托卡马克中高谐快波和低杂波协同电流驱动模拟研究
曹文虎,尹 岚,宋城邑,郑平卫,周方贝,马万坤
托卡马克中高谐快波和低杂波协同电流驱动模拟研究
曹文虎1,尹岚2,*,宋城邑1,郑平卫4,周方贝3,马万坤1
(1. 南华大学 核科学技术学院,湖南 衡阳 421001;2. 南华大学 数理学院,湖南 衡阳 421001;3. 南华大学 电气工程学院,湖南 衡阳 421001;4. 南华大学 资源环境与安全工程学院,湖南 衡阳 421001)
基于全超导托卡马克EAST上的低e运行参数,采用射线追踪和Fokker-Planck方程程序模拟研究由高场侧发射的高谐快波(HHFW)和低杂波(LHW)联合电流驱动。研究结果表明,满足一定的条件,高场侧发射的HHFW和LHW存在较大的协同效应,且从靠近芯部到离轴较宽的区域内均有正协同效应,能有效提升电流驱动效率,改善电流分布,通过分析其物理机制发现协同效应发生与两支波共振区的速度空间位置关系密切相关,并进一步分析研究了平行折射率、波频率、波功率等参数对两波联合电流驱动协同效应的影响。
低杂波;高谐快波;协同效应;电流驱动;托卡马克
在可控热核聚变装置托卡马克中,射频波电流驱动(CD)是产生等离子体电流,补充自举电流的重要方式[1]。其中低杂波电流驱动(LHCD)是目前托卡马克装置上公认效率较高的射频波电流驱动方式,物理机制是波在等离子体传播过程中通过朗道阻尼机制在平行方向上加速电子,形成环向电流。利用LHW 驱动电流是实现托卡马克稳态运行的重要手段[2-4],LHCD虽然具有很高的电流驱动效率,但存在密度极限问题,即:在高等离子体密度条件下,LHW难以传入等离子体内部,电流驱动效率迅速下降[5]。以往研究显示从高场侧发射LHW能部分缓解LHW在高密度条件下的可近性问题[6]。
