Effects of hypoxia on sodium current in rat cardiomyocytes
Bo Liang,Hui-Ling Liao,*
1School of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine,Luzhou,China. 2Cardiovascular Department,Hospital(TCM)Affiliated to Southwest Medical University,Luzhou,China.
Introduction
Hypoxia is a common clinical myocardial damage factor,which can lead to cardiac hypertrophy and myocardial fibrosis,and ultimately cause irreversible damage to cardiac function [1]. Hypoxic preconditioning has been shown to increase cardiac tolerance to major ischemic reperfusion injury[2-3],probably due to hypoxic preconditioning-induced post-translational modification of proteins in the myocardium to produce immediate cardio protection and initiate gene transcription and protein synthesis[4].Many cardiovascular adverse events are related to hypoxia.Myocardial hypoxia and reoxygenation injury are common pathophysiological phenomena after ischemic heart disease and cardiac surgery[5].Cardiac sodium current plays a prominent role in maintaining the action potential plateau,determining the action potential duration and repolarization transmural dispersion and the development of arrhythmia[6].This study aims to investigate the ion channel mechanism of hypoxia in cardiomyocytes by studying the effect of hypoxia on the persistent sodium current of rat cardiomyocytes, and may provide a feasible target for clinical treatment.
Materials and methods
Cell separationAdult SPF healthy male Sprague Dawley rats(200 g-300 g)were provided by the experimental animal center of southwest medical university,and were artificially reared for 3 days to adapt to the environment and then used for experiments. Intraperitoneal injection of heparin 2500 IU for anticoagulation, 15 min after intraperitoneal injection of 3%pentobarbital sodium 2.5 ml anesthesia,then when the anesthesia was satisfactory,the chest was quickly opened to remove the heart, and the aorta was trimmed in a calcium-free Tyrode's Solution with ice residue at 0°C.The aorta with retrograde cannula is fixed to the langendroff perfusion device and the entire process is guaranteed to be completed within 2 min.First,perfusion of calcium-free Tyrode's solution at a constant rate for about 4 minutes to drain the heart,and then digested with calcium-free Tyrode's solution containing collagenase type II 0.5g/L and bovine serum albumin 1g/L for about 25 minutes.Then take out the heart, the ventricular muscles were mechanically separated in KB solution, filtered through a 200 mesh cell sieve,and allowed to stand at room temperature for at least 1 h before recalcification then could be used for the experiment.During the separation process, the perfusate temperature was maintained at around 37°C,and the perfusate was passed through 100%oxygen.
Whole-cell patch clamp recordingThe cell suspension after recalcification was dropped into the perfusion trough on the inverted biological microscope table.After the cell sedimentation was adhered to the wall, an appropriate amount of extracellular fluid was added to select the cell that are bright,the refractive index was good,and the horizontal stripes were clear and those well-adhered cells were used for the experiment.The microthruster is used to move the electrode to the negative pressure attraction above the cell to form a seal,and then the cell membrane is sucked by a negative pressure to form a whole cell record.The electrode is drawn by a two-step glass micropipette puller device,and the internal charging electrode has a resistance of 3 MΩto 5 MΩ.The current signal is guided by the Ag/AgCl electrode,amplified by a patch clamp amplifier,filtered(frequency 2 kHz)and stored in a computer.The control of the stimulus signal,data acquisition and analysis are all performed by Clampex 10.1.The entire experiment was carried out at room temperature.
Establishment of anoxic modelThe perfusion solution of a closed container is filled with 100%nitrogen for more than 30 min.After the cell current is stabilized,it is perfused at a constant speed for more than 15 min.At the same time,a relatively closed cover is placed on the perfusion tank and inner container is filled with 100% nitrogen to prevent oxygen in the air from diffusing into the perfusion tank.The oxygen partial pressure of the perfusion liquid can be reduced to about 4-5 kpa within 3-5 min,and the oxygen partial pressure is measured by an ISO2dissolved oxygen meter.
