加装导流板的舀勺式马铃薯播种机排种器性能分析与试验
吕金庆,王英博,李紫辉,兑 瀚,刘中原,李季成,孙 贺,彭曼曼
加装导流板的舀勺式马铃薯播种机排种器性能分析与试验
吕金庆,王英博,李紫辉,兑 瀚,刘中原,李季成,孙 贺,彭曼曼
(东北农业大学工程学院,哈尔滨 150030)
马铃薯播种机排种器的投种角度、速度、高度以及种薯与土壤接触后的弹跳等对马铃薯排种器播种质量影响较大,针对上述问题,该文研制了舀勺式马铃薯排种器的投种结构,设计加装了导流板。通过对导流板的性能分析、种薯投种过程及种薯与沟底碰撞过程的运动学分析,确定了影响播种效果的因素;以主动轮转速、机组前进速度、投种高度为主要因素,株距变异系数、漏播率、重播率为试验指标进行田间试验,并进行了旋转正交试验回归分析。试验结果表明:经参数优化后的马铃薯排种器具有较好的播种质量,当主动轮转速为42 r/min、前进速度为1.2 m/s、投种高度为640 mm时,其株距变异系数平均值为12.5%、漏播率平均值为2.21%、重播率平均值为3.56%,其标准均高于传统的舀勺式排种器,播种效果提升显著(<0.01)。该研究为马铃薯排种器技术进步提供了参考。
农业机械;农作物;试验;马铃薯;排种器;导流板;弹跳;株距变异系数
0 引 言
随着马铃薯主食化进程的推进,马铃薯作为中国第四大粮食作物,其种植面积还将进一步扩大[1-3]。马铃薯单产量较低,除了马铃薯品种的因素外,机械化作业水平也是影响马铃薯产量的重要原因之一,其中较低的播种机械化水平严重制约了马铃薯产量的提高[4-7]。
在马铃薯机械化播种过程中,排种器的供种、取种、清种和投种过程均对播种质量有着不同程度的影响[8-9]。其中在投种过程中的投种角度、投种速度和投种高度,对播种后种薯落地位置和弹跳距离有着较大的影响,这也直接影响了马铃薯的播种效果[10-12]。国外的马铃薯排种器发展较迅速、种类较多,针刺式和勺带式排种器由于其较高的工作效率得到了广泛应用,但种薯落地后弹跳较远,导致株距不均的现象[13-15]。国内的马铃薯排种器应用较多的为舀勺式排种器[16],但是在投种时,由于机具自身的前进速度,对种薯的投种角度和投种速度影响较大,导致种薯落地后速度较大、弹跳距离较远、降低了播种的株距稳定性和播种质量[17]。为解决上述问题,本文在舀勺式马铃薯排种器的基础上,加装导流板,以平衡播种过程中的前进速度,提升播种效果。
通过对导流板的性能分析,以及整个种薯下落过程与落地后碰撞弹跳过程的运动学分析,采用对比试验的方法,分析不同因素对播种效果的影响,以获取影响马铃薯播种机排种器重播率、漏播率及株距变异系数等参数的定性规律,验证加装导流板能显著提升马铃薯播种机排种器的播种性能。
1 整体结构及工作原理
1.1 整体结构
该排种器主要由导种部件1、排种架2、主动轮3、清种部件4、排种导板5、排种带6、充种箱7、从动轮8、挡种部件9、导流板10组成。整体的结构如图1所示。
1.2 工作原理
排种带由传动系统驱动主动轮进行动力传递,排种带上固定有交错排列的两列舀勺,舀勺舀取充种箱中的种薯,随着排种带一起运动;挡种部件将舀勺间多余的种薯拨落,当舀勺中有多余一个种薯时,安装在主动轮下部的清种装置将多余种薯振落;种薯越过主动轮后,在重力的作用下,落到前一个舀勺的背面,沿着排种导板运动,防止种薯自由掉落,当运动到排种点后,种薯脱离舀勺,掉落的种薯与导流板接触,沿着导流板的曲面进行运动,而后落入田间,舀勺转过从动带轮,继续准备下一次的播种。
2 导流板的性能分析
2个导流板对称安装在排种器的出口位置,导流板与下落的种薯接触,改变种薯的速度方向和大小,从而改变种薯在排种过程中的运动过程。导流板用尼龙材料注塑形成,能有效的减小与种薯接触的滚动摩擦力;为了减小种子落入土壤后弹跳距离较大,以及投种时由于正碰对种薯造成损伤,导流板厚度由上到下逐渐增加,其侧面为曲面的形式,具体结构如图2所示,根据文献所述,最小位移发生在碰撞角度为75°~80°[18]。因此,将导流板工作曲面的倾斜角度为15°。为了配合排种架的安装,将导流板的整体弯折角度设置为116°,弯折半径为48 mm。
本文选取整薯为研究对象,将整个种薯理想化为质地均匀的球体;种薯与舀勺脱离后,与导流板接触,沿着导流板曲面下落,其运动为空间形式,以左侧导流板为例,分别建立以种薯质心为原点的2个坐标系,如图3所示。
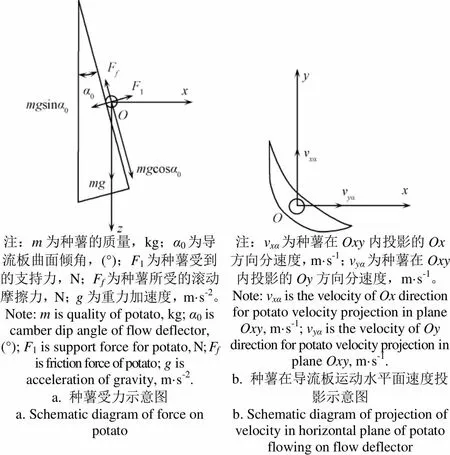