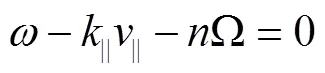
本文第2节简要描述了HHFW和LHW联合电流驱动采用的模拟方法。第3节给出了在低e运行参数下高场侧发射HHFW和LHW联合电流驱动的具体模拟结果。第4节对两支波协同效应结果进行分析和讨论。第5节给出结论。
1 模拟方法
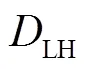
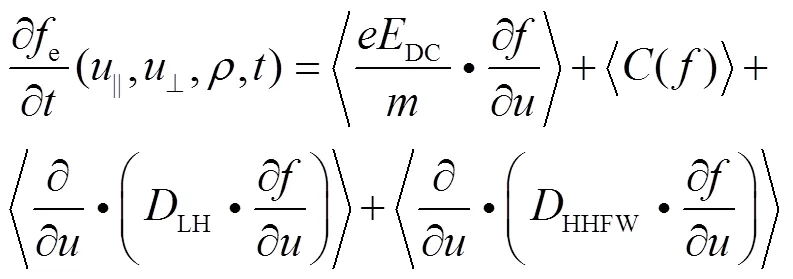
准线性扩散项的表达式如下[21]。
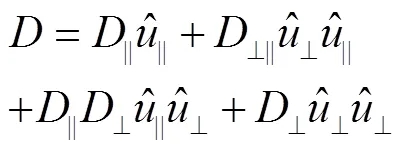
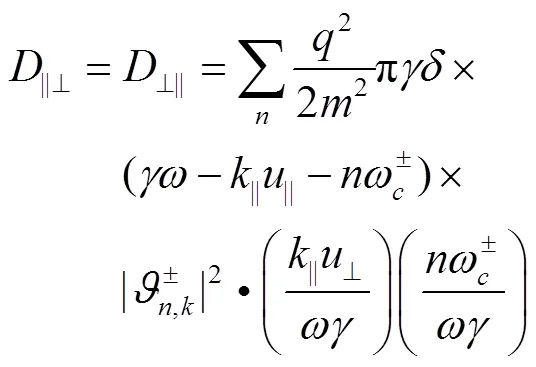
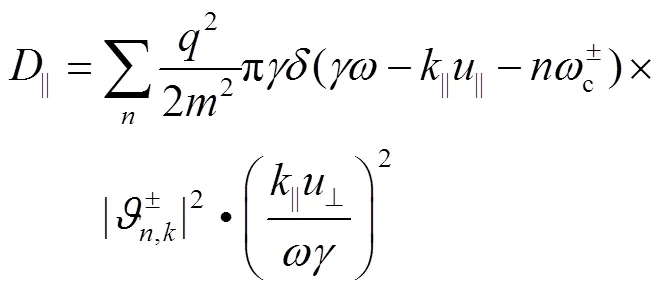
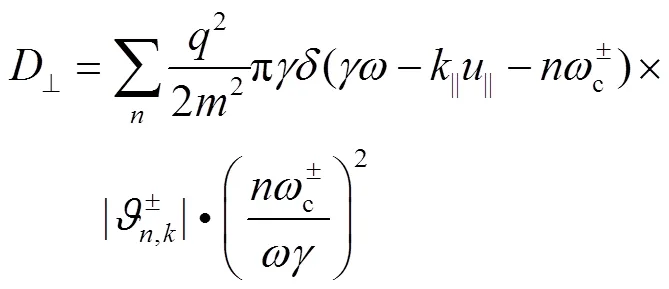
其中:
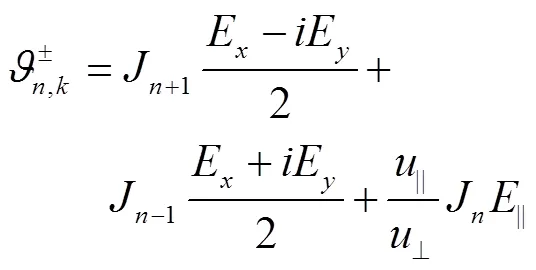
2 模拟内容
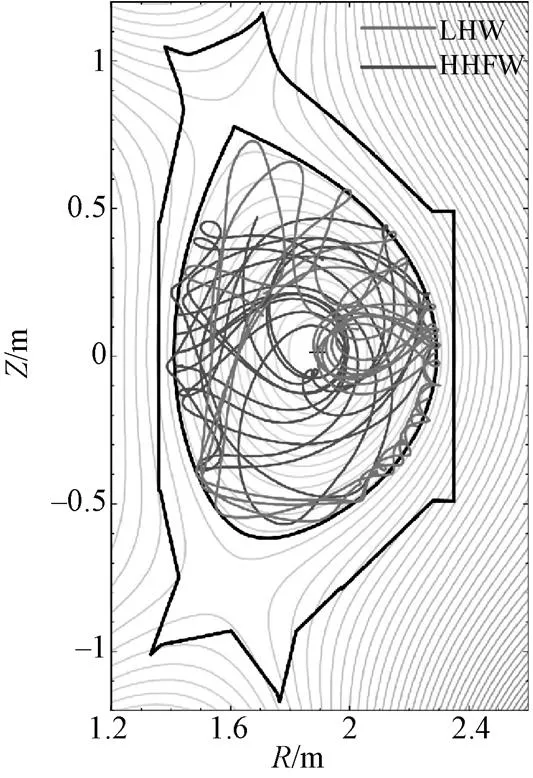
图1 磁平衡位形和波迹
模拟中从高场侧中平面发射的LHW的频率采用2.65 GHz,其平行折射率峰值为2.32,功率谱谱宽为0.1,发射机的高度为0.776 m,输入功率设置为1 MW。从高场侧中平面发射的HHFW的频率为1.8 GHz,其平行折射率峰值为2.12,功率谱谱宽为0.1,输入功率设置为1 MW。利用模拟程序GENRAY从5个不同的极向位置发射50条射线模拟波在等离子体中的传播和阻尼,由GENRAY程序计算后得到的HHFW和LHW的射线轨迹如图1所示,然后对 HHFW和LHW的准线性扩散项进行求和,求解电子分布函数,模拟联合电流驱动。