SolutionCalcium-free Tyrode's solution(in mm):NaCl 135, KCl 5.4, MgCl21, NaH2PO40.33,D-glucose 5,HEPES 10,pH adjusted to 7.4(room temperature)with NaOH.Normal extracellular fluid(in mm):choline chloride 100,NaCl 50,MgCl22,HEPES 10,D-glucose 10,4-2AP 5,CsCl 20,CdCl20.3,pH adjusted to 7.4(room temperature)with NaOH and filled with 100% O25min or more.Hypoxic extracellular fluid(in mm):choline chloride 100,NaCl 50,MgCl22,HEPES 10,sodium lactate 10,4-2AP 5,CsCl 20,CdCl20.3,pH adjusted to 6.8(room temperature) with NaOH, and filled with 100%N25min or more.Pippette solution(in mm):CsCl 130,MgCl22,NaCl 10,HEPES 10,pH was adjusted to 7.2(room temperature)with CsOH.KB solution(in mm):KOH 80,KCl 40,KH2PO425,MgSO43,glutamic acid 50,taurine 20,EGTA 0.5,HEPES 10,D-glucose 10,pH was adjusted to 7.4(room temperature)with KOH.
Main ReagentsCollagenase type II was purchased from worthington company,bovine serum albumin was purchased from Biotech, and the rest were analytical purity,made in China.
Data processingStatistical results were analyzed by one-way analysis of variance.
Result
Sodium current curve
Sodium currents were recorded by using whole cell patch clamps. After cell sealing and membrane rupture for 5 min, the clamping potential was maintained at-90 mV,and-90 mV to+30 mV was given.The depolarization stimulation was performed at a step of 5 mV.The time course was 40 ms,and the normal and hypoxic inactivation were recorded.Sodium current, stimulated every 10s, frequency 5HZ.The results(Figure 1)showed that the sodium current pattern of hypoxic cells was substantially consistent and significantly increased compared with normal cells.

Figure 1 Sodium currents in normal (A) and hypoxic(B)rat cardiomyocytes
V curve of sodium current
The peak current density values of each stimulation potential were plotted as IV curves. The results(Figure 2)showed that the morphological trajectory characteristics of the IV curve of normal and hypoxic cells were unchanged;compared with normal cells,the IV curve of hypoxic cells was significantly shifted upwards. The peak current of INa was increased by 15.68%(P<0.0001)relative to normal cells;the activation potential of normal and hypoxic cells was about-40 mV,and the maximum current peak corresponding to the stimulation voltage was-25 mV.
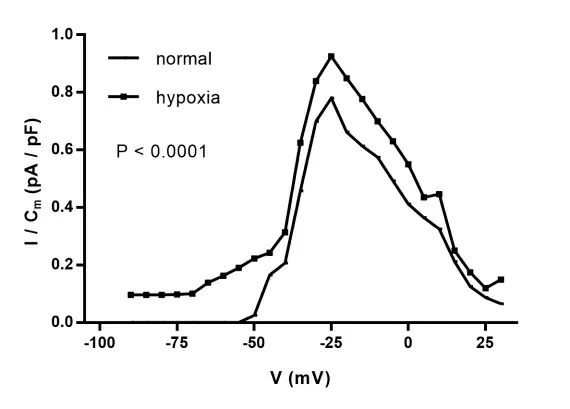
Figure 2 The I-V curve of sodium current
Discussion
Hypoxia is easily encountered in the clinic,and many cardiovascular adverse events reported in the literature are related to hypoxia[7-10].The role of voltage-gated sodium channels has been well established in neuronal cells,cardiomyocytes,and skeletal muscle cells.In cardiomyocytes,hypoxia is the main trigger for the sustained pattern of sodium current[11-12].
First,the mouse is the second mammalian species after humans,99%of mouse genes have homology in the human genome[13-15].Second,both species have a similar set of ion channel genes[16].Third,the vast majority of these ion channel genes have nearly identical sequence homology in both species.Fourth,these genes have similar expression patterns,and their protein products have similar structures,electrophysiological and pharmacological properties[16-17].Finally,the same mutation in the ion channel gene often produces a similar phenotype in both species[18].For the above reasons,we chose mice as experimental animals.
In this experiment,the changes of sodium current in normal and hypoxic rat cardiomyocytes were recorded.It was found that the sustained sodium current morphology and I-V curve were basically unchanged in hypoxic environment,but the I-V curve was significantly shifted upwards and the INa peak current was relatively up-regulated.From the above experimental results data, we speculate that the sustained sodium current will increase under anoxic environment.Changes in persistent sodium currents in cardiomyocytes during hypoxic pathology play an important role in the development of arrhythmias,which should be considered as a new therapeutic target, but this depends on changes in the physiological and pathological conditions of the sodium channel and the mechanism of regulation need a deeper research and understanding to guide clinical diagnosis and treatment.