注:m为种薯的质量,kg;α0为导流板曲面倾角,(°);F1为种薯受到的支持力,N;Ff为种薯所受的滚动摩擦力,N;g为重力加速度,m·s-2。Note: m is quality of potato, kg; α0 is camber dip angle of flow deflector, (°); F1 is support force for potato, N; Ff is friction force of potato; g is acceleration of gravity, m·s-2.a. 种薯受力示意图a. Schematic diagram of force on potato注:vxα为种薯在Oxy内投影的Ox方向分速度,m·s-1;vyα为种薯在Oxy内投影的Oy方向分速度,m·s-1。Note: vxα is the velocity of Ox direction for potato velocity projection in plane Oxy, m·s-1; vyα is the velocity of Oy direction for potato velocity projection in plane Oxy, m·s-1.b. 种薯在导流板运动水平面速度投影示意图b. Schematic diagram of projection of velocity in horizontal plane of potato flowing on flow deflector
在平面内,种薯的受力如图3a所示。
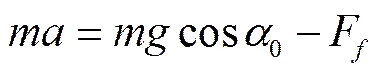
(2)
(3)
式中为种薯的质量,kg;0为导流板曲面倾角,(°);1为曲面对种薯的支持力,N;F为种薯所受的滚动摩擦力,N;为滚动摩擦系数;为重力加速度,m/s2。
由式(1)可知,种薯在导流板上的运动为沿着曲面的直线加速运动,其速度方向沿着曲面倾斜的方向,与竖直方向呈15°。
将种薯的运动速度在水平面内投影,如图3b所示,方向正向为与机具方向相反的方向,速度可以分解为沿着方向的速度v和方向的速度v。种薯方向的速度v,可使种薯向靠近排种器中间的方向运动,即两列排种带舀取的种薯交替落在对称的导流板后,可减小落入沟底的种薯纵向距离,落入垄沟内的种薯表现形式近似为一列;种薯方向的速度v,与在播种时排种器运动的方向相反,能够抵消部分速度,从而减小种薯落入田间的水平分速度,减小种薯落入沟底后的运动距离。导流板的设置还影响了种薯脱离排种器的速度,继而对种薯后续的下落和弹跳过程的轨迹也产生了影响。
3 种薯下落过程与种薯沟底碰撞过程的运动学分析
3.1 种薯下落过程的运动学分析
在种子下落的过程中,与土壤接触后会产生弹跳,根据文献[18]中所叙述,种子与土壤接触发生弹跳后,其弹跳具有空间性质,且种薯向每个方向弹跳的可能性大小相等;弹跳后的位移量不一致,方向不同,即会导致播种株距变异系数大、种薯间距合格指数低,同时不规则的弹跳过程也会增加重播率和漏播率[19-23],种薯弹跳不可避免,可以通过对运动参数的分析,尽量减少弹跳的距离,保证播种效果。
种薯与导流板接触,在重力的作用下,沿着曲面运动脱离导流板,之后的运动轨迹与种薯在导流板的运动处于同一平面内,为了便于研究空气阻力存在时的种子运动规律,建立如图4所示的000定坐标系,分析种薯脱离排种器后的运动情况,初始时刻为0=0,原点0为种薯脱离排种器的初始位置重合。

式中为空气阻力,N;()为阻力方向下与速度有关的函数关系式。
(5)
且初始时刻:
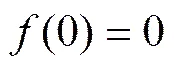
建立以种薯质心为原点的11y1二维动坐标系,种子质心所在点的轨迹的切线和法向为动坐标系的坐标轴,如图4所示。
(7)
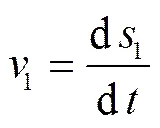
式中1为投种位移轨迹,m;1为投种过程速度,m/s;为时间,s。
分别将作用在薯块上的重力、空气阻力在动坐标系下进行投影,如式(9)所示。
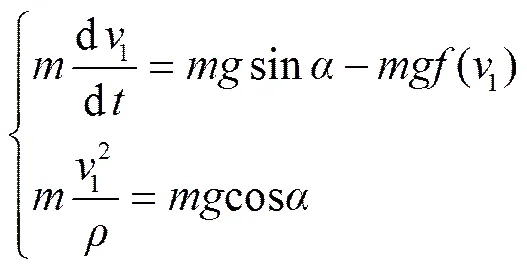
式中=()为轨迹曲率半径,m;为动坐标系11轴与竖直向下方向的夹角,(°),=()。
求得质心在动坐标系中的运动微分方程式(10)
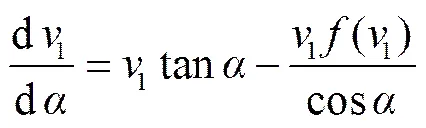
初始条件
(11)
式中v1为在投种点的速度,m/s;1为在投种点速度方向与水平轴00的夹角,(°);v0为种薯在投种点在00方向的速度,m/s;v0为投种点在00方向的速度大小,m/s。
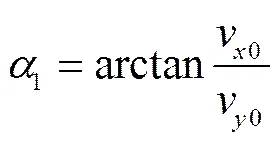
由式(9)—(12)得出下落过程薯块质心(1,1)在定坐标系中的运动坐标的运动轨迹方程为
(13)
