静吸复合依达拉奉麻醉下老年患者术后认知功能变化与围术期脑氧饱和度数值的关系
贾宝森,汪东昱,刘合年,张铁峰
静吸复合依达拉奉麻醉下老年患者术后认知功能变化与围术期脑氧饱和度数值的关系
贾宝森1*,汪东昱2,刘合年1,张铁峰3
(解放军总医院:1外科临床部麻醉手术中心,2研究生管理大队,北京 100853;3甘肃省兰州市第一人民医院麻醉科,兰州 730000)
探讨围术期脑氧饱和度(rSO2)与静吸复合依达拉奉麻醉下老年患者术后认知功能变化的关系,为临床麻醉提供指导。选取2013年1月到2014年1月期间在解放军总医院入院择期行腹部及下肢手术的60例美国麻醉医师协会(ASA)分级Ⅰ~Ⅱ级、年龄>60岁的患者。随机分为3组:依达拉奉1组(E1组:30mg依达拉奉溶于100ml 0.9% NaCl)、依达拉奉2组(E2组:60mg依达拉奉溶于100ml 0.9% NaCl)和空白对照组(C组:100ml 0.9% NaCl),每组20例,麻醉后手术中30min静脉点滴完成。麻醉前均不用术前药,入室后给予阿托品0.5mg,缓慢静注丙泊酚、芬太尼、顺阿曲库铵快速诱导气管插管,机械通气,维持呼气末二氧化碳分压(Pet CO2)在正常范围,监测术中的rSO2变化。应用简易智力状态检查(MMSE)、连线测试及凹槽拼板测试来评定3组患者术前24h,术后4,8,12,24h的认知功能变化。(1)3组患者的一般情况比较差异无统计学意义(>0.05);(2)3组患者术前MMSE、连线测试及凹槽拼板测试评分差异无统计学意义(>0.05);(3)E2组和E1组患者术后认知测试评分均明显高于C组(<0.05),术中3组患者的rSO2数值水平差异无统计学意义(>0.05)。依达拉奉在静吸复合麻醉中的应用,能降低老年患者术后认知功能障碍的发生率,可能与其独特的神经保护,消除氧自由基、抑制脂质过氧化反应和调控凋亡相关基因表达有关,提高中枢对于缺血低氧的耐受力有关。
老年人;认知障碍;脑氧饱和度;依达拉奉
术后认知功能障碍(postoperative cognitive dysfunction,POCD)是老年患者麻醉手术后常见的中枢神经系统并发症。临床表现为认知功能异常、记忆缺损、人格和社会整合能力发生改变等,严重时可出现老年性痴呆。有文献报道,老年患者术后24h内的POCD发病率可高达19%,尤其在腹部手术中发生率可高达40%[1]。认知功能的改变反映了围术期的脑功能变化,脑功能的改变必然与围术期的脑氧供需平衡变化有关。脑氧饱和度(cerebral oxygen saturation,rSO2)能反映围术期的脑氧供需变化,因而rSO2的变化可以反映认知功能的改变。认知功能的变化除了与患者的年龄、文化程度、手术类型、麻醉用药有关以外,围术期的氧供与血压也是影响因素。
依达拉奉(edaravone)[1−3]是一种新型的自由基清除剂,化学名为3−甲基−1−苯基−2−吡唑啉−5−酮,临床上主要用于缺血性脑卒中的治疗。它可通过抑制羟自由基以及羟自由基依赖性和非依赖性脂质过氧化,减少神经元诱导型一氧化氮合酶,捕获自由基,抑制脂质、神经细胞过氧化,从而减轻脑水肿和脑组织损伤,保护神经元,提高脑组织对缺血、低氧损伤的抵抗力。老年患者全麻后的认知功能变化已成为研究热点,但如何有效地在围术期调控老年患者的脑功能变化、降低老年患者术后的认知功能变化目前还有争议。本研究拟对静吸复合依达拉奉麻醉下老年患者术后认知功能变化与rSO2监测之间关系进行研究,为临床麻醉提供参考。
1 对象与方法
1.1 研究对象
选择2013年1月到2014年1月期间在解放军总医院住院的择期行腹部和下肢手术的患者60例,性别不限,年龄61~74岁,身高160~172cm,体质量58~77kg,美国麻醉医师协会(American Society Anesthesiologists,ASA)分级Ⅰ~Ⅱ级,文化程度为初中以上,无精神系统疾病、活动性肝病、慢性肾功能不全、心肺疾病、内分泌系统疾病、脑血管疾病,恶性肿瘤病史,无酗酒及吸毒史,无长期服用阿片或安定类药物,无青光眼,体质量指数(body mass index,BMI)≤30kg/m2,除外术前简易智力状态检查(Mini-Mental State Examimation,MMSE)评分≤24分的患者。