GRAPHIC ABSTRACT
FLUID MECHANICS
Mechanism of wavy vortex and sign laws in flow past a bluff body:vortex-induced vortex
L. M. Lin · S. Y. Shi · X. F. Zhong · Y. X. Wu
Intrinsic physical mechanism in wavy vortex and two sign laws is analyzed by introducing the theory of vortex-induced vortex (VIVor). Based on the analysis of the nearest-wall flow, two vortex-induced models by streamwise and vertical vortex pairs, respectively, are proposed under two boundary cases. Such two sign laws are then verifiedd. Particularly, the first sign law reveals the intrinsic physical relationship between streamwise and vertical vorticities, independent of the distribution of spanwise vortices in the whole flow field. It is also confirmed that the spanwise vortices, as well as the shear layers and wake width, wavily across the span are attributed to the introduced streamwise or vertical vortices. Through the analysis of flow past the conic shroud, two sign laws are successfully used to summarize spacial distributions of vorticity typically in three flow regions:on and near front cylinder surfaces (R-I), the separated shear layers (R-II), and near wake (R-III).

Acta Mechanica Sinica 35, 1-14 (2019)
Study on vibration of dragon wash basin and free surface waves inside
Zi-Yu Guo · Xiao-Peng Chen · Lai-Bing Jia · Bin Xu
A filled dragon wash basin (DWB) can generate humming sound and emit tiny droplets when it is rubbed with clean and wet hands. Through numerical and experimental studies, we show that it ref lects the first order vibration of the system. By compared with a theoretical model, the geometric details of the DWB is analyzed. The measurements of the water surface waves show both radial and azimuthal components are triggered as DWB is working and they satisfy the dispersion relation of capillary wave.

Acta Mechanica Sinica 35, 15-23 (2019)
Spectral measurements of hypervelocity flow in an expansion tunnel
C. K. Yuan · K. Zhou · Y. F. Liu · Z. M. Hu · Z. L. Jiang
Hypervelocity radiation measurements were carried out in the JF16 expansion tunnel with secondary shock velocity of 7.9 km/s. Results show that emission spectrum comprise several atomic lines and molecular band systems. Detailed data of radiation spectrum, shock shape, shock detached distance, and radiation intensity varies with space and wavelength was given. This valuable experimental dataset will be helpful to validate computational fluid dynamics (CFD) codes and radiation models, which equates to increased prediction accuracy of radiation heating. Also, some suggestions for spectral measurement in hypervelocity flow field were list in the end.
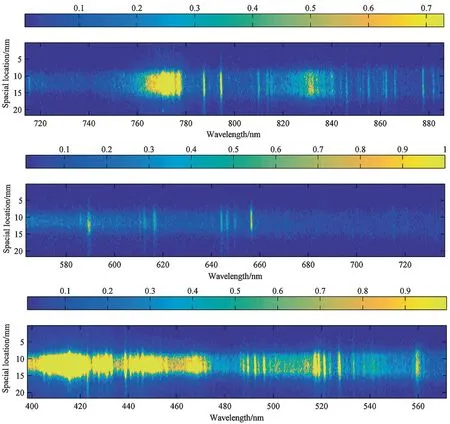
Acta Mechanica Sinica 35, 24-31 (2019)
Quasi-static simulation of droplet morphologies using a smoothed particle hydrodynamics multiphase model
Xiangwei Dong · Jianlin Liu · Sai Liu · Zengliang Li
A simple method of implementing contact angle is proposed, combined with a robust smoothed particle hydrodynamics multiphase algorithm. We simulate the evolution process of initially square liquid lumps on f lat and curved surfaces.The predictions of droplet profiles are in good agreement with the analytical solutions provided that the macroscopic contact angle is accurately implemented.Compared to the normal correction method, the present method is straightforward without the need to manually alter the normal vectors. This study presents a robust algorithm capable of capturing the physics of the static wetting.
