Immunomodulatory effect of pachymaran on cyclosporine A (CsA)-induced lung injury in mice
CHEN Kiqin,WEI Ke,YE Chun,ZHAO Tinho,ZHANG Bo,XIAO Rong,LU Fngguo,b*
a. Medicine School,Hunan University of Chinese Medicine,Changsha,Hunan 410208,China
b. Hunan Province Key Laboratory of Integrative Pathogen Biology,Hunan University of Chinese Medicine,Changsha,Hunan 410208,China
ABSTRACT Objective To investigate the immunomodulatory effect of pachymaran on cyclosporine A(CsA)-induced lung injury in mice.Methods (i) Fifty male BALB/c mice were randomly divided into five groups (10 mice in each group): normal control (NC) group,30,45,and 60 mg/kg CsA groups,and lipopolysaccharide(LPS) group. Except for the NC group,other groups underwent CsA modeling. The NC group was treated with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS),the LPS group with 10 mg/kg LPS eight hours before mice euthanized,and the 30,45,and 60 mg/kg CsA groups with corresponding doses of CsA for seven consecutive days. After treatment,the body and organ mass of each group were weighed,and the lung,thymus,and spleen indexes were calculated. Hematoxylin-Eosin (HE) staining was performed to observe histopathological changes in the lungs of the mice. The protein expression levels of interleukin (IL)-2 and IL-1β in the blood were detected using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA),and those of surfactant protein D(SP-D),IL-2,and IL-6 in lung tissues were detected by immunohistochemistry (IHC). The mRNA expression levels of SP-D,IL-1β,IL-6,and myeloperoxidase (MPO) in the lung tissues were detected by quantitative reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR).(ii) Another 60 BALB/c mice were divided into six groups (10 mice in each group) : NC group,model control (MC) group,50,100,and 200 mg/kg pachymaran groups,and polyinosinicpolycytidylic acid [poly(I:C)] group. Except for the NC group,other groups underwent 45 mg/kg CsA modeling. The NC and MC groups were treated with distilled water,the pachymaran groups with corresponding doses pachymaran,and the poly(I:C) group with 0.1 mg/kg poly(I:C) for seven days.The mice were euthanized to obtain tissues and serum for detection.Detection methods were identical to those described in (i) above.Results (i) CsA (30 mg/kg) increased the lung index of mice (P < 0.001),and decreased the spleen index (P < 0.01),thymus index (P < 0.05),and the serum level of IL-2 (P < 0.05). CsA(45 mg/kg) decreased the spleen,thymus indexes,and the serum level of IL-2 (P < 0.01) in mice,and increased the serum level of IL-1β (P < 0.05) and the protein level of lung SP-D (P <0.001). CsA (60 mg/kg) increased the lung index of mice (P < 0.01),the serum level of IL-1β (P < 0.05),the protein level of lung SP-D (P < 0.01),and the mRNA levels of lung MPO and SP-D ( P < 0.05),and decreased the thymus index of mice (P < 0.01). HE staining showed that 30,45,and 60 mg/kg CsA,and LPS caused pathological changes in the lung tissue of mice. (ii) After pachymaran intervention in MC mice,the spleen and thymus indexes (P < 0.05) were increased in the 100 and 200 mg/kg pachymaran groups,and the lung index was decreased (P < 0.05).Moreover,50 mg/kg pachymaran increased the thymus index (P < 0.05) and decreased the lung index (P < 0.01) in MC group. Pachymaran (50,100,and 200 mg/kg) improved lung tissue injury,reduced the serum level of IL-1β (P < 0.001),and the mRNA levels of MPO and SPD in lung tissues (P < 0.05) of mice. Pachymaran (100 mg/kg) increased the protein level of lung IL-2 (P < 0.01),decreased the protein level of lung SP-D (P < 0.01),and the mRNA level of IL-1β (P < 0.001) in the lung tissues of mice. Pachymaran (200 mg/kg) increased the serum level of IL-2 (P < 0.01) and lung IL-6 of mice (P < 0.05). Pachymaran (50 and 200 mg/kg) increased the mRNA level of IL-6 in the lung tissues of mice (P < 0.05).Conclusion While the immune function of mice was suppressed by CsA,the lung tissue was also damaged. Pachymaran can improve the immunosuppression induced by CsA and improve the lung tissue injury in immunosuppressed mice.
Keywords Cyclosporine A (CsA) Immunosuppression Lung injury Immunoregulation Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) Pachymaran Polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid [poly(I:C)]
1 Introduction
The lungs are the main organ for gas exchange in mammals and are thus in direct contact with the external environment. They are the main organs involved in respiratory pathogen transmission and can be pathologically injured by respiratory infectious diseases,which can result in pneumonia,acute respiratory distress syndrome(ARDS),acute lung injury (ALI),and other diseases[1]. Recent studies[2-5]have found that coronavirus,influenza virus,and other respiratory virus infections can be accompanied by lung injury,especially in young children,the elderly,and people with low immunity,but lung injury can be particularly extensive and serious in the latter group. As the host immune response may be an important factor affecting the occurrence and development of lung injury[6],enhancing immune function is of great significance for repairing and improving lung injury caused by low immune function.
