2008~2019年河北省医学科研课题查新结果分析
刘丹凤 刘斯文 李向黎
摘要:目的 分析2008~2019年河北省醫学科研课题查新结果,了解河北省医学科研水平,为完善查新咨询工作提供相应的对策。方法 对河北省2008~2019年医学查新课题的数量、查新单位、查新范围、查新级别、查新内容的新颖度进行统计分析。结果 2008~2014年查新数目保持在稳定的范围内,2015年查新数量达到高峰,2016~2019年又趋于平稳,查新项目呈逐年增高趋势。中文数量高于中外文数量,其中中文占比为82.20%~99.88%,而中外文占比仅为0.12%~17.80%;省市级单位数量高于县级单位数量,其中省市级占比为86.57%~94.26%,而县级占比仅为5.74%~15.15%;省内数量高于省外数量,其中省内占比为96.22%~99.88%,而省外占比仅为0.04%~3.78%。结论 我省医学查新项目数量逐年增加,中文、省市级、省内科研项目较多,而中外文、县级、省外科研项目较少,应加强人才队伍建设,适应知识服务一体化的要求,利用知识服务平台,更好为基层服务,并主动拓展省外查新业务。
关键词:医学查新;科研现状;查新单位
Abstract:Objective To analyze the novelty search results of medical scientific research projects in Hebei Province from 2008 to 2019, understand the level of medical scientific research in Hebei Province, and provide corresponding countermeasures for improving the novelty search consulting work.Methods A statistical analysis was made on the number of medical novelty search topics, novelty search units, novelty search scope, novelty search levels, and novelty of novelty search contents in Hebei Province from 2008 to 2019.Results The number of novelty searches remained within a stable range from 2008 to 2014. The number of novelty searches reached a peak in 2015 and stabilized again from 2016 to 2019. The number of novelty searches showed an increasing trend year by year. The number of Chinese was higher than the number of Chinese and foreign languages, of which Chinese accounted for 82.20%~99.88%, while the proportion of Chinese and foreign languages was only 0.12%~17.80%; the number of provincial and municipal units was higher than the number of county-level units, of which the provincial and municipal levels account for was 86.57%-94.26%, while the county-level proportion was only 5.74%-15.15%; the number in the province was higher than the number outside the province, of which the proportion within the province was 96.22%-99.88%, while the proportion outside the province was only 0.04%-3.78%. Conclusion The number of medical novelty search projects in our province has been increasing year by year. There were more scientific research projects in Chinese, provincial and municipal levels, and within the province, while there were fewer scientific research projects in Chinese and foreign languages, county-level, and other provinces. The construction of talent teams should be strengthened to adapt to the integration of knowledge services. It was required to use the knowledge service platform to better serve the grassroots level and actively expand the new business of investigation outside the province.