患者被随机分为3组:依达拉奉1组(E1组:30mg依达拉奉溶于100ml 0.9% NaCl)、依达拉奉2组(E2组:60mg依达拉奉溶于100ml 0.9% NaCl)和空白对照组(C组:100ml 0.9% NaCl),每组20例,麻醉后手术中30min静脉点滴完成。患者术前均不用药,入室后全麻诱导采用阿托品(atropine)0.5mg、缓慢静注丙泊酚(propofol)、芬太尼(fentanyl)、顺阿曲库铵(cisatracurium)快速诱导气管插管,机械通气,丙泊酚0.5~1.5mg/kg、顺阿曲库铵0.15mg/kg、芬太尼2~3μg/kg后行气管内插管。术中采用七氟烷复合静脉泵注丙泊酚[6~8mg/(kg·min)]和瑞芬太尼[remifentanil,0.2~0.4μg/(kg·min)]的方式维持麻醉,间断静注顺阿曲库铵(0.07~0.1mg/kg)维持肌松,间断应用芬太尼1~2μg/kg维持。吸入麻醉药控制在呼末浓度平均为1.0MAC(0.9~1.1MAC)。维持呼气末二氧化碳分压(end tidal carbon dioxide partial pressure,PetCO2)在35~45mmHg(1mmHg=0.133 kPa)。
1.2 监测
术前禁食水8~12h,入室后建立静脉通路,输注乳酸钠林格液(lactated Ringer’s solution)5~10ml/kg,应用Datex omeda监测仪监测血压、心率、血氧饱和度(SpO2)、PetCO2,应用Datex Ultima-V监测麻醉气体(均Philips Medizin Systeme Boblimgen Gmbh,德国)。INVOS(美国Somanetics公司)无创rSO2监测仪监测患者围术期的rSO2变化。
1.3 认知功能测试
应用MMSE[11]、连线测试(Trail-making Test)及凹槽拼板测试(Grooved Pegboard Test)[10]来评定3组患者术前24h,术后4,8,12,24h的认知功能变化。
1.4 统计学处理

2 结 果
2.1 3组患者一般情况比较
3组患者在年龄、身高、体质量、性别比等人口学一般情况方面差异无统计学意义(>0.05;表1)。尽量维持3组观察患者术前的血流动力学指标波动变化,如术中有下降采用血管活性药物进行调整,血压、心率和SpO2差异无统计学意义。
2.2 3组患者围术期的rSO2变化比较
rSO2在3组患者手术中与入室后及苏醒后相比明显下降(<0.05)。3组患者在围术期同一阶段下,rSO2值变化不明显,差异无统计学意义(表2)。
2.3 3组患者围术期MMSE评分比较
围术期认知功能MMSE评分,与患者入室时MMSE相比,所有患者术后4,8,12h的MMSE均明显降低(<0.05;表3)。
2.4 3组患者连线测试和凹槽拼版测试
3组患者连线测试(表4)与凹槽拼板测试(表5)试验的测试时间比较发现,术前术后的测试时间均为24h,差异无统计学意义(>0.05),在任务完成时间的差异上,依达拉奉组(E1和E2组)患者任务完成的时间明显缩短(其中E2组要好于E1组),对照组患者完成任务的时间延长。
2.5 3组患者围术期认知功能变化比较
术后4h,对照组中发生认知功能变化的患者有3例(15%),E1组患者中有2例(10%),E2组患者有1例(5%);术后8h,对照组中患者有2例(10%),E1组患者有1例(5%),E2组患者认知功能基本恢复;术后12h,仅有对照组患者中有1例(5%)出现认知功能不全,另两组患者认知功能均恢复;术后24h,所有患者的认知功能均恢复。所有患者在术后4h会发生短暂的认知功能变化,依达拉奉60mg组(E2)患者认知功能恢复得最快,空白对照组恢复得较慢,持续到术后12h(表6)。
3 讨 论
本研究采用MMSE结合连线测试与凹槽拼板测试评价老年患者的术后认知功能变化,弥补了MMSE测试的不足,当MMSE评分<24分,认为出现认知功能改变[4,5]。