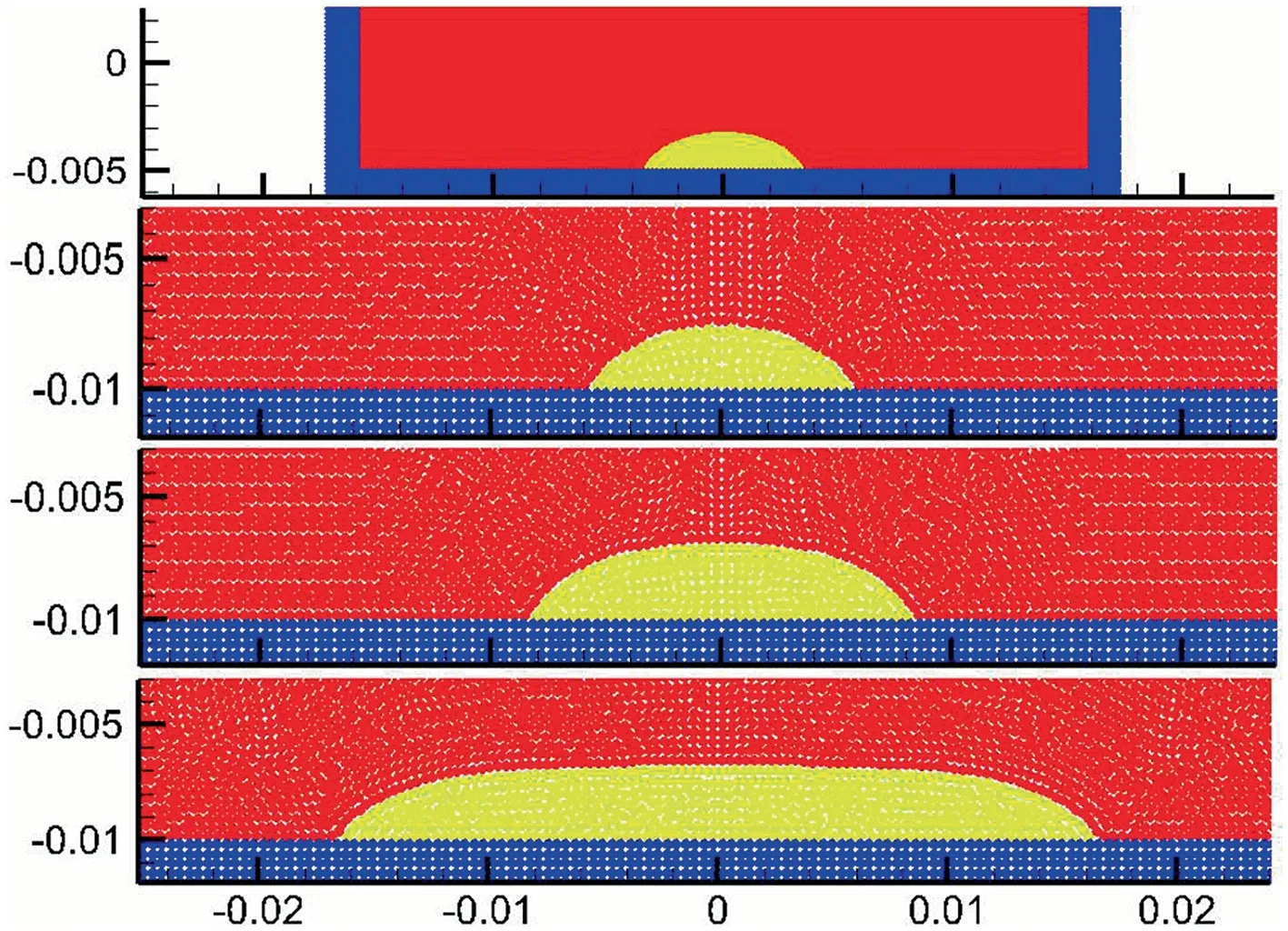
Acta Mechanica Sinica 35, 32-44 (2019)
Effect of local longitudinal shortening on the transport ofluminal contents through small intestine
Ravi Kant Avvari
A theoretical analysis of the rheological fluid flow due to peristalsis is studied.A parametric study involving the changes in local longitudinal shortening(LLS) magnitude, LLS spacing, fluid viscosity, wavelength of the wave, and occlusion of lumen caused by the wave provided insights into the dynamics of the peristalsis flow of a non-Newtonian fluid. LLS appears to have little significance in modulating the flow patterns that are caused by circular contraction (CC) alone.Results also indicate that there exists trade-off between the power requirement for peristalsis at a certain occlusion against the percentage LLS. Having mucosal folds in the inner lining of the intestine allows for one more advantage of slowing the transit due to increased friction factor and increase in time for absorption of the nutrients.