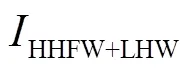
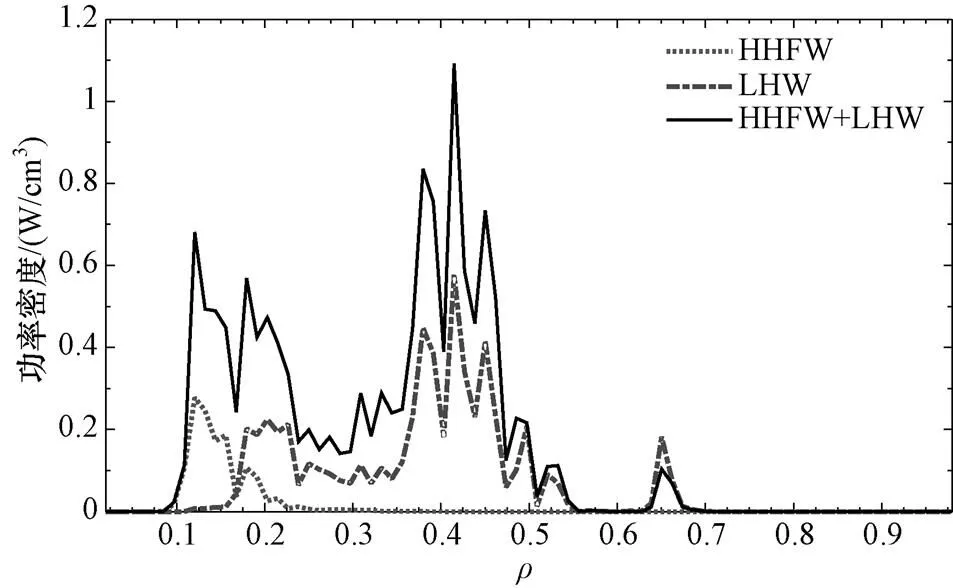
图2 HHFW、LHW和HHFW+LHW的径向功率吸收
3 分析和讨论
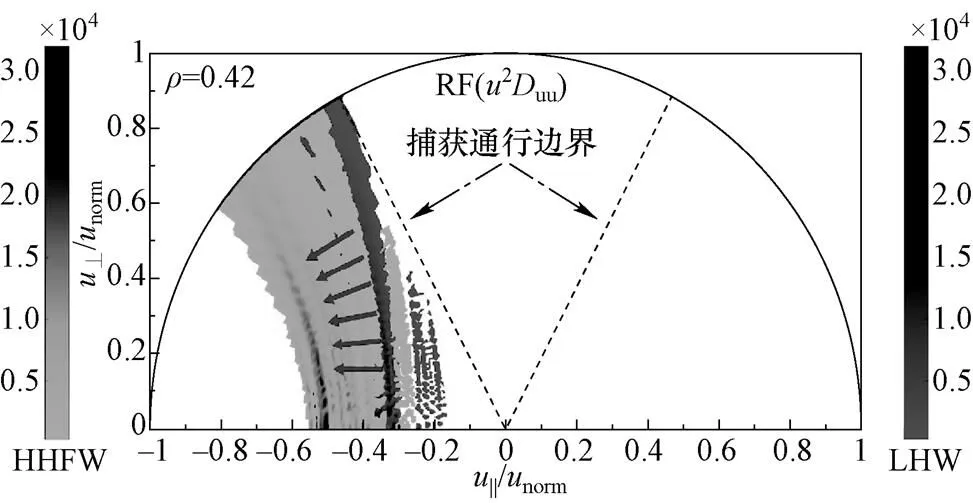
图4 速度空间中HHFW和LHW准线性扩散强度的等值线图
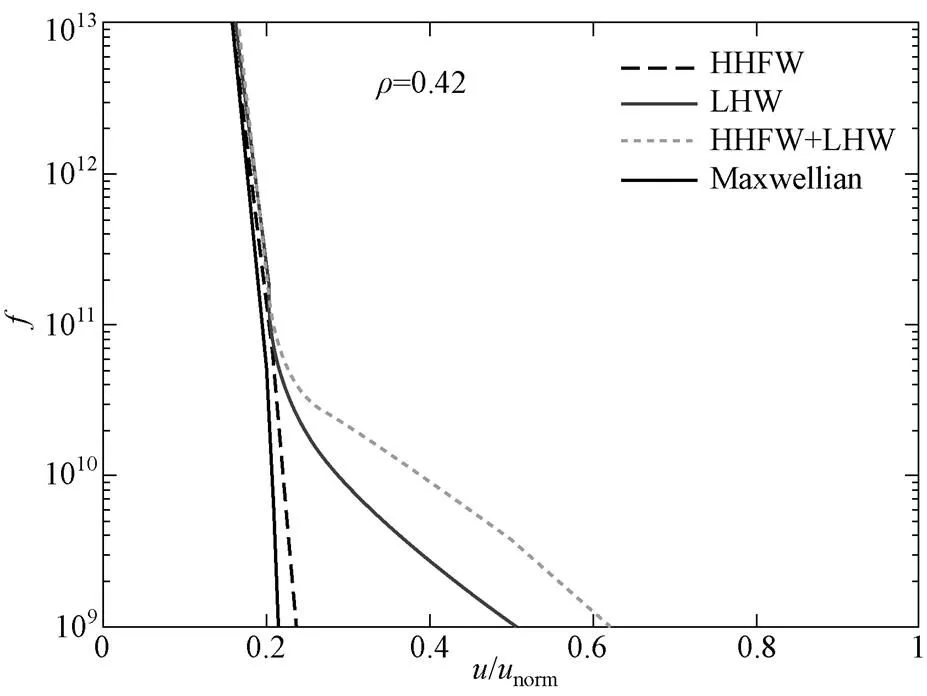
图5 ρ=0.42时电子分布函数f与归一化速度u/unorm的关系
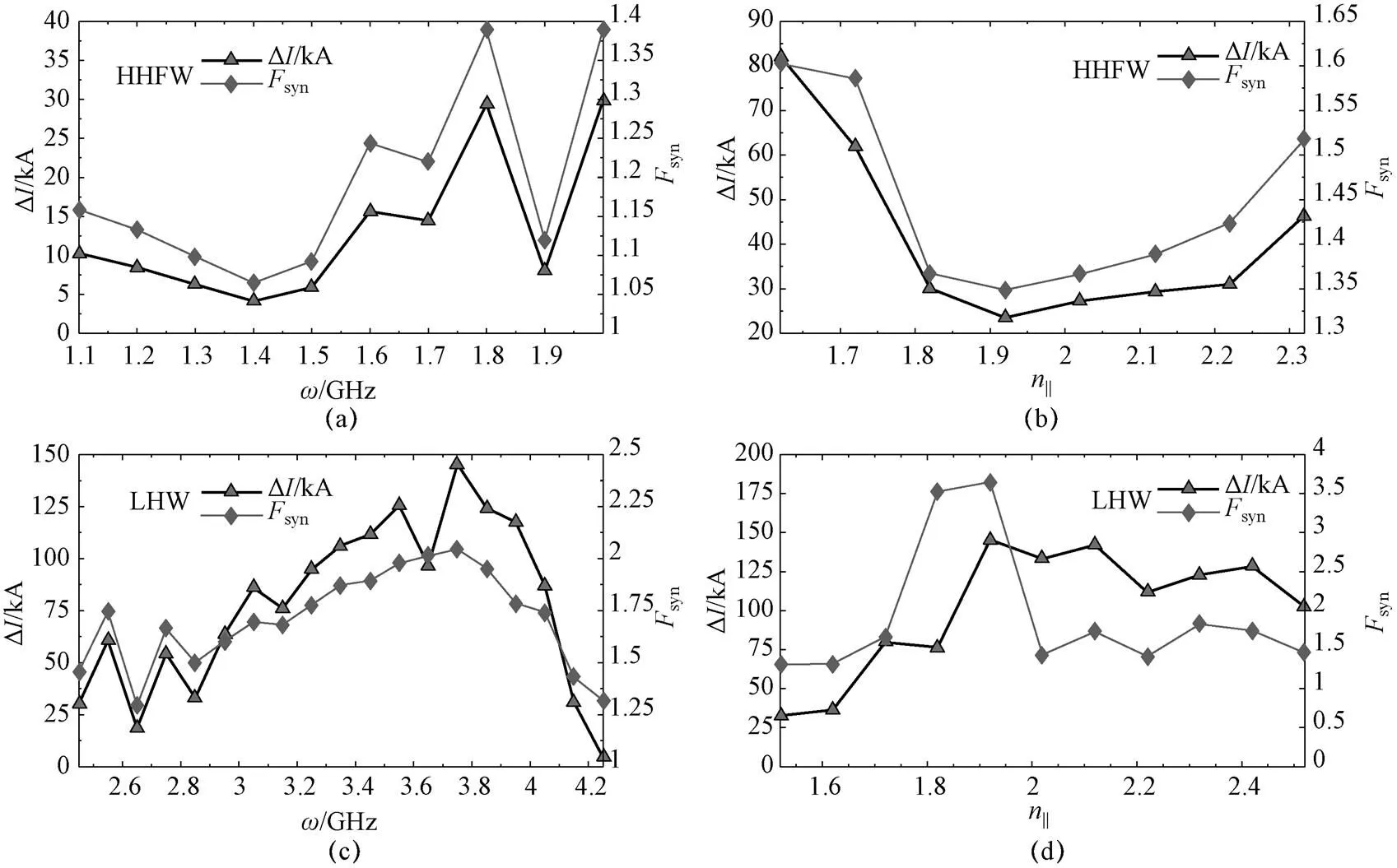
图6 协同电流和协同因子与HHFW和LHW的ω和n‖的关系
通过扫描HHFW和LHW的注入波功率(0.5~3 MW),研究了两支波的协同电流和协同因子与波功率之间的关系,结果如图7所示。模拟时注入相同功率的HHFW和LHW,当注入功率在0.5~1.5 MW时,协同电流随着注入波功率的增加而增大,这是因为注入的波功率越多相当于更多的电子被加速至高相速度波(HHFW)的共振区,当注入功率在1.5~3 MW时,协同电流几乎不受注入波功率的影响,这是因为当功率达到一定值时,不会再有新的电子被加速至高相速度波(HHFW)的共振区。总体来说,协同因子会随着注入波功率的增加而降低。
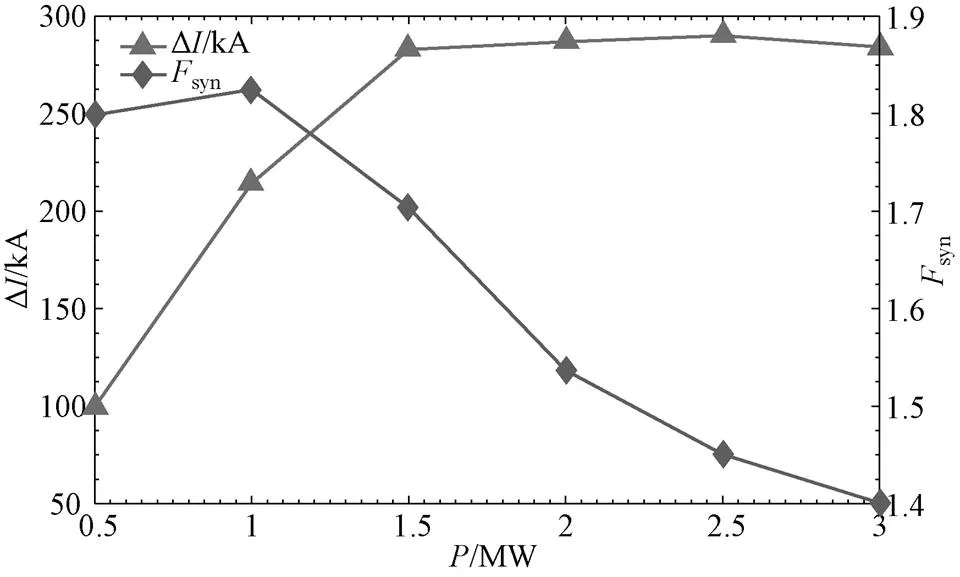
图7 协同电流和协同因子与波功率P的关系
4 结论
本文是对可控热核聚变装置EAST在低e运行参数下采用波迹程序和Fokker-Planck方程程序GENRAY/CQL3D模拟计算HHFW和LHW均在高场侧注入时的联合电流驱动。通过模拟研究表明HHFW和LHW存在显著的协同效应,由于协同效应使得总的电流驱动效率显著提高。