本试验研究对患者采用复合瑞芬太尼麻醉,术中瑞芬太尼用量为[(0.2~0.4μg/(kg·min)],并间断给予芬太尼1~2μg/kg,可以认为基本上消除了疼痛刺激[12],3组患者在麻醉后、术中、术毕的血流动力学指标均无显著改变,说明麻醉状态平稳。我们以前的研究发现老年患者在全麻后,认知功能出现变化的时间点在术后<24h[13]。结合MMSE测试,连线测试与凹槽拼板测试及rSO2监测的结果,发现老年患者在静吸复合全麻后,出现的认知功能变化基本能在术后24h恢复,这一点与陈晓光等[14]的研究相似。依达拉奉具有脂溶性高,易到达脑组织,对脑缺血具有强大的保护作用,是一种有效的脑保护剂和强效自由基清除剂及抗氧化剂。其作用机制主要与消除氧自由基、抑制脂质过氧化反应和调控凋亡相关基因表达有关。同时研究还发现,依达拉奉[6,7]可以减轻内质网功能障碍,保护神经的缺血低氧损伤,提高脑组织对缺血、低氧损伤的抵抗力[8,9,15,16],改善脑认知功能。在本研究中也观察到应用依达拉奉的患者认知功能恢复得较快。老年患者常合并多种心脑血管疾病,应用依达拉奉虽然不能完全减少POCD的发生,但仍可降低术后认知功能不全的发生率,在此类手术中应用依达拉奉对老年患者有一定益处,对于个体化的应用剂量仍需要进一步广泛的研究。

表1 3组患者一般情况的比较
E1 group: edaravone group 1 (E1: 100ml 0.9% NaCl including 30mg edaravone); E2 group: edaravone group 2 (E2: 100ml 0.9% NaCl including 60mg edaravone)
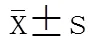
表2 3组患者围术期的rSO2变化比较
E1 group: edaravone group 1 (E1: 100ml 0.9% NaCl including 30mg edaravone); E2 group: edaravone group 2 (E2: 100ml 0.9% NaCl including 60mg edaravone). Compared with in operating room,*<0.05; compared with after awakening,#<0.05
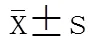
表3 3组患者围术期MMSE评分比较
E1 group: edaravone group 1 (E1: 100ml 0.9% NaCl including 30mg edaravone); E2 group: edaravone group 2 (E2: 100ml 0.9% NaCl including 60mg edaravone). Compared with 24h before operation,*<0.05,**<0.01
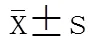
表4 3组患者连线测试的时间比较
E1 group: edaravone group 1 (E1: 100ml 0.9% NaCl including 30mg edaravone); E2 group: edaravone group 2 (E2: 100ml 0.9% NaCl including 60mg edaravone).Compared with before operation,*<0.05; compared with after operation,#<0.05
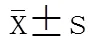
表5 3组患者凹槽拼板测试的时间比较
E1 group: edaravone group 1 (E1: 100ml 0.9% NaCl including 30mg edaravone); E2 group: edaravone group 2 (E2: 100ml 0.9% NaCl including 60mg edaravone).Compared with before operation,*<0.05; compared with after operation,#<0.05

表6 3组患者围术期认知功能变化比较
E1 group: edaravone group 1 (E1: 100ml 0.9% NaCl including 30mg edaravone); E2 group: edaravone group 2 (E2: 100ml 0.9% NaCl including 60mg edaravone).