式中1表示种薯投种运动过程在00方向的位移,m;1表示种薯投种运动过程在00方向的位移,m。为时间参数。
由式(13)可知,种子下落后落地点的位置、落地时刻的速度与初始投种速度、机具的前进速度和投种的高度有关,上述因素均能影响到种薯反弹后的初始速度大小与方向,进而影响种薯弹跳后的偏移程度。
3.2 种薯与沟底碰撞过程的运动学分析
种薯由排种器投种落到地表时,与地表发生碰撞,从而改变运动速度和方向发生弹跳,图5为种薯与沟底碰撞过程运动学分析。本文做如下假设:发生弹跳后的种薯运动轨迹仍与下落轨迹处于同一竖直平面,发生碰撞的平面为水平面,且忽略掉种薯自身旋转作用,种薯发生碰撞弹跳后的弹跳角2与入射角4大小相同[24-27]。
以碰撞点2为圆心建立如图5所示的定坐标系222;弹跳后,建立以种薯的质心为原点,运动轨迹的切线和法线为横纵坐标轴的动坐标系333。
(15)
(16)
式中2为弹跳过程位移轨迹,m;2为弹跳过程速度,m/s;3表示动坐标系33轴与竖直向下方向的夹角,(°),33()。
求得种薯质心在动坐标系中的运动微分方程
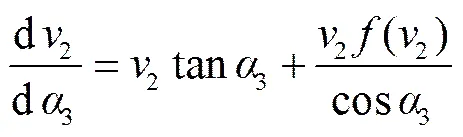
初始条件
(18)
式中v2为种薯反弹后的初速度,m/s;为碰撞恢复系数。3为入射速度,m/s。
由式(17)、式(18)得出碰撞弹跳过程薯块质心(2,2)在定坐标系中运动的轨迹方程为

式中2表示种薯碰撞弹跳过程在00方向的位移,m;2表示种薯碰撞弹跳过程在00方向的位移,m。
从式(19)可知,在导流板结构确定后,影响弹跳距离的因素包括种薯发生碰撞弹跳后的弹跳角2、动坐标系33轴与竖直向下方向的夹角3弹跳过程速度2;而2、3与种薯发生碰撞弹跳前的入射角4和投种速度v1有关,2与入射速度3有关;影响投种初始速度v1、入射速度3的因素为机具的主动轮转速、前进速度与投种高度。
因此,主动轮转速、前进速度与投种高度直接影响着投种过程种薯的位置与种薯落地弹跳后的位置,进而直接影响排种器播种质量,其具体的表现形式为重播率、漏播率及株距变异系数的大小。下文采用旋转回归正交试验、对比试验的方法,对影响马铃薯播种机排种器重播率、漏播率和株距均匀性的因素,及各因素显著性进行分析,研究各个因素对指标的影响规律。
4 田间试验
4.1 试验条件
2015年9月和2016年5月在黑龙江省农业科学院试验基地,进行加装导流板的舀勺式马铃薯播种机种器的田间试验。试验前耕整地平整,土壤为普通黑土,土壤坚实度为63.2 kPa,土壤含水率为17.0%;播种机的配套动力为59.6 kW的拖拉机;试验种薯选用东农303品种,单个种薯的平均三轴尺寸大小为45.1 mm×36.2 mm×25.1 mm,形状指数为205.8,平均质量为24.38 g,平均含水率为76.2%,净度>99%,田间作业及测量过程如图6所示。

a. 试验过程a. Experimental processb. 结果测量b. Results measure
4.2 评价指标
参照《GB/T 6242-2006 种植机械马铃薯种植机试验方法》规定的试验方法,考察加装导流板的舀勺式马铃薯播种机排种器的播种性能。种薯落地后的弹跳将直接影响排种器排种质量,其排种质量的具体表现形式为排种器的重播率、漏播率及株距变异系数的大小。以主动轮转速、前进速度和投种高度为试验因素,株距变异系数、漏播率和重播率为试验指标,进行二次正交旋转组合试验,每组试验重复3次,计算测量结果的平均值[28];播种后,选取每次播种过程中,一行的5个测量段进行数据采集,每段测量20个种薯的间距,每两个测量段相距30 m,共选取100个种薯进行株距测量,计算出株距变异系数、重播率和漏播率。
4.3 试验方案与结果分析
4.3.1 二次旋转正交组合试验设计
进行(三因素)二次旋转正交组合试验,以株距变异系数、漏播率和重播率为试验指标,各因素的水平范围为:主动轮转速32~52 r/min,前进速度0.60~1.40 m/s,投种高度600~800 mm。地轮将动力通过传动装置传递给主动轮,在进行试验时,可以通过调整中间传动装置改变不同的主动轮转速,选取试验所需水平值,进行田间试验的过程中,可根据不同的实际情况对清种装置进行调节。通过试验,对影响株距变异系数、漏播率和重播率的因素进行显著性的分析,根据实际需要对各个参数组合进行优化,试验因素水平编码表如表1所示,试验方案及试验结果如表2所示。
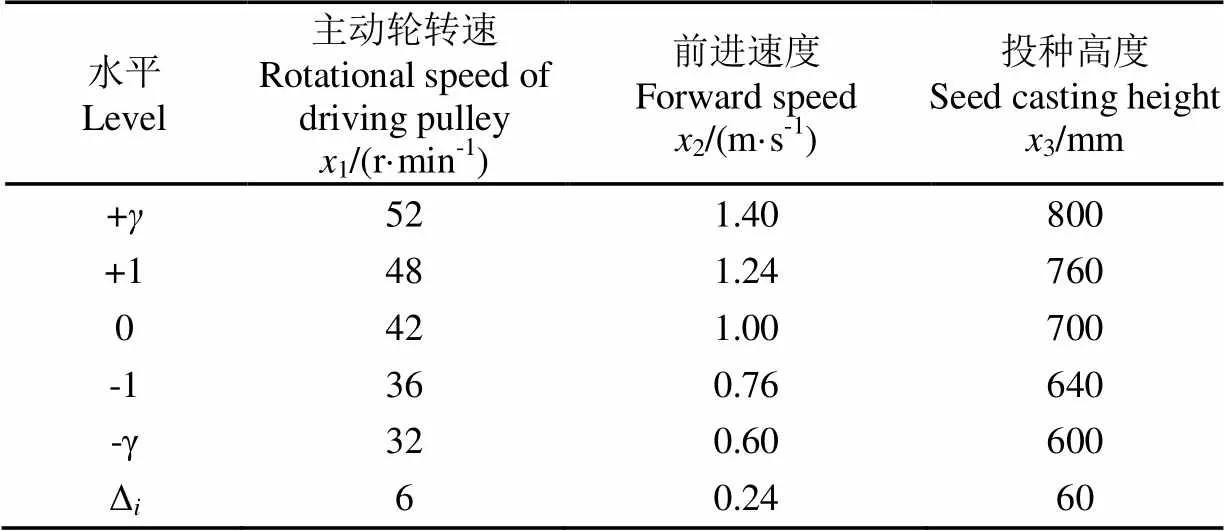
表1 试验因素水平及其编码表
注:选取中心点的试验次数为9次。
Note: Number of tests for the center point is 9 times.