和低场侧注入联合两波电流驱动在近轴区域出现负协同效应[24]不同,高场侧注入联合两波电流驱动在近轴区域和离轴区域均出现正协同效应,因此更有利于电流驱动效率的提升。其物理机制是LHW和HHFW与电子的速度共振区彼此相邻,低相速度波(LHW)与较低平行速度电子相互作用,这些电子加速后被推至高相速度波(HHFW)的共振区,导致高相速度波共振区的电子数量急剧增加,驱动出额外的电流。当注入相同功率的HHFW和LHW,在一定的注入波功率区间内,两支波的协同电流随着两支波注入功率的增加而增加,当注入波功率达到一定值时,协同电流几乎不再受注入波功率影响,而协同因子会随着注入波功率的增加而降低。此外,在对LHW和HHFW的波频率和平行折射率的扫描中,尽管协同电流和协同因子略有不同,但是不同的波频率和平行折射率的LHW和HHFW之间广泛存在正协同效应。目前EAST上采用低场侧注入低杂波的方式驱动等离子体电流,未来有可能在高场侧安装低杂波天线,研究结果为EAST和未来聚变反应堆上在高场侧应用LHW和HHFW联合高效电流驱动提供了可选择方案。
[1] Wesson J,Campbell D J. Tokamaks[M]. Oxford university press,2011.
[2] Bonoli P T,Porkolab M,Ramos J J,et al. Possible achievement of second stability by means of lower hybrid current drive[J]. Nuclear fusion,1990,30(3):533-540.
[3] Bonoli P T,Englade R C. Simulation model for lower hybrid current drive[J]. The Physics of fluids,1986,29(9):2937-2950.