[1] Aldini G, Vistoli G, Regazzoni L,. Edaravone inhibits protein carbonylation by a direct carbonyl-scavenging mechanism: focus on reactivity, selectivity, and reaction mechanisms[J]. Antioxid Redox Signal, 2010, 12(3): 381−392.
[2] Li Q, Bi MJ, Bi WK,. Edaravone attenuates brain damage in rats after acute CO poisoning through inhibiting apoptosis and oxidative stress[J]. Environ Toxicol, 2014, October 28, doi: 10.1002/fox.22052. [Epub ahead of print]
[3] Shang H, Cui D, Yang D,. The radical scavenger edaravone improves neurologic function and perihematomal glucose metabolism after acute intracerebral hemorrhage[J]. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis, 2015, 24(1): 215−222.
[4] Fines DP, Severn AM. Anaesthesia and cognitive disturbance in the elderly[J]. Contin Educ Anaesth Crit Care Pain, 2006, 6(1): 37−40.
[5] Uchino H, Nagashima F, Nishiyama R,. Pathophysiology and mechanisms of postoperative cognitive dysfunction[J]. Masui, 2014, 63(11): 1202−1210.
[6] Jiao L, Zhang J, Li Z,. Edaravone alleviates delayed neuronal death and long-dated cognitive dysfunction of hippocampus after transient focal ischemia in Wistar rat brains[J]. Neuroscience, 2011, 182: 177−183.
[7] Dohare P, Hyzinski-García MC, Vipani A,. The neuroprotective properties of the superoxide dismutase mimetic tempol correlate with its ability to reduce pathological glutamate release in a rodent model of stroke[J]. Free Radic Biol Med, 2014, 77: 168−182.
[8] Ren YX, Wei B, Song XR,. Edaravone’s free radical scavenging mechanisms of neuroprotection against cerebral ischemia: review of the literature[J]. Int J Neurosci, 2014, September 24. doi: 10.3109/00207454. 2014. 959121. [Epub ahead of print]
[9] Wada T, Yasunaga H, Inokuchi R,. Effects of edaravone on early outcomes in acute ischemic stroke patients treated with recombinant tissue plasminogen activator[J]. J Neurol Sci, 2014, 345(1−2): 106−111.
[10] Chen MH, Liao Y, Rong PF,. Hippocampal volume reduction in elderly patients at risk for postoperative cognitive dysfunction[J] J Anesth, 2013, 27(4): 487−492.
[11] Zhang MY. Manual for Psychiatric Rating Scale[M]. 2nd ed. Changsha: Hunan Science & Technology Publishing House, 1998: 184−188. [张明园. 精神科评定量表手册[M]. 第2版. 长沙: 湖南科技出版社, 1998: 184−188.]
[12] Jia BS, Zhang H, Yue Y,. The relationship between implicit memory and auditory evoked potential index under general anesthesia[J]. Chin J Anesthesiol, 2002, 22(10): 585−588. [贾宝森, 张 宏, 岳 云, 等. 全麻下听觉诱发电位指数和内隐记忆的关系[J]. 中华麻醉学杂志, 2002, 22(10): 585−588.]
[13] Jia BS, Zhang H. Relationship between cerebral oxygen saturation and postoperative cognitive dysfunction in elderly patients under isoflurane combined sevoflurane anesthesia[J]. Chin J Anesthesiol, 2004, 24(5): 348−351. [贾宝森, 张 宏. 异氟醚及七氟醚复合麻醉下老年患者脑氧饱和度与术后认知功能的关系[J]. 中华麻醉学杂志, 2004, 24(5): 348−351.]