Pachymaran is an important pharmacological substance in traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) Fuling (Poria). Studies have proven that pachymaran has important pharmacological effects and immunomodulatory,antitumor,anti-inflammatory,antioxidant,and antibacterial properties[7,8]. However,few studies to date have investigated the effect of pachymaran on improving lung tissue damage caused by immunosuppression. Published studies have shown that cyclosporine A (CsA),an immunosuppressant,can be used to establish an immunosuppressive model mainly by affecting the surface structure and recognition function of T cells and preventing T cell activation[9,10]. However,DONG et al.[11]found that immunosuppressants can lead to immune dysfunction,which can result in changes in the host’s pulmonary flora and associated pulmonary bacterial infection when inhaling pathogens from the external environment.
In this study,a CsA-induced immunosuppression mouse model was used to detect the related indexes of immune function and lung tissue injury,and the effect of CsA-induced immunosuppression on lung injury was observed in a lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced lung injury model. CsA is a well-known immunosuppressive agent that can produce selective and reversible suppression of T lymphocytes while producing low cytotoxicity,and it plays a very important role in transplantation medicine[12]. We thus selected CsA to establish an immunosuppression mouse model. The immunomodulator,polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid [poly(I:C)],was used as a positive control drug to observe the effect of pachymaran on immune function and the related indexes of lung injury in model mice. This analysis and exploration of the immunomodulatory mechanism of pachymaran provides a reliable experimental basis for the clinical application of pachymaran.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Animals
One hundred and ten male BALB/c mice of specific pathogen-free (SPF) grade weighing (18 ± 2) g were purchased from Hunan Shrek Jingda Experimental Animal Co.,Ltd. (experimental animal quality certificates No.430727211100959818 and No. 43072721110095972),and raised in the Experimental Animal Center of Hunan University of Chinese Medicine [experimental facility certificate No. SCXK (Xiang) 2019-0004]. The experimental conditions were as follows: temperature,(23 ± 1) °C; humidity,65% ± 5%. All experiments conformed to the regulations of the Animal Experimental Ethics of the Hunan University of Chinese Medicine (Approval No. LL2021051203).
2.2 Reagents and drugs
The reagents and drugs used were as follows (with the source provided in parenthesis): CsA (MCE,USA),LPS(Solarbio,China),pachymaran (Hunan Butian Pharmaceutical Co.,Ltd.,China),interleukin (IL)-2 and IL-1βenzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kit (Elabscience,China),rabbit anti-mouse IL-2 and IL-6 antibody (Abclonal,China),rabbit anti-mouse surfactant protein D (SP-D) polyclonal antibody (ZEN-BIOSCIENCE,China),DAB chromogenic kit (ZSGB-BIO,China),general two-step detection kit (ZSGB-BIO,China),TRIzol(Thermo,USA),and all-in-one 1st Strand cDNA Synthesis SuperMix (Novoprotein,China),SYBR quantitative reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (qRTPCR) SuperMix Plus (Novoprotein,China) and primers purchased from Beijing Qingke Biotechnology Co.,Ltd..
2.3 Instruments and equipments
The instruments and equipments were used as follows:BSC-1300IIA2 biosafety cabinet (Suzhou Antai Air Technology Co.,Ltd.),SW-CJ-1FD ultra-clean workbench (Suzhou Antai Air Technology Co.,Ltd.),Axioscope5 optical scanning microscope (Suzhou Zeiss Technology Co.,Ltd.),SPark multi-function enzyme labeling instrument(Tacan),LightCycler96 fluorescence quantitative PCR instrument (Roche),NanoDrop 2000 spectrophotometer(Thermo Scientific),and TP-200D Electronic Analytical balance (Xiangyi Balance Instrument and Equipment Co.,Ltd.).
2.4 Immunosuppresion mouse model stablishment
2.4.1 Immunosuppression mouse model establishment by CsA Fifty male BALB/c mice were randomly divided into five groups (10 mice in each group): normal control(NC) group,30,45,and 60 mg/kg CsA groups,and 10 mg/kg LPS group. The following intraperitoneal injection regimes were established: the NC group with phosphatebuffered saline (PBS),the LPS group with 10 mg/kg LPS for eight hours before mice euthanasia,and the 30,45,and 60 mg/kg CsA groups with corresponding doses of CsA for seven consecutive days.
The general condition of the mice was observed,and an immunosuppression mouse model was considered to be successfully constructed when the mice showed a reduction in activity and drinking,depression,and vertical hair growth accompanied by a decrease in the immune organ indexes and serum IL-2 level[9]. On the 8th day,blood collected from ocular venous plexus after euthanasia,was centrifuged for 3 000 rpm and 10 min to obtain serum,which was separated and stored in-80 °C refrigerator. The spleen,thymus and lung were dried with filter paper and divided into two parts,that is,one fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde,and the other stored in - 80 °C refrigerator for the following experiments.