In summary,the results of this experiment show that the continuous sodium current increases under anoxic environment.
1. Bian FW.Effect of high glucose or hypoxia on the expression of Nkx2-5 and Tbx5 in primary cardiomyocytes.Hebei Med Univer 2014,12:11.
2. Lu MJ,Chen YS,Huang HS,et al.Hypoxic preconditioning protects rat hearts against ischemia-reperfusion injury via the arachidonate12-lipoxygenase/transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 pathway.Basic Res Cardio 2014,109:414.
3. Ma MC, Chen YS. Hypoxic preconditioning protects rat hearts against ischemia-reperfusion injury: role of arachidonate 12-lipoxygenase.World Congress Cardio 2012,23:E737-8.
4. Nadtochiy SM,Yao H,Mcburney MW,et al.SIRT1-mediated acute cardioprotection.American J Physio Heart Circulatory Physio 2011,301:H1506-12.
5. Zhang Y,Chen G,Zhong S,et al.N-n-butyl haloperidol iodide ameliorates cardiomyocytes hypoxia/reoxygenation injury by extracellular calcium-dependent and -independent mechanisms.Oxid Med Cell Longev 2013,2013:912310.
6. Antzelevitch C.Electrical heterogeneity,cardiac arrhythmias,and the sodium channel.Circulation Res 2000,87:964.
7. Zhang C,Dong H,Ma J,Wang GF.Effects of intermittent hypoxia on HMGB1-sTLR2 /sTLR4-IL6 inflammatory pathway. The 9th Annual Conference of China Sleep Research Society 2016,China.
8. Tu XP,Wang N,Hu K.The pathogenesis of hypertension caused by chronic intermittent hypoxia.Chin J Respiratory Critical Care 2012,1:513-516.
9. Liu H. Mechanism of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α-related molecules affecting atherosclerotic plaque formation and stability:Shandong University,2016.
10.Sless RT,Hayward NE,Ryan PM.The chicken or the egg sildenafil therapy for fetal cardiovascular dysfunction during hypoxic development: studies in the chick embryo. J Physio 2017,1:90.
11.Saint DA.The cardiac persistent sodium current:an appealing therapeutic target. British J Pharmacology 2009,153.
12.Ai SD,Ke JY,Wang GP.A persistent sodium current in rat ventricular myocytes. J physio 1992,22:453.
13.Schuler G.Initial sequencing and analysis of the human genome. Med Supple 2001, 409:860-921.
14.Lander E, Linton L, Birren B, et al. Initial sequencing and analysis of the human genome.Nature 2011,23:334-346.
15.Hang WR,Kerstin L-T,Ewan B,et al.Initial sequencing and comparative analysis of the mouse genome.Nature 2002,420:6915.
16.Jenie JT,Made ZC,Serge B,et al.Evolution of the human ion channel set. Combinatorial Chemistry 2009,12:234-245.
17.Menna NK,Barry L.Knockin animal models of inherited arrhythmogenic diseases:what have we learned from them. J Cardiovascular Electrophysiology 2007,18:10.
18.Choy L,Yeo JM,Tse V,et al.Cardiac disease and arrhythmogenesis:mechanistic insights from mouse models.IJC Heart Vasculature 2016,22:3345.
19.Bocquet A,Sablayrolles S,Vacher B,et al.A new blocker of the persistent sodium current prevents consequences of hypoxia in rat femoral artery.Br J Pharmacol 2010,161:405-415.
 TMR Integrative Medicine2018年4期
TMR Integrative Medicine2018年4期
- TMR Integrative Medicine的其它文章
- Efficacy of acupuncture on treating obesity and adipose-incurred illnesses
- Review of the mechanisms of TCM in relieving the chemotherapy-induced diarrhea
- Efficacy of blood-lettingpuncture and cupping in the treatment ofperiarthritis ofshoulder:a systematic review
- Based on theprocess management of traditional Chinese medicine comprehensive intervention method on outcomes inpatients with mild/moderate chronic obstructivepulmonary disease:studyprotocol for apractical randomized controlled trial
