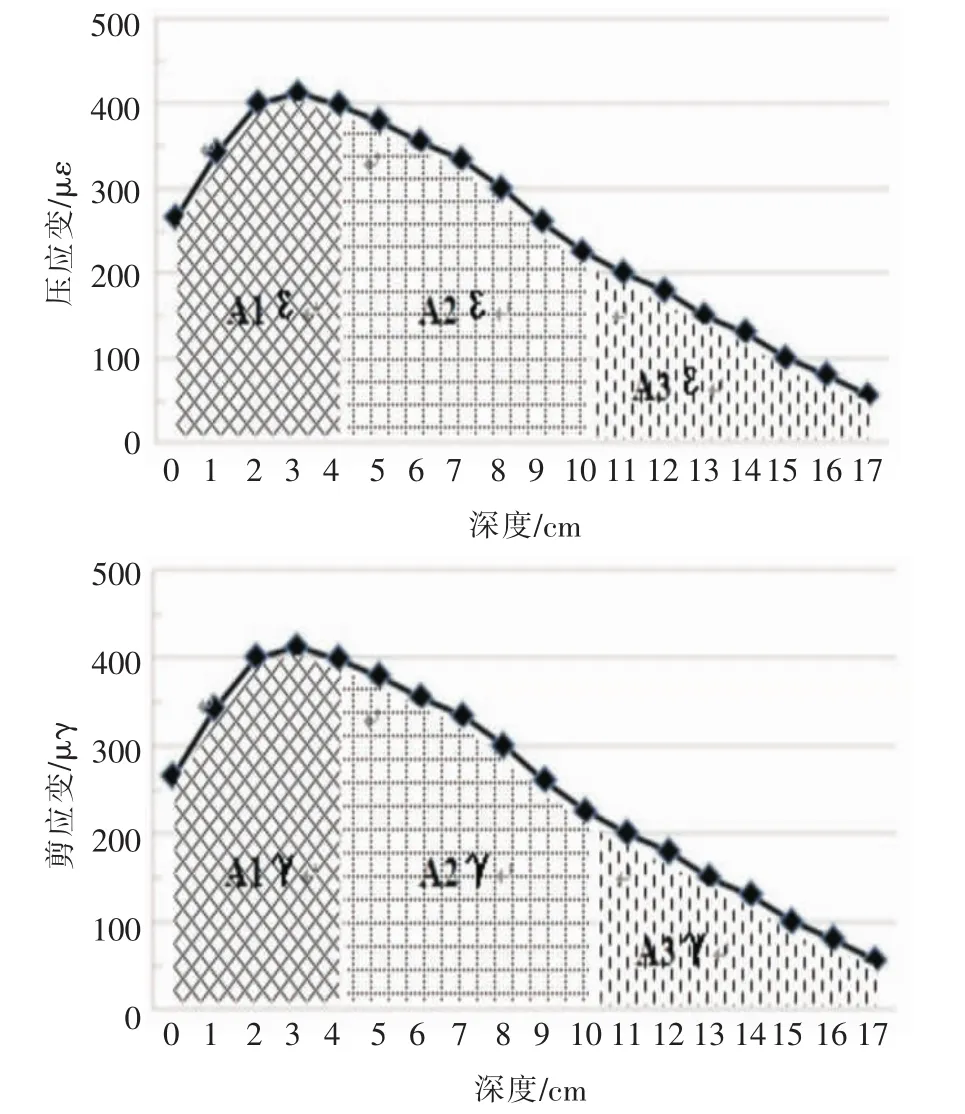
图3 压/剪应变车辙贡献率示意图Fig.3 Pressure/shear strain rut contribution
3 层间接触状态下横向力对的沥青路面车辙贡献率的影响
层间接触状态是指沥青路面各层之间的接触情况.由于沥青路面面层之间,以及面层与基层之间不是完全连续的,故在本文研究中考虑两种层间接触状态.第一种是理想状态,即考虑层间完全连续;第二种考虑层间有摩擦,且沥青路面面层之间的摩擦系数为0.7,面层与基层之间的摩擦系数为0.5[8].
计算采用标准荷载(后轴总重100 kN,胎压600 kPa,单轮负荷25 kN),走向花纹轮胎的实测竖向接地压力作为计算荷载[9],且考虑水平荷载作用.研究表明,横向轮胎接地压力一般为最大垂直轮胎接地压力的15%~50%[10].为了使计算结果更具一般性,分别取横向轮胎接地压力为最大垂直轮胎接地压力的0、15%、30%和50%进行计算分析.纵向轮胎接地压力一般为最大垂直轮胎接地压力的12%.采用表2中的路面结构参数进行计算,其中模量为实测模量.