2.4.2 Pachymaran regulating the immunosuppression mouse by oral administrated Another 60 male BALB/c mice were randomly divided into six groups (10 mice in each group): NC,model control (MC),50,100,and 200 mg/kg pachymaran,and 0.1 mg/kg poly(I:C) groups.Except for the NC group,other groups were intraperitoneally injected with 45 mg/kg CsA for seven days to establish an immunosuppressive mouse model. This was then followed by drug intervention. The NC and MC groups were intragastrically administered PBS,the 50,100,and 200 mg/kg pachymaran groups were administered with 50,100,and 200 mg/kg pachymaran,respectively,and the poly(I:C) group received an intraperitoneal injection of 0.1 mg/kg poly(I:C). Seven days after administration,blood which was collected from ocular venous plexus after euthanasia,was centrifuge for 3 000 rpm and 10 min to obtain serum. The serum was separated and stored in refrigerator at-80 °C. The spleen,thymus and lung were dried with filter paper and divided into two parts,that is,one fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde,and the other frozen in liquid nitrogen and then transferred to - 80 °C for the following experiments.
2.5 Related indexes detection in each group mice
2.5.1 Detection of spleen,thymus,and lung indexes The weight of the spleen,thymus and lung of mice of all groups in the two parts experiment were recorded by using an electronic analysis balance,and the organ index was calculated as organ index (%) = organ weight (g)/body weight (g) × 100%.
2.5.2 Detection of pathological changes in lung tissue by hematoxylin-eosin (HE) staining The lung tissues of all groups in the two parts experiment were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde,embedded in paraffin,cut into 5 μm sections,and then stained with hematoxylin for 5 min,and eosin for 3 min. The tissues sections were subsequently dehydrated in gradient ethanol and sealed with neutral resin to observe the histopathological changes in the mouse lungs under a microscope.
2.5.3 Detection of IL-2 and IL-1βin serum by ELISA Mouse serum was extracted and then centrifuged to remove impurities. Standards and samples (100 μL) were added to a 96-well plate for the IL-1βand IL-2 reactions,and incubated at 37 °C for 90 min. Then,100 μL biotinylated antibody was added to each well and incubated at 37 °C for 60 min. After washing three times,100 μL of the enzyme conjugate working solution was added and incubated at 37 °C for 30 min. After washing three times,90 μL of the substrate solution was added and incubated at 37 °C for 15 min,and the absorbance values of each well were measured sequentially at 450 nm by adding the termination solution. The actual concentration of each sample was calculated by using a standard curve.
2.5.4 Detection of SP-D,IL-2,and IL-6 protein expression levles in lung tissue by immunohistochemistry (IHC)staining The fixed lung tissues of all groups in the two parts experiment was dehydrated,embedded in paraffin,and sliced. After dewaxing,the slices were soaked in 3%H2O2for 8 min,cleaned,and then incubated in a wet box with SP-D,IL-2,and IL-6 primary antibodies (1∶100)overnight at 4 °C. After incubation,they were washed three times with PBS. This was followed by dripping of the reaction enhancement solution,with the reaction carried at room temperature for 20 min,washing three times with PBS,dripping of the secondary antibody (1∶200),with the reaction carried at room temperature for 30 min,and washing three times with PBS. Finally,DAB was added for color development,and the localization of SP-D,IL-2,and IL-6 in lung tissues was observed under a microscope. Three fields of view were randomly selected for semi-quantitative analysis of SP-D,IL-2,and IL-6 expression levels by using Image Plus Pro 6.0.
2.5.5 Detection of SP-D,IL-1β,IL-6,and myeloperoxidase (MPO) mRNA expression levels in lung tissues by qRT-PCR The lung tissues of all groups in the two parts experiment were quickly cut into pieces,and total RNA was extracted according to the Trizol one-step method.The RNA concentration was assessed by using a Nano-Drop 2000 spectrophotometer. The extracted total RNA was reverse-transcribed to synthesize cDNA by using the all-in-one 1st Strand cDNA Synthesis SuperMix according to the manufacturer’s protocol. SYBR qPCR SuperMix Plus was used to amplify the synthesized cDNA for qPCR,β-actin was used as the internal reference for the expression levels of the target gene,and 2-△△Ctmethod was used to analyze the relative expression levels of the mRNA. The primer sequences used are listed in Table 1.