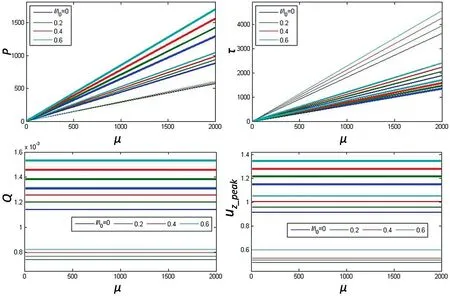
Acta Mechanica Sinica 35, 45-60 (2019)
Effects of aspect ratio on shock-cylinder interaction
Junfeng Ou · Zhigang Zhai
Effects of aspect ratio on shock-induced elliptic gas cylinder evolution are investigated. An inward jet is observed in prolate ellipse for the first time in experiments. The effects of aspect ratio on shock focusing, jet formation and material mixing are emphasized.

Acta Mechanica Sinica 35, 61-69 (2019)
SOLID MECHANICS
Dual-level stress plateaus in honeycombs subjected to impact loading:perspectives from bucklewaves, buckling and cell-wall progressive folding
Lang Li · Zhenyu Zhao · Rui Zhang · Bin Han · Qiancheng Zhang · Tian Jian Lu
Dual-level stress plateaus (i.e., relatively short peak stress plateau, followed by prolonged crushing stress plateau) in metallic hexagonal honeycombs subjected to out-of-plane impact loading are characterized. It is found that honeycombs exhibit dual-level stress plateaus when bucklewaves are initiated and propagate in cell walls, followed by buckling and progressive folding of the cell walls.Abrupt stress drop from peak to crushing plateau in the compressive stress versus strain curve can be explained in a way similar to the quasi-static buckling of a clamped plate.
Acta Mechanica Sinica 35, 70-77 (2019)
Constitutive parameters identification of thermal barrier coatings using the virtual fields method
Mengmeng Zhou · Huimin Xie · Luming Li
In this work, an inversion method based on the virtual fields method was developed and applied in the constitutive parameters identification of thermal barrier coatings. The feasibility of this method was verifiedd using simulated deformation fields of a two-layer material. The sensitivity of the identification results to the configuration of two-layer material was also investigated. As an application, the proposed inversion method for the bi-material was utilized in the constitutive parameters of thermal barrier coatings (TBCs).
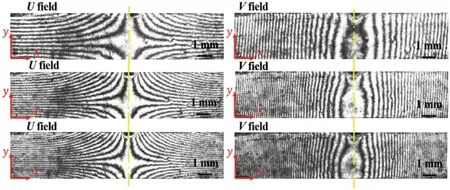
Acta Mechanica Sinica 35, 78-87 (2019)
Mechanical properties of 65Mn chiral structure with three ligaments
X. W. Su · D. M. Zhu · C. Zheng · M. M. Tomovic
The results indicate that the equivalent elastic modulus increases gradually with increase in the dimensionless ligament thickness, β , and that the equivalent elastic modulus in the X direction is larger than the one in the Y direction. The results also indicate that the equivalent Poisson's ratio remains fairly constant with increase of the dimensionless ligament thickness, and that the equivalent Poisson's ratio along the X direction is larger than the one in the Y direction.