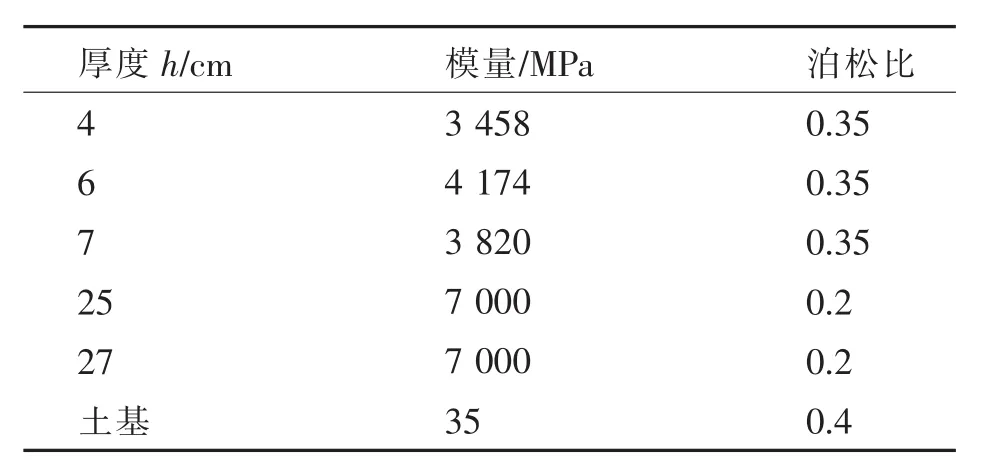
表2 路面结构计算参数Table 2 Pavement structure calculations
3.1 不同层间接触状态下横向力大小对车辙贡献率的影响
不同层间接触状态下横向力大小对车辙贡献率的影响计算结果如表3、表4所示,从表中可以看出:
a.在层间完全连续状态下,随着横向力大小的变化,中面层剪应变车辙贡献率变化较小,且表现为中面层占优,无论横向力如何变化,中面层剪应变车辙贡献率维持在40%~43%之间;在层间有摩擦条件下,各面层剪应变车辙贡献率变化均较小,且中面层占优趋势不再明显.
b.无论层间接触状态如何,随着横向力大小的变化,各面层压应变车辙贡献率变化均较小,且各面层压应变车辙贡献率相当.
c.在层间完全连续状态下,横向力大小的选取不能简单的取最大垂直轮胎接地压力的随意比例,例如30%,而是要根据所研究的具体情况具体分析.

表3 层间完全连续状态下不同横向力下沥青层各层剪应变和压应变车辙贡献率Table 3 Rutting contribution of shear strain and compressive strain in each layer at the different transverse forces under the completely continuous state of layers
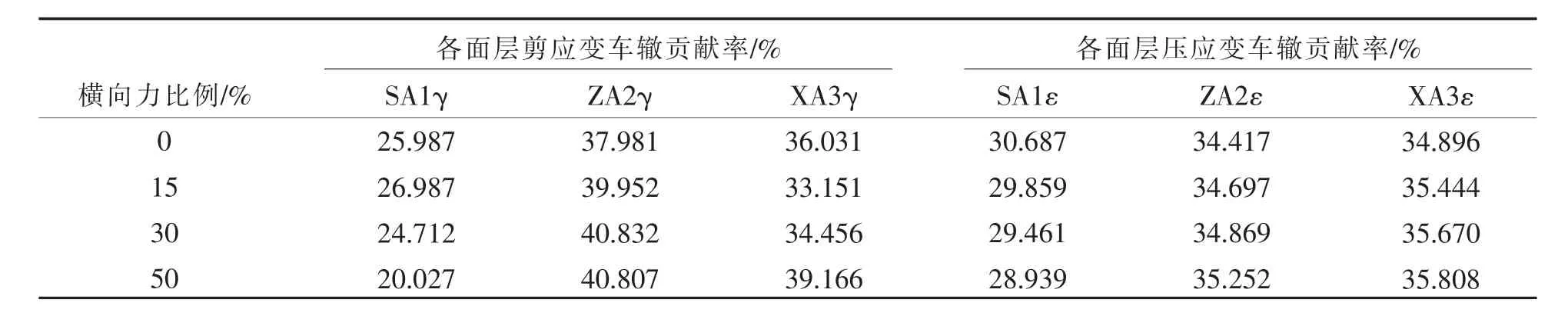
表4 层间有摩擦条件下不同横向力下沥青层各层剪应变和压应变车辙贡献率Table 4 Rutting contribution of shear strain and compressive strain in each layer at the different transverse forces under conditions of interlayer having friction
3.2 不同横向力大小下层间接触状态对车辙贡献率的影响
不同横向力大小下层间接触状态对车辙贡献率的影响计算结果如表5所示,从表中可以看出:
a.层间接触状态由完全连续到考虑摩擦,无论横向力大小如何,中面层剪/压应变车辙贡献率均减小,但减小幅度不大.