Key words:Medical novelty search;Scientific research status;Novelty search unit
随着医学科技的发展,医学科学研究也随之进步。近年来,医务工作者对医学科研工作越来越重视,涌现出大量的医学科研课题。相对于科研课题而言,科研项目是医学发展、职称晋升中一个不可或缺的环节,这就意味着对科研查新人员工作能力、工作方式方法、人才培养等方面有着更高的要求。查新咨询工作作为医学科研管理工作的一部分,其可以在一定程度上反映医学发展现状[1]。本文通过对2008~2019年河北省医学科研课题查新结果进行分析,以期找出完善查新咨询工作的对策,更好地服务河北省医学科研工作,现报道如下。
1材料与方法
1.1材料来源 选取2008~2019年河北省医学情报研究所查新咨询室保存的查新项目登记表的查新记录作为统计信息源。
1.2方法 通过对档案中查新项目信息进行核实,在此基础上对查新项目的数量、范围、单位、省份进行统计分析。
1.3统计学方法 应用SPSS 11.0统计学软件进行数据分析,计数资料以[n(%)]进行描述。
2结果
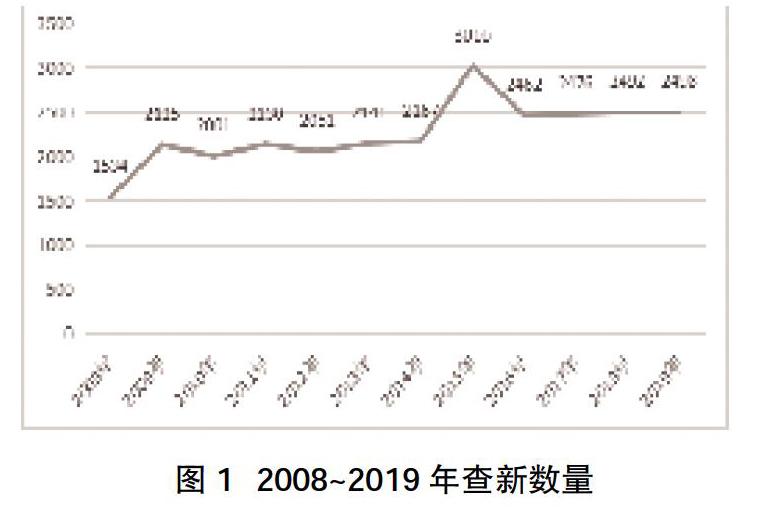
2.1查新数量 2008~2014年查新数目保持在稳定的范围内,2015年查新数量达到高峰,2016~2019年又趋于平稳,查新项目呈逐年增高趋势,见图1。
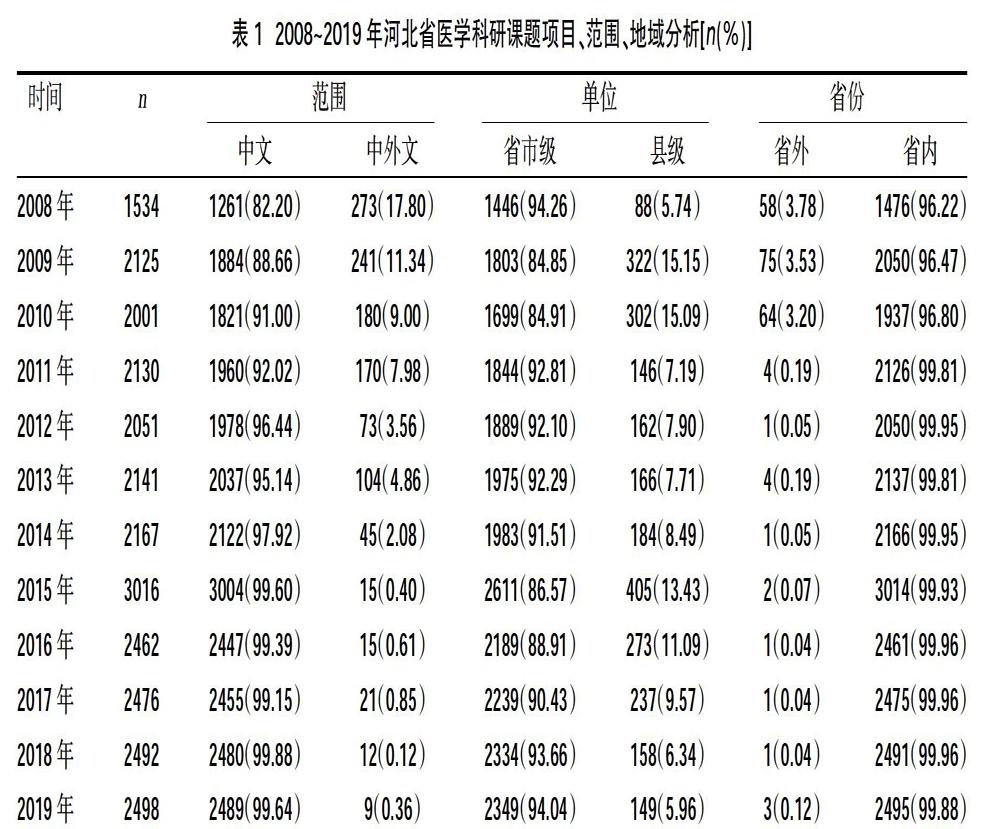
2.2河北省医学科研课题项目、范围、地域分析 查新范围:中文数量高于中外文数量,其中中文占比为82.20%~99.88%,而中外文占比仅为0.12%~17.80%;查新单位:省市级数量高于县级数量,其中省市级占比为86.57%~94.26%,而县级占比仅为5.74%~15.15%;查新省份:省内数量高于省外数量,其中省内占比为96.22%~99.88%,而省外占比僅为0.04%~3.78%,见表1。
3讨论
医学查新工作是科研管理中的重要组成部分,是科研从开始到结束的整个过程所不可缺少的部分,能为科研人员提供基本的基础知识,为科研人员与科研管理人员传递信息,避免重复和走弯路所造成的时间及物质资源的浪费[2]。查新咨询工作已经成为科研课题立项及成果申报的一个必要环节,随着科研管理与科研决策的科学化、规范化程度的不断提高,查新咨询作为医学情报工作的一部分内容在科研管理中的地位和作用越来越突出。
