阿帕替尼治疗多线化疗后复发的广泛期小细胞肺癌的效果及对患者生存的影响
张海利 董桂兰 刘丽丽 谷雪 吕立丽 胡万宁 王志武
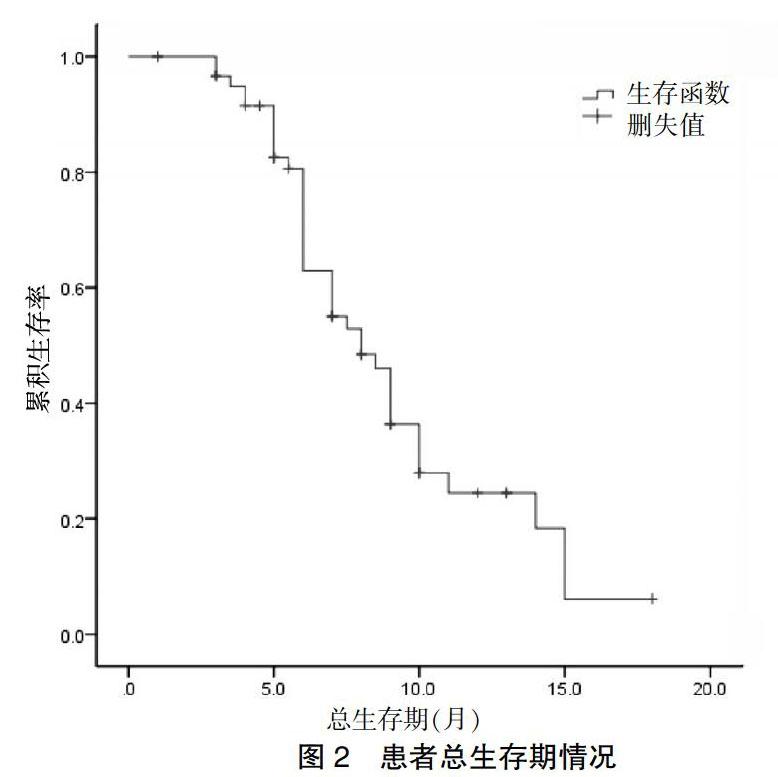
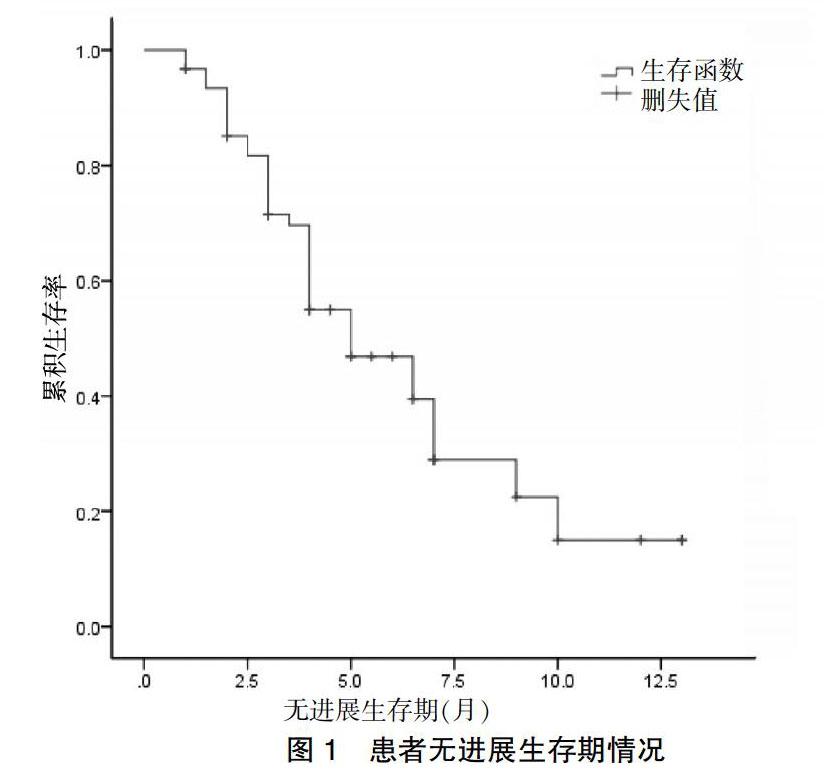
[摘要] 目的 觀察阿帕替尼治疗既往接受过多线化疗进展的广泛期小细胞肺癌(SCLC)患者的近期疗效、安全性及其对患者生存的影响。 方法 回顾性纳入2017年1月~2018年6月于唐山市人民医院放化疗科接受阿帕替尼治疗的SCLC患者62例。用药1个周期(4周)后首次评价疗效,之后每2个周期行一次疗效评价。主要研究终点为无进展生存期(PFS),次要终点为总生存期(OS),采用Kaplan-Meier曲线评估PFS,应用Log-rank对比组间生存差异,根据RECIST 1.1标准评估疗效,根据CTCAE 4.0标准评估不良反应。 结果 62例SCLC患者中无CR病例,11例(17.7%)达PR,37例(59.7%)为SD,PD为14例(22.6%)。DCR为48例(77.4%)。中位PFS为3个月(95%CI:1.13~4.87),中位OS为6个月(95%CI:4.27~7.73)。最常见不良反应为继发性高血压(28/62)和手足综合征(34/62),3级不良反应共发生3例。 结论 阿帕替尼在广泛期SCLC三线或四线治疗中有确切效果,不良反应可耐受。该结果尚需在多中心、大样本量的前瞻性研究中验证。
[关键词] 阿帕替尼;小细胞肺癌;生存分析;不良反应
[中图分类号] R734.2 [文献标识码] A [文章编号] 1673-7210(2019)09(b)-0100-04
Effect of Apatinib in the treatment of recurrent extensive small cell lung cancer after multi-line chemotherapy and its impact on the survival of patients
ZHANG Haili DONG Guilan LIU Lili GU Xue LYU Lili HU Wanning WANG Zhiwu▲
Department of Radiotherapy and Chemotherapy, Tangshan People′s Hospital, Hebei Province, Tangshan 063000, China
[Abstract] Objective To observe the short-term efficacy, safety and survival of Apatinib in the treatment of patients with extensive small cell lung cancer (SCLC) who had previously undergone multiline chemotherapy. Methods A retrospective study of 62 SCLC patients treated with Apatinib in Department of Radiotherapy and Chemotherapy, Tangshan People′s Hospital from January 2017 to June 2018. The efficacy was evaluated for the first time after 1 cycle (4 weeks). Thereafter, the efficacy was