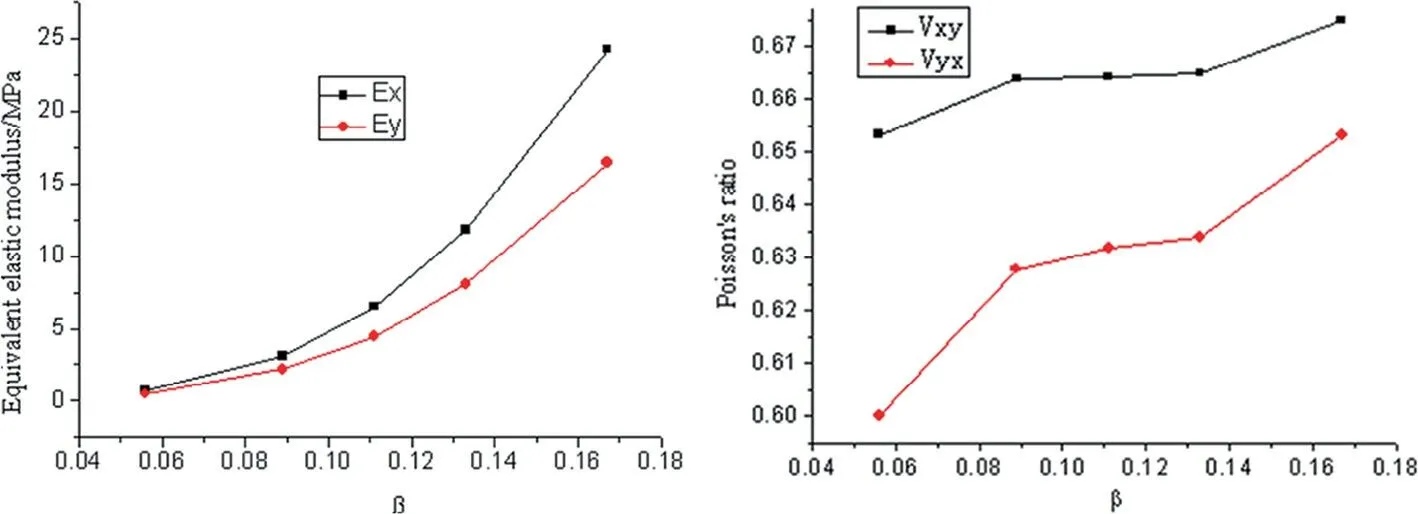
Acta Mechanica Sinica 35, 88-98 (2019)
Frictionally excited thermoelastic dynamic instability of functionally graded materials
J. Liu · L. L. Ke · Y. S. Wang
The effect of the dimensionless sliding speed (V0) on the value of bRfor some selected values of the coating gradient index λ is plotted. The results imply that we can modify the sliding stabilities, critical friction coeff icient, and critical sliding speed by adjusting the coating gradient index.

Acta Mechanica Sinica 35, 99-111 (2019)
A three-parameter single-step time integration method for structural dynamic analysis
Huimin Zhang · Yufeng Xing
By introducing a subsidiary variable into the update equations, a new three parameter single-step method is proposed, and the overall analysis of properties generates the optimal implicit and explicit schemes. Compared with the existing three-parameter methods, the present method possesses higher accuracy due to the free of the interpolation of load vector, and can be directly applied to nonlinear problems without the modif ication of motion equation.