本研究结果发现,2008~2014年查新数目保持在稳定的范围内,查新项目呈逐年增高趋势,说明我省医学科研课题项目逐年增加。省市级数量高于县级数量,说明县级和省市级医学查新水平差距大,县级医院科研水平有待提高;但2009年之后,由于查新知识的普及与科教工作的重视,县级单位的查新率较2008年有所提高,查新数量到300多项,之后2001~2014数量减少至150项左右,保持在稳定范围内,2015年数量到达高峰。相对于县级医院,省市级医院科研水平较高,科研管理系统比较健全,对科研课题申报流程有较深刻的认识,因此其科研项目远高于县级单位。另外,县级单位之所以科研项目较少,有一部分原因是不够了解科研的重要性,而医学情报研究所查新咨询室承担着整个河北省查新工作的重担,要有服务意识,主动服务基层医护人员,使其了解并组建查新服务小组,用讲课、发表书面材料、课件等形式普及科研查新知识,以期更好的调动基层科研的积极性[3]。就查新范围而言,中文数量高于中外文数量,可能是因外文数据库不够完善,科研人员的需求、查新人员人数不足等使中外文数量较少,另外也可能与一般市厅级科研课题立项、结题对于中外文查新没有硬性要求有关[4]。就查新省份而言,省内数量高于省外数量,因各个省份科研课题管理不同[5],要求查新咨询报告的要求也不同,其他省份也设有查新机构,再加上外省对本省查新机构的不了解,导致外省课题相对而言较少。
综上所述,我省医学查新项目数量逐年增加,中文、省市级、省内科研项目较多,而中外文、县级、省外科研项目较少,应加强人才队伍建设,适应知识服务一体化的要求,利用知识服务平台,更好为基层服务,并主动拓展省外查新业务。
参考文献:
[1]骆丽琳,龙玲.中国医药卫生科技查新进展[J].中国科技信息,2019,597(1):112-113.
[2]翟俊霞,赵晓东,狄岩,等.医学查新工作与科研管理相结合为基层医务人员服务[J].中华医学图书情报杂志,2010,20(5):54-55.
[3]李向黎,翟俊霞,解俊霞,等.医学情报工作结合科研管理服务基层的建议及措施[J].医学信息,2010,23(12):4446-4447.
[4]骆丽琳,王红宇.某医学查新机构2011-2015年查新项目统计分析[J].广西医学,2017,39(9):1462-1464.
[5]吴慧华,陈雪珍.医学查新工作中查新用户存在的问题及对策[J].中国社区医师,2013(4):395-396.
收稿日期:2020-04-06;修回日期:2020-04-30
编辑/杜帆

