血清降钙素原检测对异基因造血干细胞移植术后并发菌血症的诊断价值
张丹阳 冯超 何圣科 刘丽辉 施兵 叶丽萍 张永清
·论著·
血清降钙素原检测对异基因造血干细胞移植术后并发菌血症的诊断价值
张丹阳 冯超 何圣科 刘丽辉 施兵 叶丽萍 张永清
目的 探讨血清降钙素原(PCT)、C反应蛋白(CRP)和内毒素检测对异基因造血干细胞移植(allo-HSCT)术后并发菌血症患者的诊断价值。方法 回顾性分析2013年6月至2016年5月解放军第三〇九医院移植血液科行allo-HSCT术后发热的122例受者,检测血清PCT、CRP和内毒素。以血培养结果作为金标准,计算PCT、CRP、内毒素3种检测方法的灵敏度、特异度、阳性预测值和阴性预测值。绘制受试者工作特征(ROC)曲线,计算ROC曲线下面积。P<0.05为差异具有统计学意义。结果 根据血培养结果,122例allo-HSCT术后发热患者中有40例为菌血症,其中革兰阴性菌24例,革兰阳性菌16例。PCT和CRP检测ROC曲线下面积分别为0.815、0.727,差异具有统计学意义(P<0.05)。当PCT检测截断值为0.845 ng/mL时,灵敏度和特异度分别为72.5%、87.5%,阳性预测值和阴性预测值分别为74.3%、86.7%。当CRP检测截断值为55.4 mg/L,灵敏度和特异度分别为71.8%、66.3%,阳性预测值和阴性预测值分别为50.0%、80.8%。结论 血清PCT检测对于allo-HSCT术后合并菌血症患者的的临床诊断价值高于CRP和内毒素,可作为预测allo-HSCT术后发热患者是否并发细菌感染的优选诊断指标。
降钙素原; 菌血症; 异基因造血干细胞移植; C反应蛋白
异基因造血干细胞移植(allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation,allo-HSCT)是目前治愈恶性血液病的唯一手段。由于allo-HSCT受者粒细胞缺乏,免疫抑制剂、糖皮质激素的应用,静脉导管及各种侵入性操作,因此极易发生感染。然而,allo-HSCT受者感染的病原体广泛,病原学检查阳性率低,且临床症状和体征常常不典型,与一些非感染性疾病如移植物抗宿主病(graft-versus-host disease,GVHD)、植入综合征(engraftment syndrome,ES)[1]等难以鉴别,给临床医师早期诊断和治疗带来极大难度。一旦未能及时、准确地给予治疗,感染进展迅速,极易发展为败血症,甚至感染性休克或弥漫性血管内凝血,死亡率高[2]。因此,寻找可靠的临床指标,辅助临床医师早期诊断allo-HSCT受者感染是临床医务人员和研究者共同关注的问题。国内外已经有大量研究显示,血清降钙素原(procalcitonin,PCT)对恶性血液病粒细胞缺乏患者菌血症有良好的诊断效能[3]。本研究旨在探讨血清PCT、C反应蛋白(C-reaction protein,CRP)、内毒素在allo-HSCT术后感染患者中的诊断价值。
1 资料和方法
1.1 研究对象
回顾性分析2013年6月至2016年5月解放军第三〇九医院移植血液科行allo-HSCT术后发热的122例受者,中位年龄36.5岁(13~58岁),男性64例,女性58例。原发病包括急性白血病79例,骨髓增生异常综合征12例,其他31例。HLA相合58例,HLA不相合64例。
1.2 检测方法