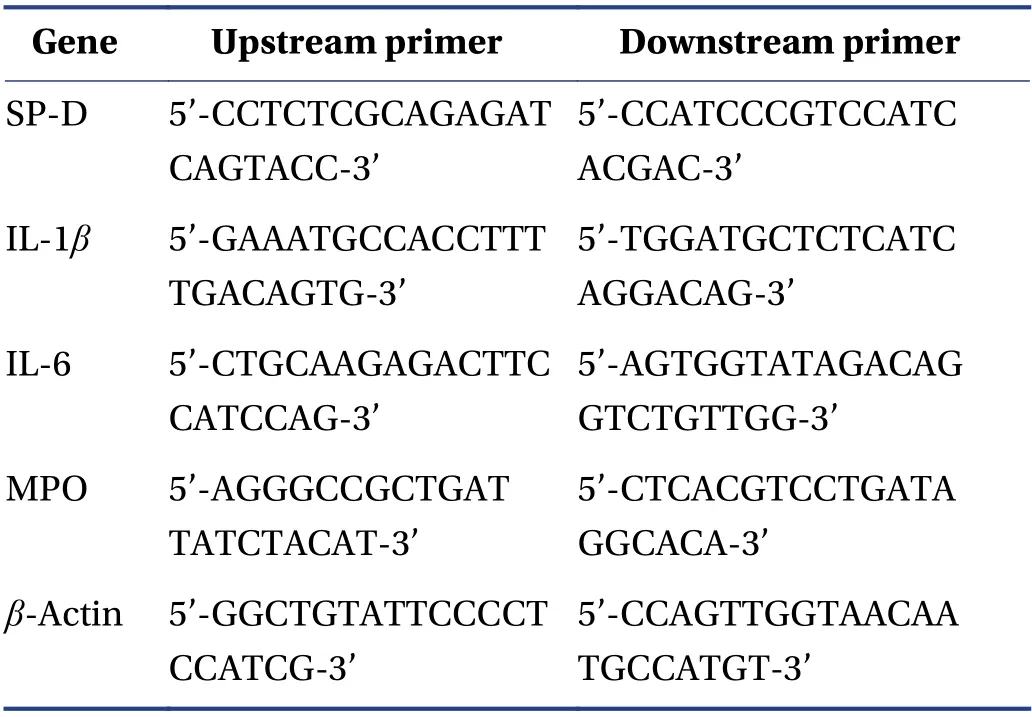
Table 1 Primer sequences for qRT-PCR
2.6 Statistical analysis
The data were analyzed by using SPSS 26.0 and plotted by using GraphPad Prism 9. The measurement data were expressed as the mean ± standard deviation (SD). A oneway ANOVA was used to make comparisons between multiple groups,andP< 0.05 was considered to be statistically significant.
3 Results
3.1 Spleen,thymus,and lung indexes in each group mice
Compared with the NC group,there were significant decreases in the spleen index of the 30 and 45 mg/kg CsA and LPS groups (P< 0.01,P< 0.01,andP< 0.05,respectively),and significant decreases in the thymus index of the 30,45,and 60 mg/kg CsA,and LPS groups (P< 0.05,P< 0.01,P< 0.01,andP< 0.05,respectively). There were also significant increases in the lung index of the 30 and 60 mg/kg CsA and LPS groups (P< 0.001,P< 0.01,andP< 0.05,respectively) (Figure 1A - 1C).
After drug intervention,compared with the MC group,there were significant increases in the spleen index of the 100 and 200 mg/kg pachymaran and poly(I:C) groups(P< 0.01,P< 0.05,andP< 0.001,respectively),and the thymus index of the 50,100,and 200 mg/kg pachymaran,and poly(I:C) groups (P< 0.05,P< 0.001,P< 0.05,andP<0.05,respectively). However,there were significant decreases in the lung index of the 50,100,and 200 mg/kg pachymaran,and poly(I:C) groups (P< 0.01,P< 0.05,P<0.001,andP< 0.05,respectively) (Figure 1D - 1F).
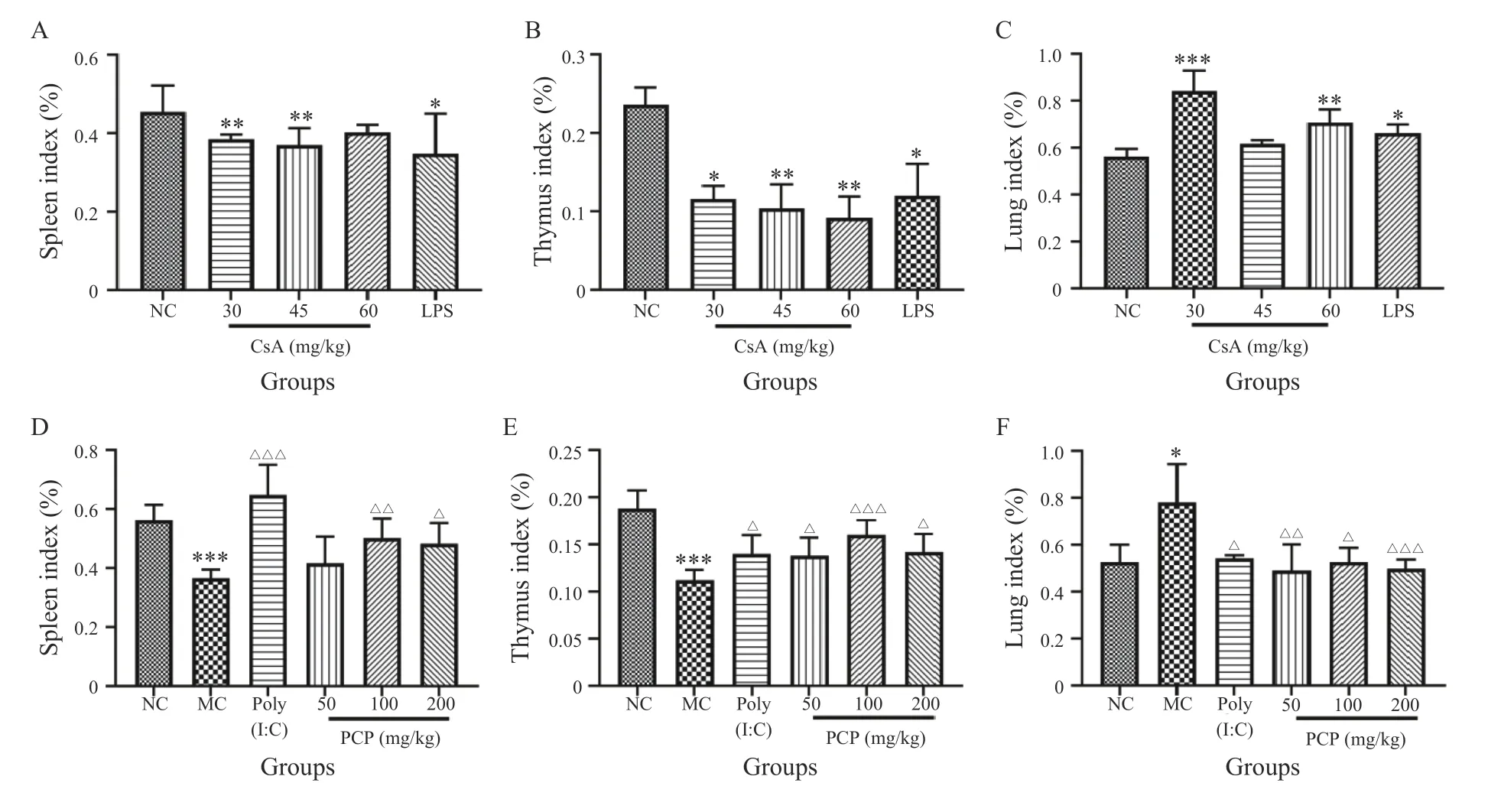
Figure 1 The spleen,thymus,and lung indexes in each group mice
3.2 Pathological changes in the lung tissues of mice