[4] Bonoli P T,Ott E. Accessibility and Energy Depositon of Lower-Hybrid Waves in a Tokamak with Density Fluctuations[J]. Physical Review Letters,1981,46(6):424.
[5] Fisch N J. Theory of current drive in plasmas[J]. Reviews of Modern Physics,1987,59(1):175.
[6] Bonoli P T,Wallace G M,Shiraiwa S,et al. High field side lower hybrid wave launch for steady state plasma sustainment[J]. Nuclear Fusion,2018,58(12):126032. 1-35.
[7] Torreblanca H,Moeller C,Fishler B,et al. A high-power helicon antenna for the DIII-D tokamak and its electromagnetic aspects[J]. Fusion Engineering and Design,2019,146:626-630.
[8] Lau C,Jaeger E F,Bertelli N,et al. Using AORSA to simulate helicon waves in DIII-D[C]. AIP Conference Proceedings. AIP Publishing LLC,2015,1-4.
[9] Kojima T,Okuda T,Taka S. Radio Frequency current generation by helical slow-wave antennas in a torus[J]. Plasma physics,1983,25(12):1469.
[10]Paul M K,Bora D. Wave-induced helicity current drive by helicon waves[J]. Physics of Plasmas,2007,14(8):082507. 1-6.
[11]Kaye S M,Bell M G,Bell R E,et al. Progress towards high performance plasmas in the National Spherical Torus Experiment(NSTX)[J]. Nuclear fusion,2005,45(10):S168-S180.
[12]Wilson J R,Bell R E,Bernabei S,et al. Exploration of high harmonic fast wave heating on the National Spherical Torus Experiment[J]. Physics of Plasmas,2003,10(5):1733-1738.
[13]Li X,Liu H,Xiang N,et al. Theoretical analysis of helicon wave current drive in EAST with higheoperation[J]. Physics Letters A,2020,384(30):126779. 1-4.