allo-HSCT受者术后体温高于38.5 ℃或伴寒战时进行血培养(抗生素应用前),并在24 h内、应用抗生素前抽取3 mL静脉血检测血清PCT、CRP和内毒素。采用免疫荧光法检测血清PCT,PCT≥0.5 ng/mL为阳性;采用激光免疫比浊法检测CRP,CRP≥3.0 mg/L为阳性;采用鲎试剂基质偶氮显色定量法检测内毒素,内毒素≥20 pg/mL为阳性。
1.3 统计学方法
采用SPSS 17.0统计软件进行数据分析。非正态分布计量资料采用中位数表示。以血培养结果作为金标准,计算PCT、CRP、内毒素3种检测方法的灵敏度、特异度、阳性预测值和阴性预测值。绘制受试者工作特征(receiver operating curve,ROC)曲线,计算ROC曲线下面积。P<0.05为差异具有统计学意义。
2 结 果
2.1 临床资料
根据血培养结果,122例allo-HSCT术后发热的患者中有40例为菌血症,其中革兰阴性菌24例,革兰阳性菌16例。检出病原体中,以大肠埃希菌感染为主(9例),其次为肺炎克雷伯菌(8例)。
2.2 血清PCT、CRP和内毒素检验效能比较
以血培养结果作为金标准,allo-HSCT术后并发菌血症患者血清PCT、CRP和内毒素检测结果见表1~3。3种检测方法的诊断价值见表4。
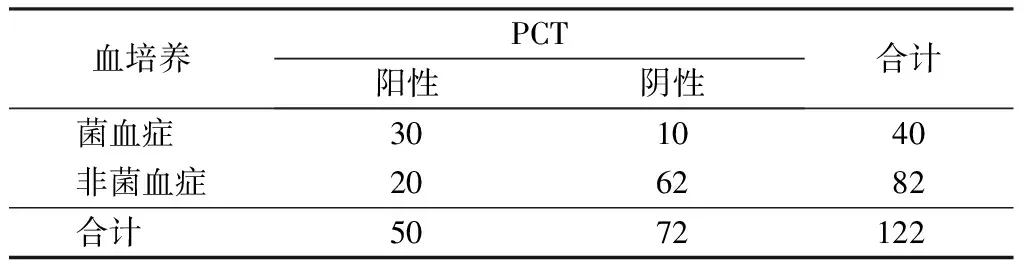
表1 allo-HSCT术后并发菌血症患者血清PCT检测结果(例)
注: PCT. 降钙素原;allo-HSCT. 异基因造血干细胞移植

表2 allo-HSCT术后并发菌血症患者CRP检测结果(例)
注: CRP. C反应蛋白;allo-HSCT. 异基因造血干细胞移植
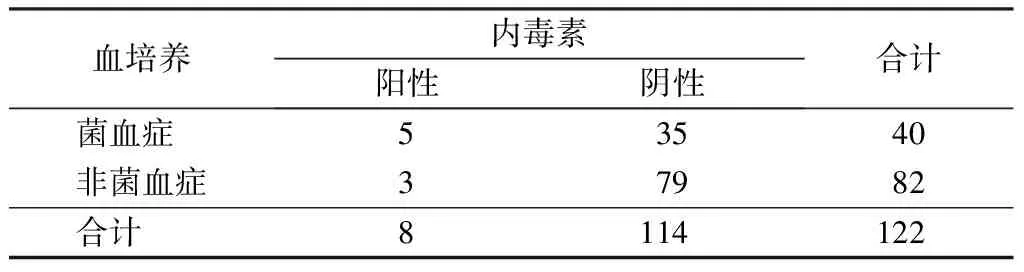
表3 allo-HSCT术后并发菌血症患者内毒素检测结果(例)
注: allo-HSCT. 异基因造血干细胞移植
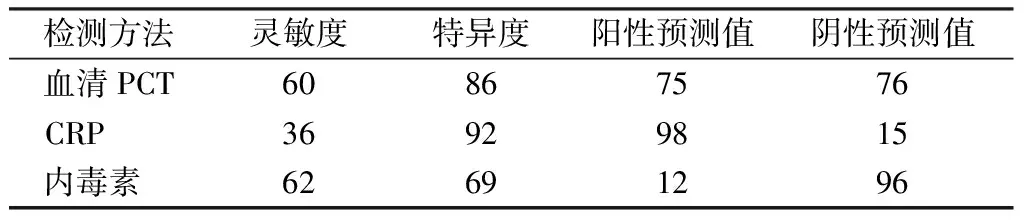
表4 血清PCT、CRP和内毒素对allo-HSCT术后
注: PCT. 降钙素原;CRP. C反应蛋白;allo-HSCT. 异基因造血干细胞移植
PCT和CRP检测all-HSCT术后菌血症的ROC曲线下面积分别为0.815、0.727,差异具有统计学意义(P<0.05)。PCT检测截断值为0.845 ng/mL时,灵敏度和特异度分别为72.5%、87.5%,阳性预测值和阴性预测值分别为74.3%、86.7%。CRP检测截断值为55.4 mg/L时,灵敏度和特异度分别为71.8%、66.3%,阳性预测值和阴性预测值分别为50.0%、80.8%。见图1。
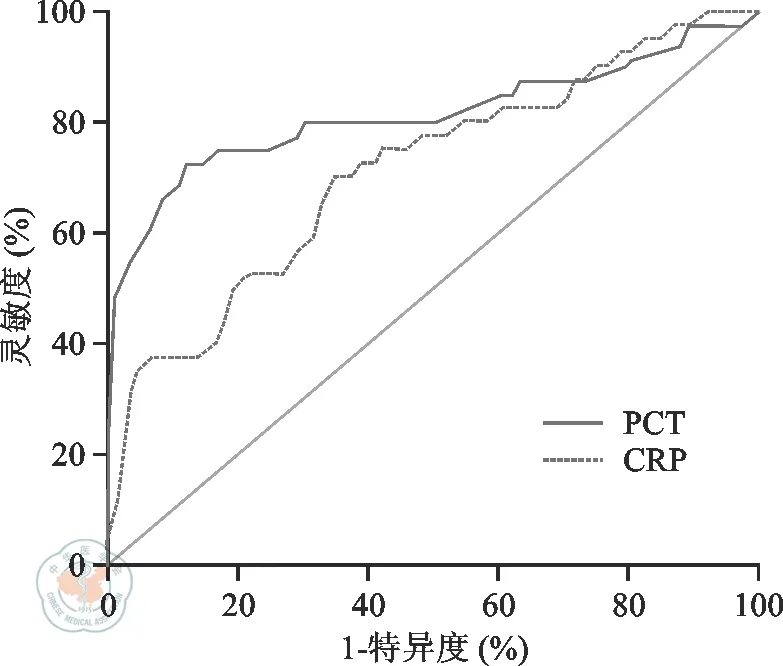
注: PCT. 降钙素原;CRP. C反应蛋白;ROC. 受试者工作特征曲线图1 血清PCT和CRP检测异基因造血干细胞移植术后菌血症ROC曲线
3 讨 论
PCT是降钙素的前体, 主要由甲状腺滤泡旁细胞分泌,是由116个氨基酸残基组成的多肽,无生物学活性,分子量为13 000。生理状态下血液中水平极低,不超过0.05 ng/mL,体内半衰期为25~30 h,体外稳定性好[4]。严重细菌感染时,细菌内毒素、单核/粒细胞释放的TNF-α、IL-6以及脂多糖诱导全身各种组织、实质细胞分泌PCT。PCT用于鉴别细菌和非细菌感染有较高的准确性[5]。此外,PCT在恶性血液病化疗后粒细胞缺乏合并感染时的诊断价值优于传统免疫炎性因子CRP、IL-6等,可作为早期辅助诊断感染的可靠指标[6]。