Histopathological sections of the lung tissues of mice in each group were observed under a light microscope. The alveoli and alveolar septum of the mice in the NC group were well-defined and structurally intact. Obvious histopathological changes were observed in the 30,45,and 60 mg/kg CsA,and LPS groups,and these were mainly characterized by alveolar collapse,alveolar wall hyperplasia,pulmonary hyperemia,and edema,accompanied by inflammatory cell infiltration and large-area necrosis and consolidation (Figure 2A - 2E).
After drug intervention,compared with the MC group,there were significant improvements in the histopathological injury of lung tissues in the 50,100,and 200 mg/kg pachymaran,and the poly(I:C) groups. The main manifestations were as follows: reduced pulmonary congestion and edema,decreased inflammatory cell infiltration,and a decreased pulmonary necrotic consolidation area.This improvement was most obvious in the 200 mg/kg pachymaran and poly(I:C) groups. The outline of the alveoli in the 50 and 100 mg/kg pachymaran groups was clear,the alveolar wall was thickened locally,and a small amount of inflammatory cell infiltration was observed(Figure 2F - 2J).
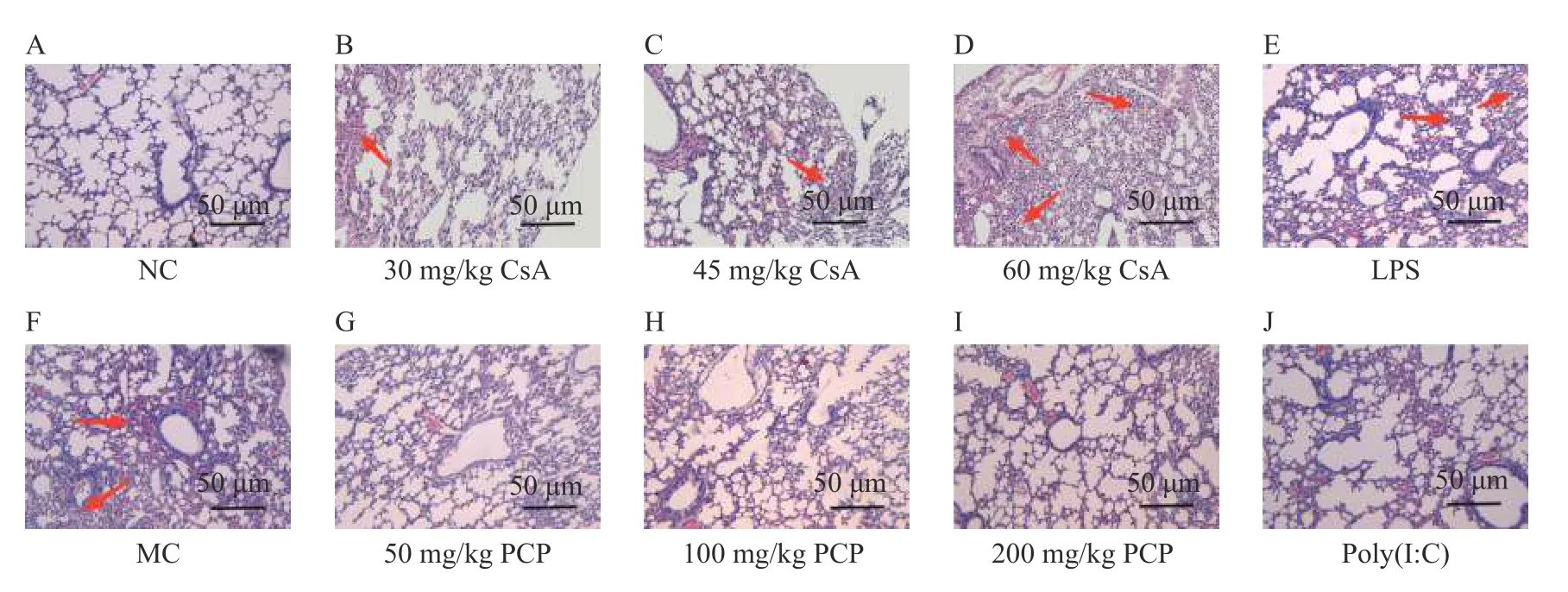
Figure 2 Pathological changes of lung tissue in each group mice
3.3 IL-1 β and IL-2 levels in serum of mice
Compared with the NC group,the serum level of IL-1βwas significantly increased in the 45 and 60 mg/kg CsA and LPS groups (P< 0.05,P< 0.05,andP< 0.001,respectively),and was significantly decreased in the 30 and 45 mg/kg CsA groups (P< 0.05 andP< 0.01,respectively)(Figure 3A and 3B).