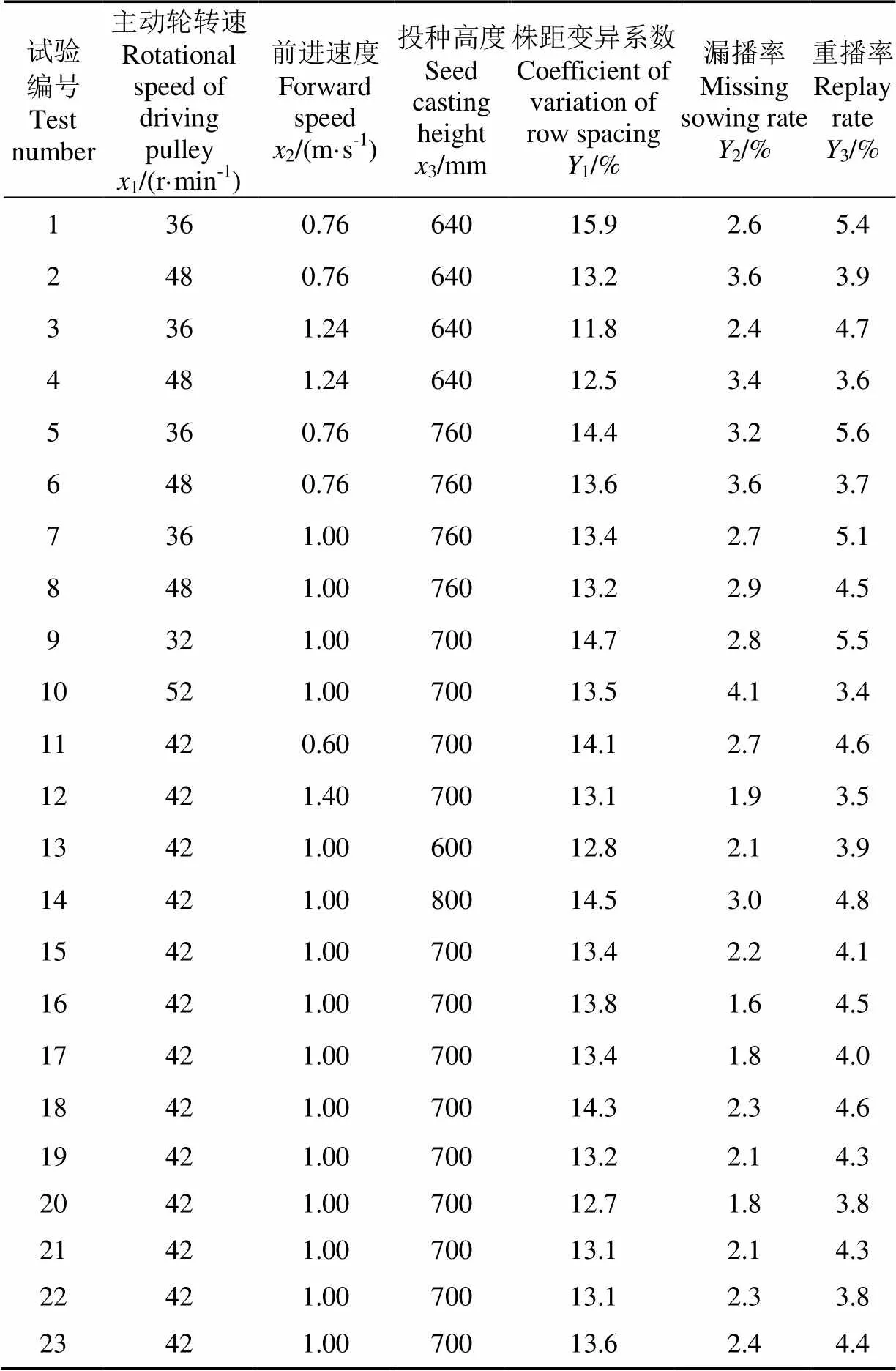
表2 试验方案及试验结果
4.3.2 试验结果分析与回归模型建立
利用Design Expert 8.0.6软件对试验结果进行二次回归分析,并进行多元回归拟合,得到株距变异系数1、漏播率2、和重播率3,3个试验指标的回归方程,并检验其显著性。
1)株距变异系数1的显著性分析
通过对试验数据的分析和拟合,株距变异系数1方差分析如表3所示。由表3可知,试验整体模型极显著(<0.01),主效应中前进速度2对于试验指标株距变异系数1影响最大,交互项中前进速度与主动轮转速的交互项12对指标影响最大,主动轮转速1、投种高度3、主动轮转速与投种高度的交互项23均有显著或较显著影响,其他各项不显著。各因素对株距变异系数影响的主次顺序是2>1>3。将其中不显著的交互作用项的回归平方和、自由度并入残差项,再次进行方差分析,结果如表3所示。得到各因素对株距变异系数1影响的回归方程如式(20)所示。
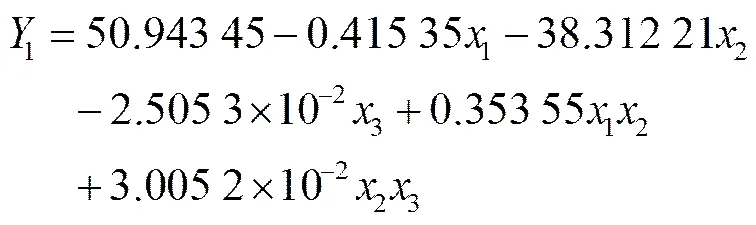
式中1为主动轮转速r/min;2为前进速度m/s;3为投种高度,mm。
对上述回归方程进行失拟性检验,如表3所示,其中>0.1,不显著。证明试验指标和试验因素存在显著的二次关系。
2)漏播率2的显著性分析
通过对试验数据的分析和拟合,漏播率2方差分析如表3所示。由表3可知,试验整体模型极显著,主效应中主动轮转速1对于试验指标漏播率2影响最大,交互项中主动轮转速与投种高度的交互项13对指标影响最大,前进速度2、投种高度3及3个因素的二次项均有显著和较显著影响,其他各项不显著。各因素对漏播率影响的主次顺序是1>2>3。将其中不显著的交互作用项的回归平方和、自由度并入残差项,进行方差分析,结果如表3所示。得到各因素对漏播率2影响的回归方程如式(21)所示。
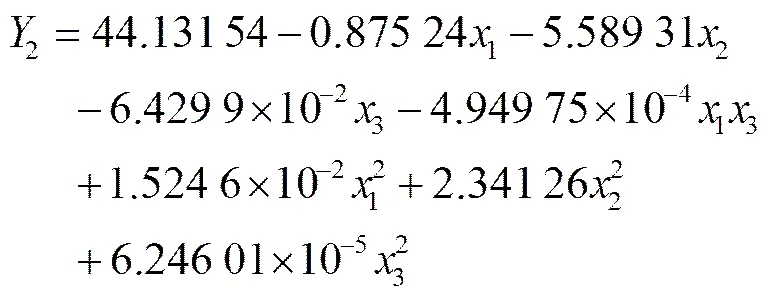
对上述回归方程进行失拟性检验,如表3所示,其中>0.1,不显著。证明试验指标和试验因素存在显著的二次关系。
3)重播率3的显著性分析