b.层间接触状态由完全连续到考虑摩擦,无论横向力大小如何,各面层的剪/压应变车辙贡献率变化幅度均比较小.由此可以看出,在各种水平的横向力大小情况下,层间接触状态对沥青路面车辙贡献率的影响较小.
4 结语
通过以上研究得出如下结论:
a.在层间完全连续状态下,横向力大小的选取不能简单的取最大垂直轮胎接地压力的一定比例,例如30%,而是要根据所研究的具体情况具体分析.
b.在各种水平的横向力大小情况下,层间接触状态对沥青路面车辙贡献率的影响较小.在以后的研究中,为了减小计算量同时又不影响研究的准确性.在适当的情况下,可以忽略层间接触状态,即假定层间完全连续.
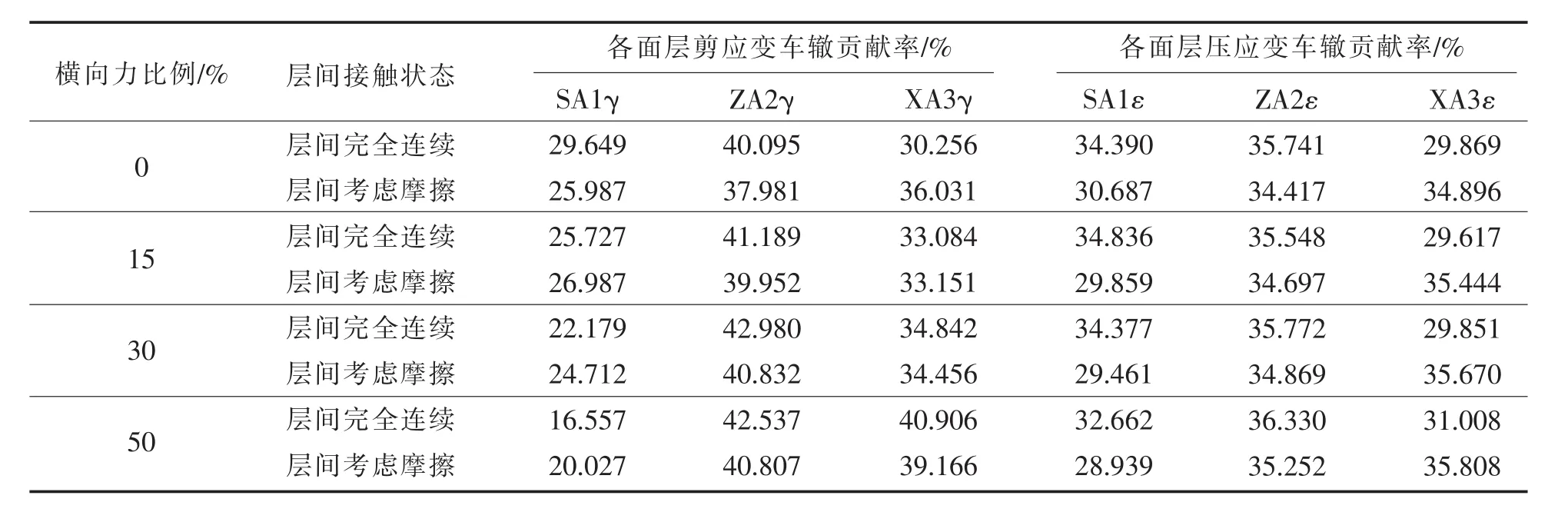
表5 不同横向力下层间接触状态下沥青层各层剪应变和压应变车辙贡献率Table 5 Rutting contribution of shear strain and compressive strain in each layer at the different transverse forces under the contact between layers
致谢
感谢云南建工集团直属总承包二部为本研究提供的支持和帮助!
[1]胡萌,张久鹏,黄晓明.半刚性基层沥青路面车辙特性分析[J].公路交通科技,2011,28(6):15-18.