After drug intervention,compared with the MC group,the serum level of IL-1βwas significantly decreased in the 50,100,and 200 mg/kg pachymaran,and poly(I:C)groups (P< 0.001),whereas the serum level of IL-2 was significantly increased in the 200 mg/kg pachymaran and poly(I:C) groups (P< 0.01 andP< 0.05,respectively)(Figure 3C and 3D).
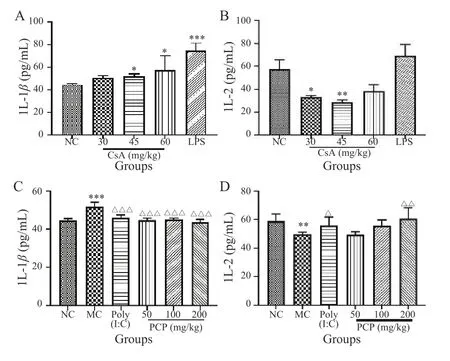
Figure 3 Levels of IL- β and IL-2 in serum of mice in each group
3.4 Protein expression levels of IL-6,IL-2,and SP-D in lung tissues of mice
The results of IHC staining showed obvious histopathological changes in the lung tissues of mice in the 30,45,and 60 mg/kg CsA,and the LPS groups compared with the NC group. The main manifestations were alveolar structure disorder,alveolar cavity collapse,alveolar wall thickening,pulmonary interstitial edema,capillary congestion or hemorrhage,alveolar cavity,and pulmonary interstitial infiltration of a large number of inflammatory cells. Compared with the NC group,the results of IHC staining showed a significant decrease in the average optical density of IL-6 and IL-2 in the 30 and 60 mg/kg CsA groups(P< 0.01 andP< 0.05,respectivelyP< 0.001 andP< 0.05,respectively),whereas the average optical density of SP-D was significantly increased in the 45 and 60 mg/kg CsA and LPS groups (P< 0.001,P< 0.01,andP< 0.05,respectively) (Figure 4A - 4D).
After pharmacological intervention,lung histopathological changes were alleviated in the 50,100,and 200 mg/kg pachymaran,and poly(I:C) groups compared with the MC group. The main manifestations were as follows: a reduction in the destruction of the alveolar structure,a reduction in edema,and a reduction in inflammatory cell infiltration. Compared with the MC group,the average optical density of IL-6 was significantly increased in the 200 mg/kg pachymaran group (P<0.05),and the average optical density of IL-2 was significantly increased in the 100 mg/kg pachymaran group (P<0.01). Moreover,the average optical density of SP-D was significantly decreased in the poly(I:C) and 100 mg/kg pachymaran groups (P< 0.001 andP< 0.01,respectively)(Figure 4E - 4H).

Figure 4 Protein expression levels of IL-6,IL-2,and SP-D in lung tissues of mice in each group
3.5 mRNA expression levels of IL-1β,IL-6,MPO,and SP-D in lung tissues of mice
Compared with the NC group,the qRT-PCR results showed a significant increase in the mRNA level of lung IL-1βin the 60 mg/kg CsA and LPS groups (P< 0.01 andP< 0.001 respectively),whereas the mRNA level of lung IL-6 was significantly decreased in the 30 and 60 mg/kg CsA groups (P< 0.05 andP< 0.01,respectively).Moreover,the mRNA levels of lung MPO and SP-D were significantly increased in the 60 mg/kg CsA and LPS groups (P< 0.05 andP< 0.001,respectively;P< 0.01 andP< 0.001,respectively) (Figure 5A - 5D).
After drug intervention,compared with the MC group,qRT-PCR results showed that the mRNA level of lung IL-1βwas significantly decreased in the 100 mg/kg pachymaran,and poly(I:C) groups (P< 0.001),while the mRNA level of lung IL-6 was significantly increased in the 50 and 200 mg/kg pachymaran and poly(I:C) groups (P< 0.001,P< 0.01,andP< 0.01,respectively). Moreover,the mRNA levels of lung MPO and SP-D were significantly decreased in the 50,100,and 200 mg/kg pachymaran,and poly(I:C) groups (P< 0.05,P< 0.01,P< 0.01,andP< 0.05,respectively;P< 0.05,P< 0.01,P< 0.05,andP< 0.001,respectively) (Figure 5E - 5H).
