儿童百日咳与类百日咳综合征的病原学分析及临床特征分析
陈云龙 盛文彬

[關键词] 儿童;百日咳;类百日咳综合征;病原学分析;临床特征
[中图分类号] R516.6 [文献标识码] A [文章编号] 1673-9701(2021)22-0020-04
Etiology analysis and clinical characteristics of pertussis and pertussis-like syndrome in children
CHEN Yunlong SHENG Wenbin
Respiratory Department, Hangzhou Children's Hospital, Hangzhou 310006, China
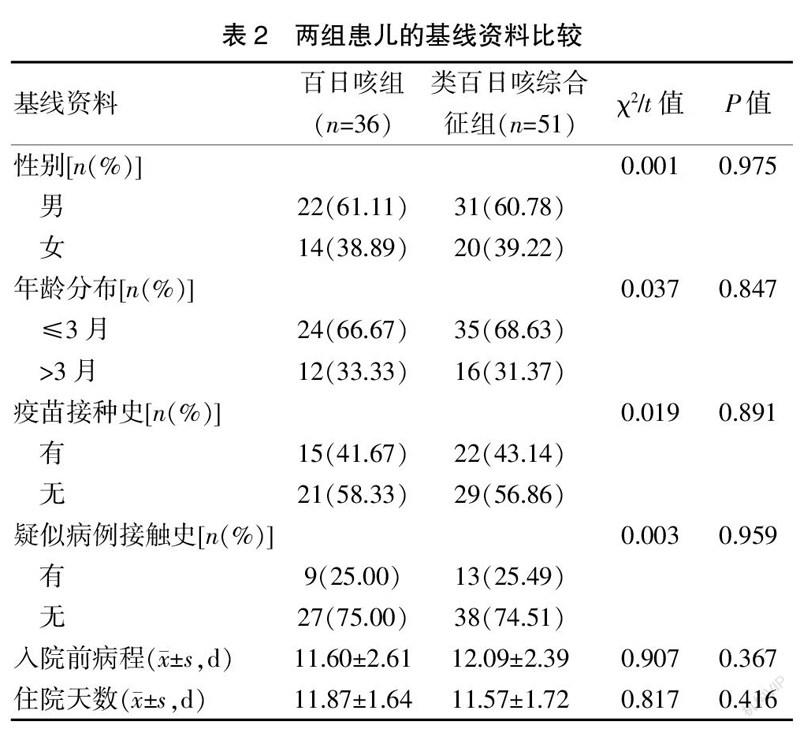
[Abstract] Objective To analyze the etiology and clinical characteristics of pertussis and pertussis-like syndrome in children. Methods The clinical data of 87 patients with suspected pertussis treated in our hospital from January 2019 to October 2020 were analyzed by the retrospective analysis. Nasopharyngeal secretions of all patients were collected for PCR detection, bacterial culture and etiology detection of Bordetella pertussis. Patients with positive PCR result were included into the pertussis group (n=36), and patients with negative PCR result were included into the pertussis-like syndrome group (n=51). The baseline information, etiological detection result and clinical characteristics difference in the two groups were compared. Results There were no statistically significant differences in baseline information such as gender, age distribution, vaccination history, contact history of suspected cases, course of disease before hospitalization, length of hospital stay in the two groups (P>0.05). In the pertussis group, 1 pathogen was detected in 17 patients, 2 pathogens were detected in 14 patients, 3 pathogens were detected in 2 patients, 4 pathogens were detected in 1 patient, and no other pathogens were detected in 2 patients; in the pertussis-like syndrome group, 1 pathogen was detected in 15 patients, 2 pathogens were detected in 28 patients, 3 pathogens were detected in 4 patients, 4 pathogens were detected in 2 patients, and no other pathogens were detected in 2 patients. There was no statistically significant difference in the etiological detection results between the two groups (P>0.05). Both groups of children had the highest detection rate of influenza A virus, followed by rhinovirus and parainfluenza virus. The detection rate of other viruses and pathogens was low. The number of patients with paroxysmal cyanosis in the pertussis group was more than that in the pertussis-like syndrome group, and the levels of white blood cell count and lymphocyte count in the pertussis group was significantly higher than those in the pertussis-like syndrome group, with statistically significant differences (P<0.05). There were no statistically significant differences in the clinical characteristics in the two groups (P>0.05). Conclusion If children with suspected pertussis have paroxysmal cyanosis and significantly increased levels of white blood cell count and lymphocyte count, the consideration was pertussis; influenza A virus, rhinovirus, and parainfluenza virus are the main pathogens that cause pertussis-like syndrome, which often appear together.