evaluated every two cycles. The primary endpoint was progression-free survival (PFS) and the secondary endpoint was total survival (OS). Kaplan-Meier curve was used to evaluate PFS. Log-rank was used to compare survival differences between groups. The efficacy was evaluated according to RECIST 1.1 criteria, and adverse reactions were evaluated according to CTCAE 4.0 criteria. Results Among the 62 patients with SCLC, there were no CR cases, 11 cases (17.7%) with PR, 37 cases (59.7%) with SD and 14 cases (22.6%) with PD. DCR was 48 cases (77.4%). The median PFS was 3 months (95%CI: 1.13-4.87) and the median OS was 6 months (95%CI: 4.27-7.73). The most common adverse reactions were secondary hypertension (28/62) and hand-foot syndrome (34/62), and grade 3 adverse reactions occurred in 3 cases. Conclusion Apatinib has a definite effect in the third or fourth line treatment of extensive SCLC, and the adverse reactions are tolerable. The results need to be validated in a multi-center, large-sample prospective study.
本研究的主要缺陷是回顧性研究,存在产生偏倚结果的风险,且样本量较小,不足以进行多因素分析,不能进一步探讨影响阿帕替尼治疗敏感性的相关因素。因此我们期待目前正在进行中的前瞻性研究的最终结果,同时也计划开展自己的前瞻性研究来进一步观察阿帕替尼的疗效。本研究是目前报道的关于阿帕替尼用于SCLC治疗的研究中样本量最大的研究。研究发现阿帕替尼作为三线或四线治疗,在广泛期SCLC中疗效确切,不良反应可耐受。该结果尚需在多中心、大样本量的前瞻性研究中验证。
[参考文献]
[1] Tsoukalas N,Aravantinou-Fatorou E,Baxevanos P,et al. Advanced small cell lung cancer(SCLC):new challenges and new expectations [J]. Ann Transl Med,2018,6(8):145.
[2] Koinis F,Kotsakis A,Georgoulias V. Small cell lung cancer(SCLC):no treatment advances in recent years [J]. Transl Lung Cancer Res,2016,5(1):39-50.