allo-HSCT受者术后不仅伴有粒细胞缺乏,而且可能出现各种并发症。部分研究显示,免疫抑制剂治疗GVHD,抑制T细胞分泌IFN-γ,可能影响血清PCT浓度[7]。因此,PCT在鉴别allo-HSCT术后感染和其他可引起发热并发症中的作用尚存在争议。
虽然有研究结果显示,CRP>9.5 mg/L时诊断感染的价值优于PCT[7],但CRP为非特异性指标,除细菌感染外,移植后病毒感染、GVHD、移植相关性闭塞性细支气管炎均可引起CRP升高[8],故不推荐CRP作为早期辅助诊断感染的实验室指标。Sato等[9]研究显示,局部感染合并PCT水平升高时,菌血症发生风险明显升高。本研究结果显示,PCT检测allo-HSCT术后菌血症的ROC曲线下面积为0.815,优于CRP(0.727)。当PCT 检测截断值为0.845 ng /mL时,灵敏度达72.5%,特异度达87.5%,阳性预测值和阴性预测值分别为74.3%、86.7%,均优于CRP。因此,与内毒素、CRP相比,PCT可作为移植后受者早期辅助鉴别诊断感染的实验室指标。
PCT在脓毒血症中表现出良好的诊断效能,大部分学者认为PCT可有效鉴别感染与GVHD[10],但仍有30%的GVHD或ES患者PCT阳性,这可能是因为allo-HSCT受者术后发生肠道GVHD,单核细胞产生大量细胞因子(如TNF-α)刺激PCT生成增加[11]。allo-HSCT术后腺病毒感染的出血性膀胱炎患者PCT呈弱阳性[7],因此仅PCT阳性并不能及时、准确地反映细菌感染,明确PCT检测截断值有助于早期鉴别感染与allo-HSCT术后免疫性发热。本研究allo-HSCT术后发生菌血症的PCT检测截断值为0.845 ng/mL,在无血培养鉴定结果时,可作为直观的数值辅助临床医师判定患者是否发生菌血症。
研究显示,PCT水平与感染的严重程度成正相关,PCT水平越高,预后越差[12];而且PCT在鉴别革兰阳性菌和革兰阴性菌方面具有高度的特异性[13]。因此,我们下一步的研究拟动态记录抗生素治疗过程中PCT变化,探讨PCT水平与allo-HSCT术后合并感染患者的预后和病原特异性关系。
综上所述,PCT对allo-HSCT术后并发菌血症患者的诊断价值高于CRP和内毒素。当PCT为0.845 ng/mL时,具有较高的灵敏度和特异度。定量检测血清PCT可作为实验室指标辅助临床医师早期诊断allo-HSCT术后感染,以及时合理地使用抗生素。
1 Spitzer TR. Engraftment syndrome following hematopoietic stem cell transplantation[J]. Bone Marrow Transplant, 2001, 27(9): 893-898.
2 Young JH, Logan BR, Wu J, et al, Infections following transplantation of bone marrow or peripheral-blood stem cells from unrelated donors[J], Biology of Blood & Marrow Transplantation Journal of the American Society, 2015, 22(2):359-370.