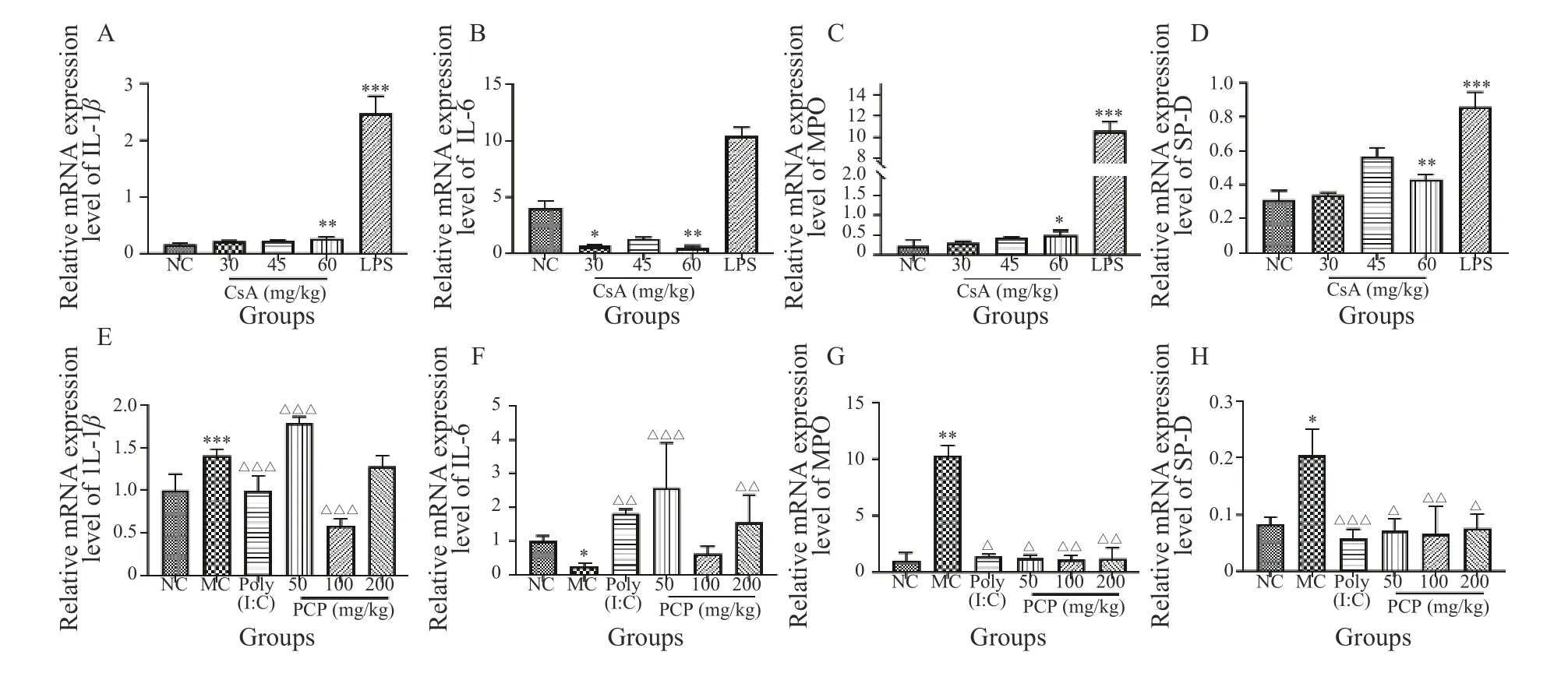
Figure 5 mRNA expression levels of IL-1β,IL-6,MPO,and SP-D in lung tissues in each group mice
4 Discussion
Immunosuppressants inhibit the immune response of the body,and the proliferation and function of cells related to the immune response[13]. However,the certain modern medical methods (such as organ transplantation),or treated with immunosuppressants when patients with autoimmune diseases (such as corticosteroids) for a long period will cause immune insufficiency[14].An increasing number of people are suffering from low immunity[15]. The respiratory system is connected to the external environment[16],and when the immune function of the body is low,the body’s resistance to changes in pulmonary flora and the inhalation of pathogenic bacteria in the external environment is reduced,which can easily result in secondary bacterial infection and subsequent lung injury[17]. Severe respiratory infection is the main cause of not only hospitalization and death in patients with immune insufficiency,but also of acute respiratory failure and sepsis[18,19]. Pulmonary infection in patients with low immune function has become a major challenge in the clinical diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary infections in China[20].