Acta Mechanica Sinica 35, 112-128 (2019)
Nonlinear vibration analysis of a circular micro-plate in two-sided NEMS/MEMS capacitive system by using harmonic balance method
Milad Saadatmand · Alireza Shooshtari
Forced nonlinear vibration of a circular micro-plate under two-sided electrostatic,two-sided Casimir and external harmonic forces is investigated, analytically.Analytical solutions, based on single-mode Galerkin method and first-order harmonic balance method (HBM), yield to closed-form expressions for frequency response relations and have been validated by numerical methods up to 2/3 of the gap. The analytical results for three cases: (1) semi-linear vibration, (2)weakly nonlinear vibration, and (3) highly nonlinear vibration, are validated by comparing with the numerical solutions.

Acta Mechanica Sinica 35, 129-143 (2019)
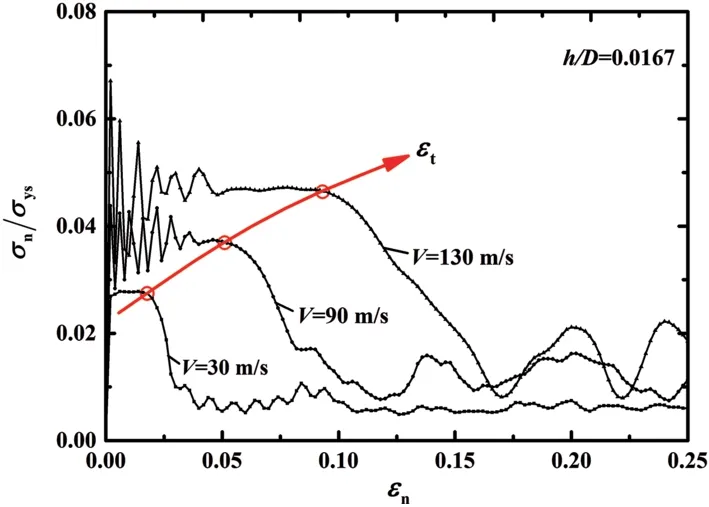
Numerical and experimental analysis of the closed-cell aluminium foam under low velocity impact using computerized tomography technique
S. Talebi · M. Sadighi · M. M. Aghdam
Low velocity impact on closed-cell aluminum foams is studied numerically and experimentally. In order to assess 3D microstructure of closed-cell aluminum foams, computerized tomography technique is employed. The effect of foam density and the velocity of impactor on foam dynamic behavior are investigated.The results show that at a constant velocity, an increase in foam density leads to the increase in peak stress but has no remarkable influence on the energy absorption and by the increase in the impactor velocity, both peak stress and energy absorption increase considerably.
Band gap analysis of periodic structures based on cell experimental frequency response functions (FRFs)
Li-Jie Wu · Han-Wen Song
Transfer function is usually performed to gain band gap. Previous scholars regard estimation of the transfer function as a forward problem assuming known cell mass and stiffness matrices. We treat the estimation as an inverse problem by employing modal identification and curve f itting. Transfer matrix is then established by parameters identif ied through modal analysis. Influence of modal parameters on band gap are then shown.