[14] Chen XG, Wang JK, Wang SY. Effects of desflurane and sevoflurane on postoperative cognitive function in elderly patients[J]. Chin J Anesthesiol, 2002, 22(4): 211−213. [陈晓光, 王俊科, 王淑月. 地氟醚与七氟醚麻醉对老年病人术后认知功能的影响[J]. 中华麻醉学杂志, 2002, 22(4): 211−213.]
[15] Dalle-Donne I, Aldini G, Carini M,. Protein carbonylation, cellular dysfunction, and disease progression[J]. J Cell Mol Med, 2006, 10(2): 389−406.
[16] Weiss DJ, Casale GP, Koutakis P,. Oxidative damage and myofiber degeneration in the gastrocnemius of patients with peripheral arterial disease[J]. J Transl Med, 2013, 11: 230.
(编辑: 李菁竹)
Relationship of peri-operative cerebral oxygen saturation with post-operative cognitive function in elderly patients after edaravone injection combined with intravenous and inhalational anesthesia
JIA Bao-Sen1*, WANG Dong-Yu2, LIU He-Nian1, ZHANG Tie-Feng3
(1Anesthesia and Operation Center, Clinical Division of Surgery,2Postgraduate School, Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing 100853, China;3Department of Anesthesiology, First People’s Hospital of Lanzhou City, Lanzhou 730000, China)
To investigate the relationship of peri-operative cerebral oxygen saturation (rSO2) with post-operative cognitive function in the elderly patients under edaravone injection combined with intravenous and inhalation anesthesia in order to establish the guides for clinical anesthesia practice.Sixty ASA Ⅰ-Ⅱ elderly patients (>60 years old) who were scheduled for selective abdominal surgeries or surgeries on lower limb in our hospital from January 2013 to January 2014 were enrolled in the study. The patients were randomly divided into 3 groups (=20), edaravone group 1 (E1: 100ml 0.9% NaCl containing 30mg edaravone), edaravone group 2 (E2: 100ml 0.9% NaCl containing 60mg edaravone), and control group (C, 100ml 0.9% NaCl). The above fluids were intravenously infused in 30 min during operation. All patients were not premeditated before anesthesia and given with atropine 0.5mg until entering the operation room. Anesthesia was induced with intravenous infusion of propofol, fentanyl and cisatracurium slowly. After tracheal intubation, all patients were mechanically ventilated to maintain partial pressure of CO2at end-tidal (PetCO2) at normal range. rSO2was continuously monitored and recorded during operation. Mini-mental state examination (MMSE), trail-making test, and grooved pegboard test were used to access cognitive function at 24h before and at 4, 8, 12 and 24h after surgery.(1) There was no significant difference in the general status among the 3 groups (>0.05). (2) No obvious difference was found in the scores of MMSE, trail-making test and grooved pegboard test among the 3 groups at 24h before operation (>0.05). (3) The patients of groups E2 and E1 had higher scores of cognitive tests than those of group C (<0.05), but there was no difference in the value of rSO2among the 3 groups (>0.05).Edaravone injection combined with intravenous and inhalational anesthesia reduces the incidence of postoperative cognitive dysfunction in the elderly patients, which may be related to its unique neuroprotective effect, elimination of free oxygen radicals, inhibition of lipid peroxidation, regulation of the relative apoptotic genes, and enhancement of tolerance to ischemia and hypoxia in central nervous system.
aged; cognitive disorders; cerebral oximeter; edaravone
(CWS12J022).
R592; R741.041
A
10.11915/j.issn.1671-5403.2015.06.093
2015−03−23;
2015−05−11
全军医药卫生科研课题项目(CWS12J022)
贾宝森, E-mail: jiabaosen99@sohu.com