通过对试验数据的分析和拟合,重播率3方差分析如表3所示。由表3可知,试验整体模型极显著,主效应中主动轮转速1对于试验指标重播率3影响最大,交互项中前进速度与主动轮转速的交互项12对指标影响最大,前进速度2、投种高度3、主动轮转速的二次项均有显著和较显著影响,其他各项不显著。各因素对重播率影响的主次顺序是1>3>2。将其中不显著的交互作用项的回归平方和、自由度并入残差项,进行方差分析,结果如表3所示。得到各因素对重播率3影响的回归方程如式(22)所示。
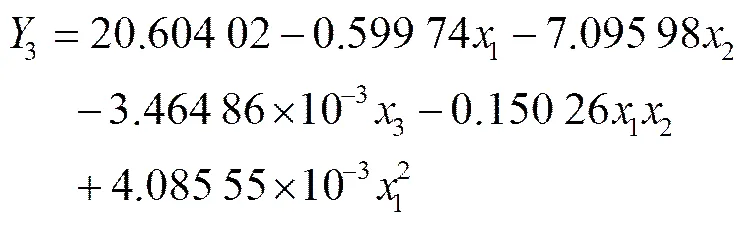
对上述回归方程进行失拟性检验,如表3所示,其中>0.1,不显著。证明试验指标和试验因素存在显著的二次关系。
4.3.3 响应曲面分析
通过Design-Expert 8.0.6 软件对数据的处理,得出主动轮转速、前进速度、投种高度之间的显著和较显著交互作用对株距变异系数、漏播率、重播率3个试验指标影响的响应曲面,如图(7)-图(9)所示。
对于株距变异系数1,当投种高度为700 mm时,主动轮转速和前进速度的交互作用影响如图7a所示。当主动轮转速一定时,前进速度与株距变异系数呈负相关,其最优的前进速度范围为0.95~1.24 m/s;当前进速度保持一定时,主动轮转速与株距变异系数呈负相关,其最优的主动轮转速范围为44.5~47.9 r/min;在机具作业过程中,前进速度为影响株距变异系数的主要因素。前进速度与投种高度的交互作用影响如图7b所示。对于机具主动轮转速为42 r/min时,当投种高度保持不变时,前进速度与株距变异系数呈负相关,其最优的速度范围为0.95~1.24 m/s;当主动轮转速保持一定时,投种高度与株距变异系数呈正相关,其最优的投种高度为640.5~700.0 mm,其中投种高度是影响指标的主要因素。
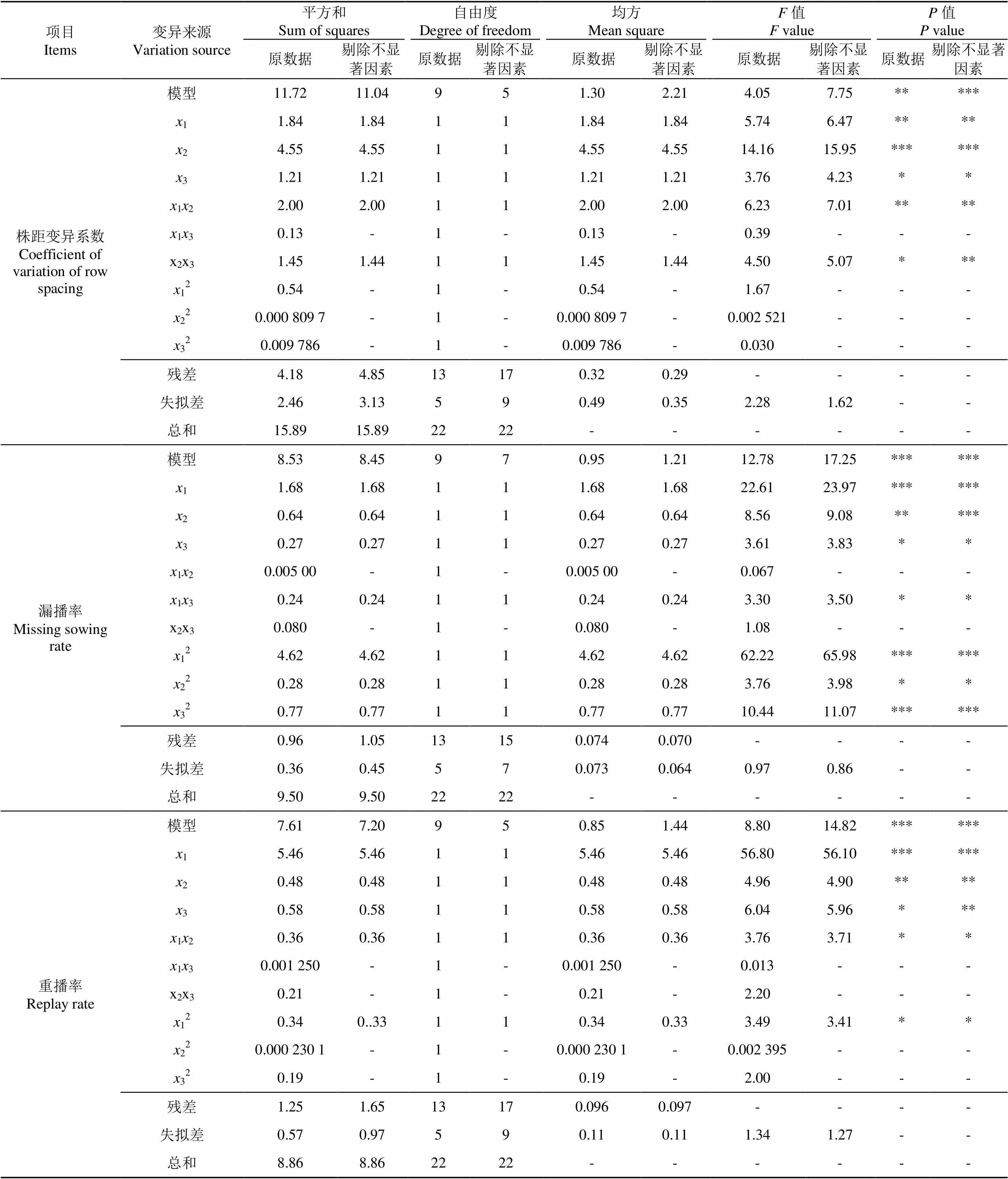
表3 株距变异系数、漏播率及重播率的方差分析表
注: “***”表示极显著(<0.01);“**”表示显著(0.01≤<0.05);“*”表示较显著(0.05≤<0.1),下同。
Note: “***” means highly significant (<0.01); “**” means very significant (0.01≤<0.05); “*” means significant (0.05≤<0.1), the same below.