Immune regulation plays an important role in this process. Pachymaran has been proven to not only regulate innate immunity,but also regulate cellular immunity and humoral immunity[8]. Pharmacological studies have shown that pachymaran has many positive biological properties,such as anti-tumor,immune regulatory[21],anti-inflammatory[8],and anti-atherosclerosis[22]properties. It is also non-toxic and biodegradable,and as it has a significant immune enhancement effect,it has recently been used as a new adjuvant in vaccine development[13].In a previous study,we found that pachymaran regulated immunity by enhancing the expression of the immune factors TNF-αand IL-2[23]. It is also known to enhance the therapeutic effects of vinorelbine and cisplatin on lung cancer,and ameliorate the side effects of chemotherapy by regulating EGFR expression[24]. However,few studies have reported its effect on improving and repairing lung injury caused by low immune function.
In this study,in order to explore the effect of low immune function on lung injury and the effect of intervention with pachymaran and its mechanism,we used immunosuppressant CsA was used to establish a model of immune dysfunction. CsA is an immunosuppressant that mainly inhibits cellular immune function and can result in immune disorders[25]. Its use is of great significance for studying acute lung injury-related diseases caused by immune dysfunction,and it also greatly expands the value of applying pachymaran and other TCM polysaccharides,and as such is conducive to the high-quality development of the TCM industry in China. Therefore,in this study,an immunosuppressive mouse model was established via an intraperitoneal injection of 30,45,and 60 mg/kg CsA,and the lung injury of mice in each group was observed. As previous studies have found that the mouse model of acute lung injury induced by LPS showed obvious consolidation of lung tissue in a short period[26-28],we used LPS-treated mice as a positive model group to compare the related indexes of lung injuries induced by CsA. In addition,different concentrations of pachymaran were used to interfere with the model mice,and the specific mechanism of the immunomodulatory effect of pachymaran was explored by detecting relevant indexes.
As immune organs,the thymus and spleen are the sites where immune cells occur,differentiate,mature,and settle down[29]. Cytokines,such as IL-2,IL-6,and IL-1β,play important roles in immunity[30]. IL-2 has a positive regulatory effect on the immune response and is mainly produced by activated CD4+and CD8+T cells. It is a growth factor of all T cell subsets,and it mainly acts in autocrine and paracrine ways. IL-2 can promote the proliferation of activated B cells,and it plays an important role in immune regulation[31]. IL-1βalso plays an important role in the inflammatory cascade and waterfall effects,and its serum expression level is positively correlated with the severity of lung injury[32,33]. Furthermore,IL-6 is a proinflammatory factor that assists the body in stimulating a complete immune response by inducing the production of more inflammatory factors[34]. Low immune function is a major pathogenic factor in potential lung infection,and inflammation plays an important role in the occurrence and development of lung injury caused by infection[35]. According to related studies,neutrophils usually gather at inflammatory sites to produce MPO,which results in tissue oxidative damage[36,37]. In addition,SP-D is a component of the pulmonary surfactant system[38],and its level is proportional to the severity of lung injury[39].
The experimental results showed changes in the following indexes of immunosuppressive mice administration of CsA: the spleen and thymus indexes decreased,the lung index increased,serum IL-2 level decreased,and serum IL-1βlevel increased. A certain degree of lung tissue injury was also observed in the MC group,which indicated that when the body is in a state of low immunity caused by immunosuppression,the lungs are prone to infection and damage. After administration,the results showed that pachymaran and poly(I:C) had different effects on lung injury in immunosuppressed mice.Compared with the MC group,the immune organ indexes increased,and the lung index decreased. By adjusting the levels of serum cytokines,congestion,edema,inflammatory cell infiltration,and necrotizing consolidation areas of the lung tissue were observed. Our results suggest that pachymaran can improve immune function and lung injury by regulating the indexes of immune organs and the levels of serum IL-2 and IL-1β. In addition,our results showed there was no significant difference in the curative effect between poly(I:C) and pachymaran.
5 Conclusion
In summary,CsA suppresses immune function,which can result in lung tissue damage via infection.Pachymaran ameliorates immunosuppression caused by CsA,and improves lung tissue injury in immunosuppressed mice by exerting immune regulatory effects. This study provides insights for the scientific development of medicines and homologous health foods by using pachymaran to regulate immunity.
Fundings
National Natural Science Foundation of China (8207425),Hunan Provincial Natural Science Foundation(2021JJ30508 and 2020JJ4063),Hunan Provincial Scientific Research Project of Chinese Medicine (2021055),Changsha Outstanding and Innovative Youth Training Program (kq2106060),Key Discipline of Hunan University of Chinese Medicine (Basic Medicine 1),and the Excellent Teaching Team of Postgraduates in Hunan Province (Postgraduate Teaching Team of Basic Medicine,118)
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
 Digital Chinese Medicine2022年2期
Digital Chinese Medicine2022年2期
- Digital Chinese Medicine的其它文章
- Visualization analysis of the international standard ISO/TC 249 for traditional Chinese medicine
- MEDICLOUD: a holistic study on the digital evolution of medical data
- Ancient and modern medication laws of aromatic Chinese medicines in treating angina pectoris based on data mining
- Intra-set correlation analysis of medical records of thyroid cancer treated by traditional Chinese medicine Master ZHOU Zhongying
- Traditional Chinese medicine Master XIONG Jibo’s medication experience in treating arthralgia syndrome through data mining
- Screening influencing factors of blood stasis constitution in traditional Chinese medicine