3 Mizuki Aimoto, Hideo Koh, Takako Katayama, et al. Diagnostic performance of serum high-sensitivity procalcitonin and serum C-reactive protein tests for detecting bacterial infection in febrile neutropenia[J]. Infection, 2014, 42(6):971-979.
4 Sjøqvist C, Snarski E. Inflammatory markers in patients after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation[J]. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz), 2013, 61(4):301-307.
5 Meisner M, Reinhart K. Biomarkers in the critically ill patient: pro-calcitonin[J]. Crit Care Clin, 2011, 27(2):253-263.
6 付阳, 江虹, 李立新, 等. 降钙素原和免疫炎性因子在粒细胞减少的恶性血液病菌血症患者中的临床应用价值[J]. 中国实验血液学杂志, 2013, 21(5):1296-1300.
7 Mori Y, Miyawaki K, Kato K, et al. Diagnostic value of serum procalcitonin and C-reactive protein for infections after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation versus nontransplant setting[J]. Intern Med, 2011, 50(19):2149-2155.
8 Lyu YX, Yu XC, Zhu MY. Comparison of the diagnostic value of procalcitonin and C-reactive protein after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Transpl Infect Dis, 2013, 15(3): 290-299.
9 Sato M, Nakasone H, Terasako-Saito K, et al, Prediction of infectious complications by the combination of plasma procalcitonin level and localized infection before allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation[J]. Bone Marrow Transplant, 2014, 49(4):553-560.
10 Koya J, Nannya Y, Ichikawa M, et al. The clinical role of procalcitonin in hematopoietic SCT[J]. Bone Marrow Transplant, 2012, 47(10):1326-1331.
11 Teshima T, Ordemann R, Reddy P, et al. Acute graft-versus-host disease does not require alloantigen expression on host epithelium[J].Nat Med, 2002, 8(6):575-581.
12 Massaro K, Costa SF. Role of biomarkers as predictors of infection and death in neutropenic febrile patients after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation[J]. Mediterr J Hematol Infect Dis, 2015, 7(1):e2015059.
13 Sandri MT, Passerini R, Leon ME, et al. Procalcitonin as a useful marker of infection in hemato-oncological patients with fever[J]. Anticancer Res, 2008, 28(5B):3061-3065.
(本文编辑:杨扬)
张丹阳, 冯超, 何圣科, 等. 血清降钙素原检测对异基因造血干细胞移植术后并发菌血症的诊断价值[J/CD]. 中华移植杂志: 电子版, 2016, 10(4):186-189.
Diagnostic value of serum procalcitonin in bacteriemia after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
ZhangDanyang,FengChao,HeShengke,LiuLihui,ShiBing,YeLiping,ZhangYongqing.
DepartmentofHematologicalTransplantation,the309thHospitalofChinesePeople′LiberationArmy,Beijing100091,ChinaCorrespondingauthor:ZhangYongqing,Email:zhangyongqing0725@163.com
Objective To evaluate the diagnositic value of serum procalcitonin (PCT), C-reactive protein (CRP) and endotoxin in bacteremia after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (allo-HSCT). Methods A retrospective analysis was performed on 122 patients who got allo-HSCT and with fever after operation in the Department of Hematological Transplantation, the 309th Hospital of Chinese People′s Liberation Army between June 2013 and May 2016. Serum PCT, CRP and endotoxin were detected, respectively.The result of blood culture was regard as gold criteria for diagnosis of bacteremia. Sensitivity, specificity, positive and negitive predictive value of the three above detection methods were caculated. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves and areas under the curve was diagrammed and caculated, respectively. AP<0.05 was considered statistically significant. Results There were 40 cases of bacteremia among 122 allo-HSCT recipients according to the results of blood culture, and twenty-four cases were Gram-negative bacteria positive and sixteen cases were Gram-positive bacteria positive.The area under the ROC curve of PCT and CRP was 0.815 and 0.727,respectively, and the difference between the two methods was statistically significant (P<0.05). The sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative predictive value of PCT detection was 72.5%, 87.5%, 74.3% and 86.7% respectively when cut-off value was 0.845 ng/mL.The sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative predictive value of CRP detection was 71.8%, 66.3%, 50.0% and 80.8% respectively when the cut-off value was 55.4 mg/L. Conclusions Serum PCT detection showed higher diagnositic value in bacteremia after allo-HSCT than CRP and endotoxin detection, which could served as a preferential diagnostic indicator.
Procalcitonin; Bacteremia; Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation; C-reaction protein
10.3877/cma.j.issn.1674-3903.2016.04.009
100091 北京,解放军第三〇九医院移植血液科
张永清. Email: zhangyongqing0725@163.com
2016-06-12)