对于漏播率2,当前进速度为1 m/s时,主动轮转速和投种高度的交互作用影响如图8所示,当投种高度一定时,漏播率随着主动轮转速的增加,先减小后增加,其最优的主动轮转速范围为36.1~44.5 r/min;当主动轮转速一定时,漏种率随着投种高度的增加,先减小后增加,其最优的投种高度为640.5~759.5 mm。2个交互作用项中主动轮转速为影响试验指标的主要因素。
对于重播率3,当投种高度为700 mm时,主动轮转速和前进速度的交互作用影响如9所示,当前进速度一定时,主动轮转速与重播率呈负相关,其最优的主动轮转速范围为43.0~47.9 r/min;当主动轮转速保持一定时,前进速度与重播率呈负相关,其最优的前进速度为0.97~1.24 m/s;2个交互作用项中前进速度为影响试验指标的主要因素。
为获得排种器最佳排种性能作业参数,利用Design Expert 8.0.6软件中的优化模块对上述3个回归模型进行约束目标优化求解,根据播种机的实际工作条件、作业要求及相关理论的分析选择优化的约束条件[29]。目标及约束函数:
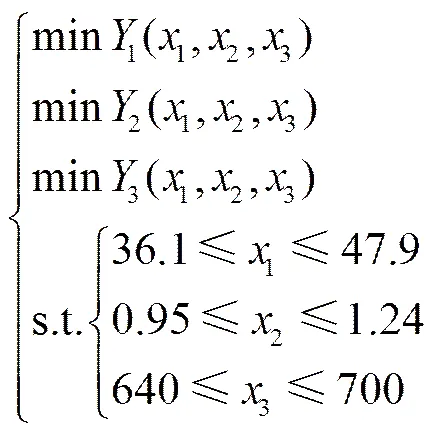
对目标函数中的3个参数进行优化求解,能够得到多种参数组合。考虑到实际的工作要求,为满足马铃薯种植的农艺要求,得到优化结果为:当主动轮转速为41.29~43.33 r/min,前进速度为1.2~1.3 m/s,投种高度为640.0~667.5 mm时,理论的株距变异系数范围为12.1%~12.6%,漏播率范围为2.01%~2.25%,重播率范围为3.5%~3.9%。
4.4 验证试验
4.4.1 试验条件
试验地点为黑龙江省农业科学院试验基地。土壤为平整地表,含水率为18.2%。以文献[30]中的试验方法进行试验,试验重复3次,取均值,试验方法与田间试验相同。
4.4.2 试验结果与分析
经过参数优化的马铃薯播种机排种器性能指标与文献[31]中规定的指标值对比,以及与传统的舀勺式排种器结果性能对比、方差结果如表4所示[30-31]。播种机的参数选择为主动轮转速42 r/min、前进速度1.2 m/s、投种高度640 mm。试验结果表明,经过参数优化的马铃薯排种器株距变异系数平均值为12.5%、漏播率平均值为2.21%、重播率平均值为3.56%,与所得的优化结果基本一致,且优于相应的国家标准;相较于传统的舀勺式马铃薯排种器,装有导流板的排种器的株距变异系数降低了4.8%,漏播率降低了1.19%,重播率降低了0.22%;加装导流板对于排种器的各个作业指标的影响均为极显著(<0.01)。这是由于导流板的安装抵消了部分机具的前进速度,减小了水平速度,减小种薯落入沟底后的水平距离。投种高度的设置较低,主动轮转速较小,减少了种薯在与土壤平面发生接触时的入射角度和速度,从而减小了种薯的弹跳距离,验证了公式的合理性。试验验证了优化参数的合理性,按照优化后的参数进行作业能够满足要求。
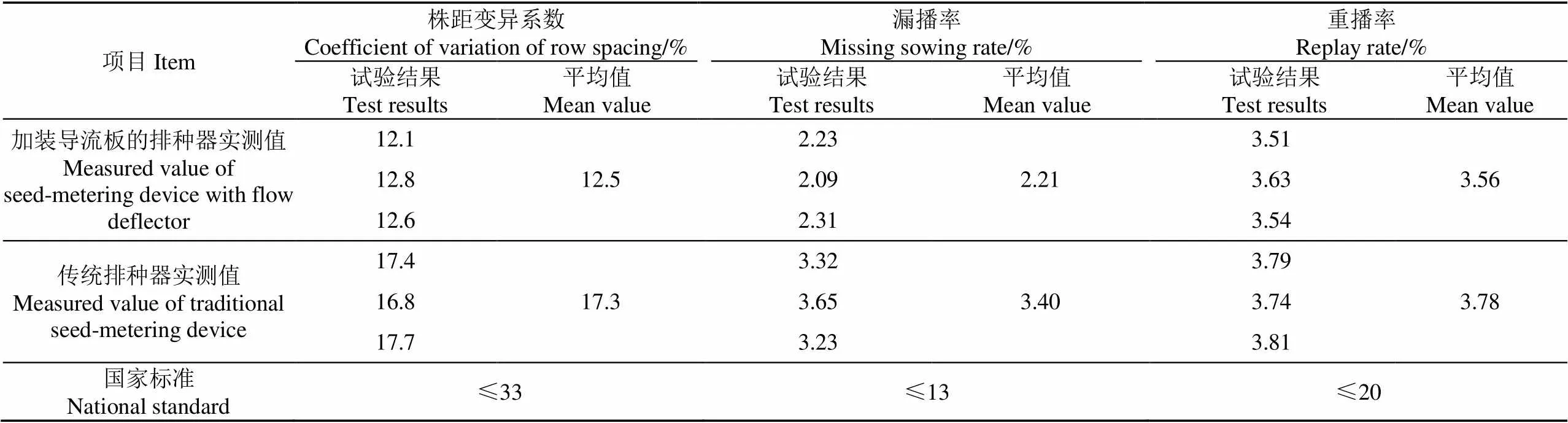
表4 优化后机具作业性能比对
5 结论与讨论
舀勺式马铃薯播种机排种器下部加装导流板,减少了种薯落入沟底的纵向距离,使落入垄沟内的种薯表现形式近似为一列;导流板能有效减小种薯落入田间的水平分速度,减小种薯落入沟底后弹跳距离。通过对排种器投种弹跳过程的运动学分析,得出了影响种薯落地后弹跳距离的因素为投种角度、投种速度、投种高度。
对安装有导流板的舀勺式马铃薯排种器进行了二次正交旋转组合的田间试验,建立了试验指标与影响因素间的回归模型。通过对比试验验证了安装有导流板的排种器的播种性能,当主动轮转速为42 r/min、前进速度为1.2 m/s、投种高度为640 mm时,排种器株距变异系数平均值为12.5%、漏播率平均值为2.21%、重播率平均值为3.56%,优于相应的国家标准;相较于传统的排种器,株距变异系数降低了4.8%,漏播率降低了1.19%,重播率降低了0.22%,验证了加装导流板能显著提高排种器的播种精度及理论公式的合理性。在种薯播种过程中,种薯与土壤接触后弹跳过程的分析将在后续研究中分不同品种、不同土壤类型进行具体计算和分析。
本文通过导流板的性能分析、对种薯排种过程的运动学分析,为马铃薯播种机排种器技术进步提供了参考。
[1] Kempenaar C,Struik P C. The canon of potato science: Haulm killing[J]. Potato Research, 2008, 50(3): 341-345.