[14]Zhai X M,Chen J L,Xiang N,et al. Synergy of two lower hybrid waves with different frequencies on EAST[J]. Physics of Plasmas,2019,26(5):052509. 1-7.
[15] Smirnov A P,Harvey R W. The GENRAY ray tracing code[J]. CompX Report No. CompX-2000-01,2001.33-59.
[16]Bertelli N,Wallace G,Bonoli P T,et al. The effects of the scattering by edge plasma density fluctuations on lower hybrid wave propagation[J]. Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion,2013,55(7):074003. 1-10.
[17]Wallace G M,Parker R R,Bonoli P T,et al. Absorption of lower hybrid waves in the scrape off layer of a diverted tokamak[J]. Physics of Plasmas,2010,17(8):082508. 1-10.
[18]Harvey R W,McCoy M G. The cql3d fokker-planck code[C]. Proceedings of the IAEA Technical Committee Meeting on Simulation and Modeling of Thermonuclear Plasmas, 1992:489-526.
[19]Petrov Y V,Harvey R W. A fully-neoclassical finite-orbit- width version of the CQL3D Fokker-Planck code[J]. Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion,2016,58(11):115001. 1-19.
[20]Harvey R W,Petrov Y V,Kim C C,et al. Time-dependent runaway electron simulations:Ampere-Faraday equations implemented in CQL3D[J]. Nuclear Fusion,2019,59(10):106046. 1-8.
[21]Kennel C F,Engelmann F. Velocity space diffusion from weak plasma turbulence in a magnetic field[J]. The Physics of Fluids,1966,9(12):2377-2388.
[22]Lao L L,John H S,Stambaugh R D,et al. Reconstruction of current profile parameters and plasma shapes in tokamaks[J]. Nuclear fusion,1985,25(11):1611-1622.
[23]Yang Y,Xiang N,Hu Y M. Synergy effects during current drive by two lower-hybrid waves[J]. Physics of Plasmas,2017,24(3):032502. 1-6.
[24]Yin L,Zheng P,Gong X,et al. New synergy effects of the lower hybrid wave and the high harmonic fast wave current drive[J]. Nuclear Fusion,2022,62(6):066023. 4-7.
Simulation Study of High Harmonic Fast Wave and Low Hybrid Wave Synergy Current Drive in Tokamak
CAO Wenhu1,YIN Lan2,*,SONG Chengyi1,ZHENG Pingwei4,ZHOU Fangbei3,MA Wankun1
(1. School of Nuclear Science and Technology,University of South China,Hengyang of Hunan Prov.421001,China;2. School of Mathematics and Science,University of South China,Hengyang of Hunan Prov.421001,China;3. School of Electrical Engineering,University of South China,Hengyang of Hunan Prov.421001,China;4. School of Resource Environment and Safety Engineering,University of South China,Hengyang of Hunan Prov.421001,China)
Based on the loweoperating parameters on the fully superconducting Tokamak EAST, ray tracing and the Fokker-Planck equation codes are used to simulate the combined current drive of high harmonic fast wave (HHFW) and low hybrid wave (LHW) with high field side emission. The results show that under certain conditions, there is a large synergistic effect between the HHFW and LHW emitted from the high-field side, and there is a positive synergistic effect from close to the core to the wider off-axis region, which can effectively improve the current drive efficiency and improve the current distribution. The physical mechanism is analyzed and it is found that the synergistic effect is closely related to the spatial position of the velocity in the resonance region of the two waves. In addition, the effects of parallel refractive index, wave frequency, wave power and other parameters on the synergistic effect of the two-wave joint current drive are also studied.
Low hybrid wave; High harmonic fast wave; Synergy effects; Current drive; Tokamak
TL11
A
0258-0918(2023)05-1167-07
2022-09-29
国家磁约束核聚变能发展研究专项(2022YFE03090001);国家自然科学基金资助项目(11805096);湖南省教育厅优秀青年项目(20B502);湖南省自然科学基金项目(2022JJ50157)
曹文虎(1993—),男,山东省滨州人,硕士研究生,现从事核聚变与等离子体物理方面研究。
尹 岚,E-mail:yinlan82@126.com