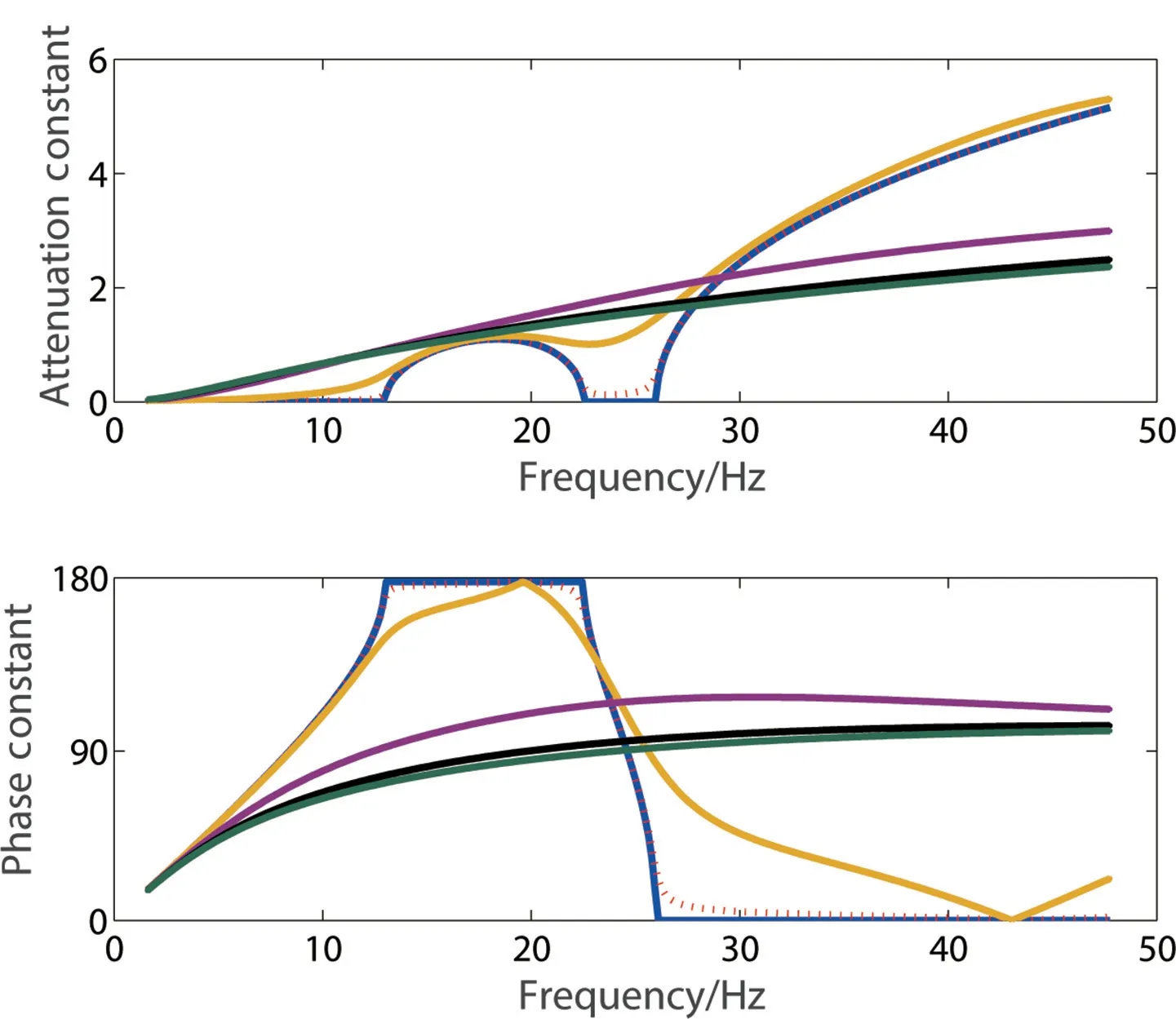
Acta Mechanica Sinica 35, 156-173 (2019)
Buckling analysis of functionally graded plates partially resting on elastic foundation using the differential quadrature element method
Arash Shahbaztabar · Koosha Arteshyar
Functionally graded materials are a class of composites that usually produced by mixing ceramic and metal materials. Smooth stress distribution property of functionally graded materials (FGMs) gives them precedence over the laminated composites. The critical buckling loads of the structures are the essential information required in the design of structures. For structures with discontinuities in geometry and loading, numerical or experimental methods should be used.In this research the application of the differential quadrature element method is extended to the buckling analysis of FG plates partially resting on the elastic support. It is found that by increasing the values of power law exponent the critical buckling load decreases.

Acta Mechanica Sinica 35, 174-189 (2019)
Damage and fracture model for eutectic composite ceramics
Jinfeng Yu · Xinhua Ni · Xiequan Liu · Yunwei Fu · Zhihong Du
The study of damage and fracture model is a subject of considerable importance to analyze the fracture mechanism of eutectic composite ceramics because there is no accurate fracture model for this material. This work presents a damage and fracture model that predicts the damage and fracture of eutectic composite ceramics through the analysis of defect stability and damage localization band.It provides theoretical basis for further study of damage mechanics of eutectic composite ceramics and guiding engineering application of this material.