[2] 柳俊. 我国马铃薯产业技术研究现状及展望[J]. 中国农业科技导报,2011,13(5):13-18.
Liu Jun. Research status and prospects of potato industry in China[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2011, 13(5): 13-18. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 杨帅,闵凡祥,高云飞,等. 新世纪中国马铃薯产业发展现状及存在问题[J]. 中国马铃薯,2014,28(5):311-316.
Yang Shuai, Min Fanxiang, Gao Yunfei, et al. Status quo and challenges of China potato industry of the 21st century[J]. Chinese Potato Journal, 2014, 28(5): 311-316. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 李伟红. 2CM-2型马铃薯播种机的结构与性能研究[J]. 农
业科技与装备,2012(5):16-19.Li Weihong. Research on the structure and performance of 2CM-2 potato planter[J]. Agricultural Science & Technology and Equipment, 2012(5): 16-19. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 杜宏伟,尚书旗,杨然兵,等. 我国马铃薯机械化播种排种技术研究与分析[J]. 农机化研究,2011,33(2):214-217.
Du Hongwei, Shang Shuqi, Yang Ranbing, et al. Research and analysis on mechanized potato seed sowing techniques[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2011,33(2): 214-217. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 吕金庆,韩休海,杨金砖,等. 2CMF-2型马铃薯施肥种植机[J]. 农机化研究,2009,31(6):103-105. Lü Jinqing, Han Xiuhai, Yang Jinzhuan, et al. 2CMF-2-type potato plant fertilizing machine[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2009, 31(6): 103-105. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 杨然兵,张翔,李建东,等. 锥体帆布带式排种器参数优化与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2016,32(3):6-13.
Yang Ranbing, Zhang Xiang, Li Jiandong, et al. Parameter optimization and experiment on cone canvas belt type seed-metering device[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2016, 32(3): 6-13. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 孙伟,王关平,吴建民. 勺链式马铃薯排种器漏播检测与补种系统的设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2016,32(11):8-15.
Sun Wei, Wang Guanping, Wu Jianmin. Design and experiment on loss sowing testing and compensation system of spoon-chain potato metering device[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2016, 32(11): 8-15. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 吕金庆,杨颖,李紫辉,等. 舀勺式马铃薯播种机排种器的设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2016,32(16):17-25.
Lü Jinqing, Yang Ying, Li Zihui, et al. Design and experiment of cup-belt type potato seed-metering device[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2016, 32(16): 17-25. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 王泽明. 舀勺式马铃薯播种机排种器的设计与试验研究[D]. 哈尔滨:东北农业大学,2015.
Wang Zeming. Design and Experimental of Metering Device of Cup-belt Type Potato Planter[D].Harbin: Northeast Agricultural University, 2015. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 段青天,盛国成. 2CM-1型马铃薯种植机的研究与设计[J].中国农机化学报,2016,37(2):39-42.
Duan Qingtian, Sheng Guocheng. Research and design of 2CM-1 type potato planting machine[J]. Journal of Chinese Agricultural Mechanization, 2016, 37(2): 39-42. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 李成松,冯玉磊,坎杂,等. 单行悬挂式马铃薯施肥种植机的研制[J]. 江苏农业科学,2013,41(6):369-371. Li Chengsong, Feng Yulei, Kan Za, et al. The development of single row suspension type potato fertilization planter[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2013, 41(6): 369-371. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 陶桂香,衣淑娟,毛欣,等. 水稻植质钵盘精量播种装置投种过程的动力学分析[J]. 农业工程学报,2013,29(21):33-39.
Tao Guixiang, Yi Shujuan, Mao Xin, et al. Dynamic analysis on dropping processing of precision sowing device forseedling-growing tray made of paddy-straw in rice[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2013, 29(21): 33-39. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 杨丹. 单圆盘开沟器作用下种子触土后弹跳滚动位的测定与分析[D]. 长春:吉林大学,2006.
Yang Dan. The Measure and Analysis of Seed Bounce and Rolling Displacement after Touching Soil on Furrow Opener of Single Disk[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2006. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] Karayel D, Wiesehoff M, Muller J. Laboratory measurement of seed drill seed spacing and velocity of fall of seeds using high-speed camera system[J]. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 2006(50): 89-96.
[16] Buftan L P. Seed displacement after impact on a soil surface[J]. Agricultural Engineer Research, 1974, 19: 327-338.
[17] Tanaka H, Momotzu M, Oida A, et al. Simulation of soil deformation and resistance at bar penetration by the distinct element method[J]. Journal of Terramechanics, 2000, 37: 41-56.
[18] 张波屏. 播种机械设计原理[M]. 北京:机械工业出版社,1982:362-382.
[19] Arzu Yazgi. Adnan Degirmencioglu. Optimisation of the seed spacing uniformity performance of a vacuum-type precision seeder using response surface methodology[J]. Biosystems Engineering, 2007(97): 347-356.
[20] 马成林. 精密播种理论[M]. 长春:吉林科学技术出版社,1999.
[21] 史嵩,张东兴,杨丽,等. 气压组合孔式玉米精量排种器设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2014,30(5):10-18.
Shi Song, Zhang Dongxing, Yang Li, et al. Design and experiment of pneumatic maize precision seed-metering device with combined holes[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CASE), 2014, 30(5): 10-18. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 周军平,刘立晶,刘忠军,等. 精密播种机株距均匀性影响因素分析[J]. 农机化研究,2014,36(7):49-53.
Zhou Junping, Liu Lijing, Liu Zhongjun, et al. Influence factors analysis of the plants distance uniformity of precision planter[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2014,36(7): 49-53. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 王未,马旭,袁锐,等.基于均匀设计的种子弹跳滚动位移的试验研究[J]. 吉林农业大学学报,2006,28(6):694-696,701.