HU Meng,ZHANG Jiu-peng,HUANG Xiao-ming.Analysis of rutting characteristics of semi-rigid base asphalt pavement[J].Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development,2011,28(6):15-18.(in Chinese)
[2]黄晓明,范要武.高速公路沥青路面高温车辙的调查与试验分析[J].公路交通科技,2007,24(5):17-20.
HUANG Xiao-ming,FAN Yao-wu.Investigation and test of expressway asphalt pavement high-temperature performance[J].Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development,2007,24(5):17-20.(in Chinese)
[3]董轶.中面层对沥青混凝土路面抗车辙性能影响研究[J].中外公路,2010,30(4):8-13.
DONG Yi.The surface layer of asphalt concrete pavement rutting performance impact study[J].Journal of China&Foreign Highway,2010,30(4):8-13.(in Chinese)
[4]王辉,李雪连,张起森.高温重载作用下沥青路面车辙研究[J].土木工程学报,2009,42(6):140-144.
WANG Hui,LI Xue-lian,ZHANG Qi-sen.Ruttinginasphaltpavementunderheavyloadandhightemperature[J].ChinaCivilEngineeringJournal,2009,42(6):140-144.(in Chinese)
[5]KENIS W,WANG W.Calibrating mechanistic flexible pavement rutting models from full scale accelerated tests[C]//Eighth international conference on asphalt pavements.Seattle,Washington,Federal:Highway Administration,1997,(1):663-672.
[6]李杰,仲甡,胡小弟.实测轮载接地压力的沥青路面车辙贡献率研究[J].华中科技大学学报,2014,42(3):102-106.
LI Jie,ZHONG Shen,HU Xiao-di.Research on rutting contribution rate under measured tire-pavement contact pressure in asphalt pavement[J].Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology.2014,42(3):102-106.(in Chinese)
[7]封基良,许爱华,席晓波.沥青路面车辙预测的粘弹性分析方法[J].公路交通科技,2004,21(5):12-18.
FENG Ji-liang,XU Ai-hua,XI Xiao-bo.Visco-elastic method for prediction of asphalt pavement rutting[J].Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development,2004,21(5):12-18.(in Chinese)
[8]ROMANOSCHI A S,METCALF B J.Effects of interface condition and horizontal wheel loads on the life on flexible pavement structures[J].Transportation Research Record:Journal of Transportation Research Board Academies,2001,1778:123-131.
[9]HU Xiao-di,LU Binda F Walubita.Modeling mechanistic responses in asphalt pavements under three-dimensional tire-pavement contact pressure[J].Journal of Central South University of Technology,2011,18(1):250-258.
[10]D de Beer,C Fisher,Fritz J Jooste.Determination of pneumation tyre.Pavement interface contact stresses under moving loads and some effects onpavements with thin asphalt surfacing lagers[C]//8th International Conference on Asphalt Pavement,1997.
Influence of interlayer contact state and lateral tire-pavement contact pressure on rutting contribution rate
ZHONG Shen1,LI Jie2,HUANG Min2
1.Yunnan Construction Engineering Group Co.LTD,Kunming 650000,China;2.School of Resource and Civil Engineering,Wuhan Institute of Technology,Wuhan 430074,China
The rutting contribution rate,as a main parameter which can reflect the degree of rutting disease of each structural layer on asphalt pavement,can be used to guide the design and construction of asphalt pavement.In this paper,the three-dimensional finite element calculation software was used to establish three-dimensional finite element model for theoretical analysis.With the comparison of the result of the finite element calculation with the theoretical solution,the reliability of the 3D finite element model was verified.Considering the different interlayer contact state and the lateral force,the rutting contribution rate of Asphalt Pavement was analyzed by using the data of measured tire contact pressure and finite element calculation.According to the results,if the interlayer is completely continuous,the size of lateral force can not be simply decided by a certain proportion of the largest vertical value of tire grounding pressure,instead,it should be analyzed on the specific situation.The interlayer contact condition can be ignored in the research of rutting contribution rate on asphalt pavement,that is,the interlayer contact condition can be assumed completely continuous.
asphalt pavement;rutting contribution rate;interlayer contact state;magnitude of lateral tire-pavement contact pressure
U411
A
10.3969/j.issn.1674-2869.2015.02.002
1674-2869(2015)02-0005-05
本文编辑:龚晓宁
2015-01-22
仲甡(1990-),男,河南驻马店人,硕士研究生,研究方向:道路工程.*通信作者