Acta Mechanica Sinica 35, 190-200 (2019)
Variable-stiffness composite cylinder design under combined loadings by using the improved Kriging model
Jifan Zhong · Yaochen Zheng · Jianqiao Chen · Zhao Jing
This paper focuses on the anti-buckling performance of variable stiffness(VS) cylindrical structures under combined loads. To increase the computation eff iciency, an adaptive Kriging meta-model incorporated with a mixed updating criterion is proposed to approximate the cylinders' responses. Optimal design solutions of VS cylinders under bending moment or combined loads are obtained by using genetic algorithms. Numerical examples show that the buckling deformation in an optimized VS cylinder distributes more extensively as compared to the quasi-isotropic (QI) cylinder, leading to a greater buckling load in the former.

Acta Mechanica Sinica 35, 201-211 (2019)
Numerical solutions for cracks in an elastic half-plane
N. R. F. Elfakhakhre · N. M. A. Nik Long · Z. K. Eshkuvatov
The stress intensity factor (SIF) at the tips of cracks subjected to uniaxial tensionwith free traction boundary condition in half plane elasticity is studied.The modif ied complex potential is used to formulate the problem into singular integral equations with the distribution dislocation function as unknown. The problem solved numerically by using appropriate quadrature formulas together with curve coordinate method. Numerical examples exhibit the values of SIF are influenced by the distance between the cracks to the boundary of the half plane,and the configuration of the cracks.

Acta Mechanica Sinica 35, 212-227 (2019)
DYNAMICS, VIBRATION, AND CONTROL
An R(x)-orthonormal theory for the vibration performance of a non-smooth symmetric composite beam with complex interface
Chein-Shan Liu · Bo-Tong Li
An R(x)-orthonormal theory is developed, where R(x) is an integrable exural rigidity function. The R(x)-orthonormal bases in the linear space of boundary functions are constructed, of which the second-order derivatives of boundary functions are asked to be orthonormal with respect to the weight function R(x).When the vibration modes of the symmetric composite beam are expressed in terms of the R(x)-orthonormal bases we can derive an eigenvalue problem endowing with a special structure of the coecient matrix A := [aij], aij= 0 if i + j is odd. Based on the special structure we can prove two new theorems, which indicate that the characteristic equation of A can be decomposed into the product of the characteristic equations of two sub-matrices with dimensions halflower.

Acta Mechanica Sinica 35, 228-241 (2019)
Instability inspection of parametric vibrating rectangular Mindlin plates lying on Winkler foundations under periodic loading of moving masses
E. Torkan · M. Pirmoradian · M. Hashemian
Within the framework of Mindlin plate theory, dynamic instability of moderately thick rectangular plates resting on elastic foundations under moving mass excitation is investigated via incremental harmonic balance method. All inertial components of the moving masses are adopted in the dynamical formulation.Instability survey is carried out for three different loading trajectories considerably interested in many practical applications of the issue, i.e. rectilinear, diagonal and orbiting trajectories. It is found that increasing the foundation stiffness leads to further stability of the parametrically excited system at lower frequencies.

Acta Mechanica Sinica 35, 242-263 (2019)
- Acta Mechanica Sinica的其它文章
- Instability inspection of parametric vibrating rectangular Mindlin plates lying on Winkler foundations under periodic loading of moving masses
- Mechanism of wavy vortex and sign laws in flow past a bluff body:vortex-induced vortex
- Study on vibration of dragon wash basin and free surface waves inside
- Spectral measurements of hypervelocity flow in an expansion tunnel
- Quasi-static simulation of droplet morphologies using a smoothed particle hydrodynamics multiphase model
- Effect of local longitudinal shortening on the transport ofluminal contents through small intestine