Wang Wei, Ma Xu, Yuan Rui, et al. Experimental study on displacement of seed bounce and rolling based on uniform design[J]. Jounal of Jilin Agricultural University, 2006, 28(6): 694-696,701. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] 李成华,夏建满,何波.倾斜圆盘勺式精密排种器投种过程分析[J]. 农业机械学报,2005,36(3):48-50.
Li Chenghua, Xia Jianman, He Bo. Analysis of seed throwing procedure by declined scope metering device[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2005, 36(3): 48-50. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] 袁锐. 精密播种机开沟器对种子触土后位移的控制及部件的研究[D]. 长春:吉林大学,2006.
Yuan Rui. Research of its Displacement after Seeds Touching Soil Controlled by the Furrow Opener of Precision Planter and its Parts[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2006. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] 眭晋. 大豆种子与土壤的碰撞过程试验研究与仿真分析[D]. 长春:吉林大学,2016.
Sui Jin. Research on Experiment and Simulation Analysis of Soybean Collision with Soil[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2016. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[27] 马旭,于海业,杨海宽.种子落于种沟后弹跳滚动位移的测定及建模[J]. 农业机械学报,1998,29(增刊):58-62.
Ma Xu, Yu Haiye, Yang Haikuan. The determining and model establishing of seed bouncing and rolling displacement after impact on a furrow[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 1998, 29(Supp.): 58-62. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[28] 韩恒,陈伟,杜文亮,等.影响带勺式马铃薯播种机排种性能的因素分析与试验[J]. 农机化研究,2016(3):209-212,217.
Han Heng, Chen Wei, Du Wenliang, et al. Analysis and test of the factors influence the seeding performance of potato planters[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2016(3): 209-212, 217. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[29] 葛宜元. 试验设计方法与Design-Expert软件应用[M]. 哈尔滨:哈尔滨工业大学出版社,2014:155-164.
[30] 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 马铃薯种植机械:GB/T 6242-2006[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社,2007.
[31] 中华人民共和国农业部. 马铃薯种植机质量评价技术规范:NY/T 1415-2007[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社,2011.
Performance analysis and experiment of cup-belt type patato seed-metering device with flow deflector
Lü Jinqing, Wang Yingbo, Li Zihui, Dui Han, Liu Zhongyuan, Li Jicheng, Sun He, Peng Manman
(150030,)
In order to enhance seeding accuracy and seeding quality of potato, this paper analyses and tests the bouncing and casting process of the cup-belt type potato seed-metering device and the performance of flow deflector. The cup-belt type potato seed-metering devices have the problems such as the nonuniformity of plant spacing, and the higher replay rate and missing rate due to different casting angle, casting speed, casting height and potato bouncing when contacting with furrow. This paper contains the main structure and working principle of cup-belt type potato seed-metering device, and the working principle of the flow deflector is that potato drops out from seed-metering device to the deflector, and then flows along the surface. The flow deflector can reduce longitudinal distance that potato drops into furrow to make the form of potato seed in approximately one column. Flow deflector can also reduce the horizontal velocity of potato seed to decrease the distance of potato dropping into furrow. During the sowing process of seed-metering device, in addition to the contact with the flow deflector, bouncing after contact with soil will also have an influence on seeding results. In the event of seed bounce, the images of bounce process have spatial properties, a circular point uniform density of position of potato in furrow after bounce was formed, each bounce direction has the same possibility after jumping, and the displacement of potato after bounce is inconsistent. The above phenomenon will lead to a higher coefficient of variation for sowing spacing, and a lower qualified rate of seeding. The process of irregular bounce will also increase the replay rate and missing rate. This paper also obtains the main factors that influence bounce distance through the kinematic analysis of casting and bouncing process during potato seeding. The field experiment was carried out; the rotational speed of the driving pulley, the forward speed of the device, and the seed casting height were taken as the experiment factors, and the coefficient of variation of row spacing, the missing rate and the replay rate as the test indices. The test was implemented in Heilongjiang Academy of Agricultural Sciences in September, 2015 and May, 2016. Potato in this test was prepared by Northeast Agricultural University, the shape index of potato was 205.8, and the average mass of potato was 24.38 g. The experimental data were processed and optimized by software Design-Expert 8.0.6. The test result showed the primary and secondary order of influencing factors for each test index. For the coefficient of variation of row spacing, the order was the forward speed of the device, the rotational speed of driving pulley and the casting height of potato seed. For the missing rate, the order was the rotational speed of the driving pulley, the forward speed of the device and the casting height of potato seed. The order for the replay rate was as follows: The rotational speed of the driving pulley, the forward speed of the device and the casting height of potato seed. And results also showed that the coefficient of variation of row spacing was 12.5%, the missing rate was 2.21% and the replay rate was 3.56%, when the rotational speed of driving pulley was 42 r/min, the forward speed of the device was 1.2 m/s and the potato casting height was 640 mm. This device had a good seeding effect compared with the national standards. Through the performance analysis of flow deflector, the theoretical analysis of the casting progress and bouncing process of potato, and the field experiment, it has been verified that the cup-belt type potato seed-metering device which has been optimized can enhance the potato seeding accuracy and sowing effect. This research not only provides the theoretical and technical reference for improvement and optimization of potato seed-metering devices, but also other precision sowing seed-metering devices.
agriculture machinery; crops; experiments; potato; seed-metering device; flow deflector; bounce; coefficient of variation of row spacing
10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.09.003
S233.2
A
1002-6819(2017)-09-0019-10
2016-11-16
2017-04-05
十三五国家重点研发计划智能农机装备专项“薯类高效收获技术与装备研发”(2016YFD0701600);现代农业产业技术体系建设专项资金(CARS-10-P22);黑龙江省重大科技攻关项目“马铃薯规模化种植关键技术装备研究”(GA15B401)
吕金庆,男,黑龙江哈尔滨人,研究员,国家马铃薯产业技术体系岗位科学家,主要从事马铃薯新型技术及装备方面研究。哈尔滨 东北农业大学工程学院,150030。Email:ljq8888866666@163.com
吕金庆,王英博,李紫辉,兑 瀚,刘中原,李季成,孙 贺,彭曼曼. 加装导流板的舀勺式马铃薯播种机排种器性能分析与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2017,33(9):19-28. doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.09.003 http://www.tcsae.org
Lü Jinqing, Wang Yingbo, Li Zihui, Dui Han, Liu Zhongyuan, Li Jicheng, Sun He, Peng Manman. Performance analysis and experiment of cup-belt type patato seed-metering device with flow deflector[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2017, 33(9): 19-28. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.09.003 http://www.tcsae.org