[3] Tanno S,Ohsaki Y,Nakanishi K,et al. Human small cell lung cancer cells express functional vegf receptors,vegfr-2 and vegfr-3 [J]. Lung Cancer,2004,46(1):11-19.
[4] Salven P,Ruotsalainen T,Mattson K,et al. High pre-treatment serum level of vascular endothelial growth factor (vegf) is associated with poor outcome in small-cell lung cancer [J]. Int J Cancer,1998,79(2):144-146.
[5] Hong W,Li H,Jin X,et al. P1.07-053 apatinib for chemotherapy-refractory extensive stage SCLC:results from a single-center retrospective study:topic:SCLC/neuroendocrine tumors in general [J]. J Thorac Oncol,2017:12(1):S729.
[6] Liu Y,Hu X,Jiang J,et al. P3.04-007 a prospective study of apatinib in advanced small cell lung cancer patients failed from two or more lines of chemotherapy [J]. J Thorac Oncol,2017,12(11):S2287.
[7] Yan X,Ma Z,Wang H,et al. P33 the retrospective analysis of apatinib as maintenance therapy in extensive-stage small cell lung cancer [J]. J Thorac Oncol,2018,13(9):S174.
[8] Schwartz LH,Litière S,de Vries E,et al. Recist 1.1-update and clarification:from the recist committee [J]. Eur J Cancer,2016,62:132-137.
[9] Ready NE,Dudek AZ,Pang HH,et al. Cisplatin,irinotecan,and bevacizumab for untreated extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer:Calgb 30306,a phase ii study [J]. J Clin Oncol,2011,29(33):4436.
[10] Pujol JL,Lavole A,Quoix E,et al. Randomized phase Ⅱ–Ⅲ study of bevacizumab in combination with chemotherapy in previously untreated extensive small-cell lung cancer:results from the IFCT-0802 trial [J]. Ann Oncol,2015,26(5):908-914.
[11] Allen JW,Moon J,Gadgeel SM,et al. Swog 0802:a randomized phase Ⅱ trial of weekly topotecan with and without ave0005 (aflibercept) in patients with platinum-treated extensive-stage small cell lung cancer (E-SCLC)[M].ASCO,2012.
[12] Ready NE,Pang HH,Gu L,et al. Chemotherapy with or without maintenance sunitinib for untreated extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer:a randomized,double-blind,placebo-controlled phase Ⅱ study-calgb 30504 (alliance) [J]. J Clin Oncol,2015,33(15):1660.
[13] Ding J,Chen X,Gao Z,et al. Metabolism and pharmacokinetics of novel selective vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 inhibitor apatinib in humans [J]. Drug Metab Dispos,2013,41(6):1195-1210.
[14] Li J,Qin S,Xu J,et al. Randomized,double-blind,placebo-controlled phase Ⅲ trial of apatinib in patients with chemotherapy-refractory advanced or metastatic adenocarcinoma of the stomach or gastroesophageal junction [J]. J Clin Oncol,2016,34(13):1448-1454.
[15] Liao X,Li H,Liu Z,et al. Clinical efficacy and safety of apatinib in patients with advanced colorectal cancer as the late-line treatment [J]. Medicine ,2018,97(50):e13635.
[16] Lu W,Jin XL,Yang C,et al. Comparison of efficacy between tace combined with apatinib and tace alone in the treatment of intermediate and advanced hepatocellular carcinoma:a single-center randomized controlled trial [J]. Cancer Biol Ther,2017,18(6):433-438.
[17] Miao M,Deng G,Luo S,et al. A phase Ⅱ study of apatinib in patients with recurrent epithelial ovarian cancer [J]. Gynecol Oncol,2018,148(2):286-290.
[18] Liu Y,Hu X,Zhou S,et al. P1.12-03 a prospective study of apatinib in advanced small cell lung cancer patients failed from two or more lines of chemotherapy [J]. J Thorac Oncol,2018,13(10):S573-S574.
[19] Fan Y,Huang Z,Li W,et al. P1.12-01 a single-arm multi-center phase Ⅱ study of apatinib in patients with ES-SCLC after second/third-line chemotherapy [J]. J Thorac Oncol,2018,13(10):S573.
[20] Baize N,Monnet I,Greillier L,et al. Second-line treatments of small-cell lung cancers [J]. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther,2017,17(11):1033-1043.
(收稿日期:2019-02-13 本文編辑:李亚聪)

