系统性红斑狼疮并发银屑病15例临床特点
陈 雱,刘淑毓,吴秀华,郑文洁
(中国医学科学院 北京协和医学院 北京协和医院风湿免疫科,风湿免疫病学教育部重点实验室,北京 100730)
系统性红斑狼疮(systemic lupus erythematosus,SLE)是一种自身免疫性疾病,主要特点是多种自身抗体的产生以及多系统器官损害,女性患病率显著高于男性,且中国人比欧洲人更常见[1]。银屑病(psoriasis,Ps)是一种常见皮肤病,大量研究证明,Ps是免疫介导的炎症性皮肤病[2],西欧出生人群发生率约为2%~5%[3],美国人群发生率约为1%~3%[4],东亚人种患病率约为0.1%~0.3%[5-6]。虽然SLE可以重叠其他多种自身免疫性疾病,如类风湿关节炎(rheumatoid arthritis,RA)、系统性硬化症、混合性结缔组织病、自身免疫性甲状腺炎、恶性贫血等[7],但国内外罕见SLE并发Ps的报道。本文回顾性分析了北京协和医院收治的SLE并发Ps患者的临床资料,总结两种疾病共存的临床及免疫学特点,以探讨两种疾病共存的可能机制。
对象和方法
对象
纳入1990年1月至2015年6月北京协和医院门诊或住院的SLE并发Ps患者。SLE诊断均符合美国风湿病协会(American College of Rheumatology,ACR)1997年修订的SLE分类标准[8],且经皮肤科专科医师确诊Ps。
方法
收集患者以下资料:一般资料、Ps与SLE确诊的时间间隔、Ps类型、SLE系统受累、实验室检查及治疗等。
统计学方法
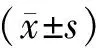
结 果
一般资料
共纳入15例SLE并发Ps患者,其中女13例(86.67%),男2例;年龄为17~59岁,平均年龄为(37.6±12.97)岁。12例(80.00%,1215)为Ps先发于SLE(包括1例自幼患病者并伴有家族遗传史,2例PsA先发但具体确诊时间不详),3例SLE先发于Ps。Ps与SLE确诊的时间间隔1~24年,中位间期8年(表1)。
临床特点
Ps类型:寻常型10例,脓疱型1例,红皮病型1例,可疑银屑病关节炎(psoriatic arthritis,PsA)1例,另有2例类型不详(表1)。
12例患者抗核抗体(antinuclear antibody,ANA)均为阳性,抗ds-DNA(double-stranded DNA)抗体阳性9例,抗SmRNP(Smithribonucleoprotein)抗体阳性9例,抗SSA(Sjögren syndrome antigen A)抗体阳性8例,抗SSB(Sjögren syndrome antigen B)抗体阳性3例。其中1例为RA起病的SLE患者,伴高滴度类风湿因子(rheumatoid factor,RF)和抗环瓜氨酸肽(anticyclic citrullinated peptide,CCP)抗体。1例既往Ps皮疹类型不详的Ps患者,确诊SLE时虽无现患Ps,但影像学出现部分末节指骨呈笔尖样改变,可疑PsA。
治疗及临床结局
SLE治疗:所有患者均使用激素治疗,根据狼疮器官受累和活动情况,甲泼尼龙冲击治疗者2例(0.5~1.0 gd,3 d),8例初始应用大剂量激素(相当泼尼松≥1 mg·kg-1·d-1)。13例患者应用免疫抑制剂治疗(环磷酰胺9例、甲氨蝶呤8例、来氟米特5例、环孢素3例、硫唑嘌呤2例、霉酚酸酯2例等),其中7例患者使用羟氯喹治疗。
Ps治疗:外用药(如维生素D3类似物、糖皮质激素、维A酸、他克莫司等)、全身口服用药(如免疫抑制剂、糖皮质激素、维A酸类等)及生物制剂等,其中1例患者先后使用过依那西普、英夫利昔单抗。
经上述治疗后,15例患者狼疮病情好转,Ps皮疹缓解,无Ps皮疹加重现象(表1)。
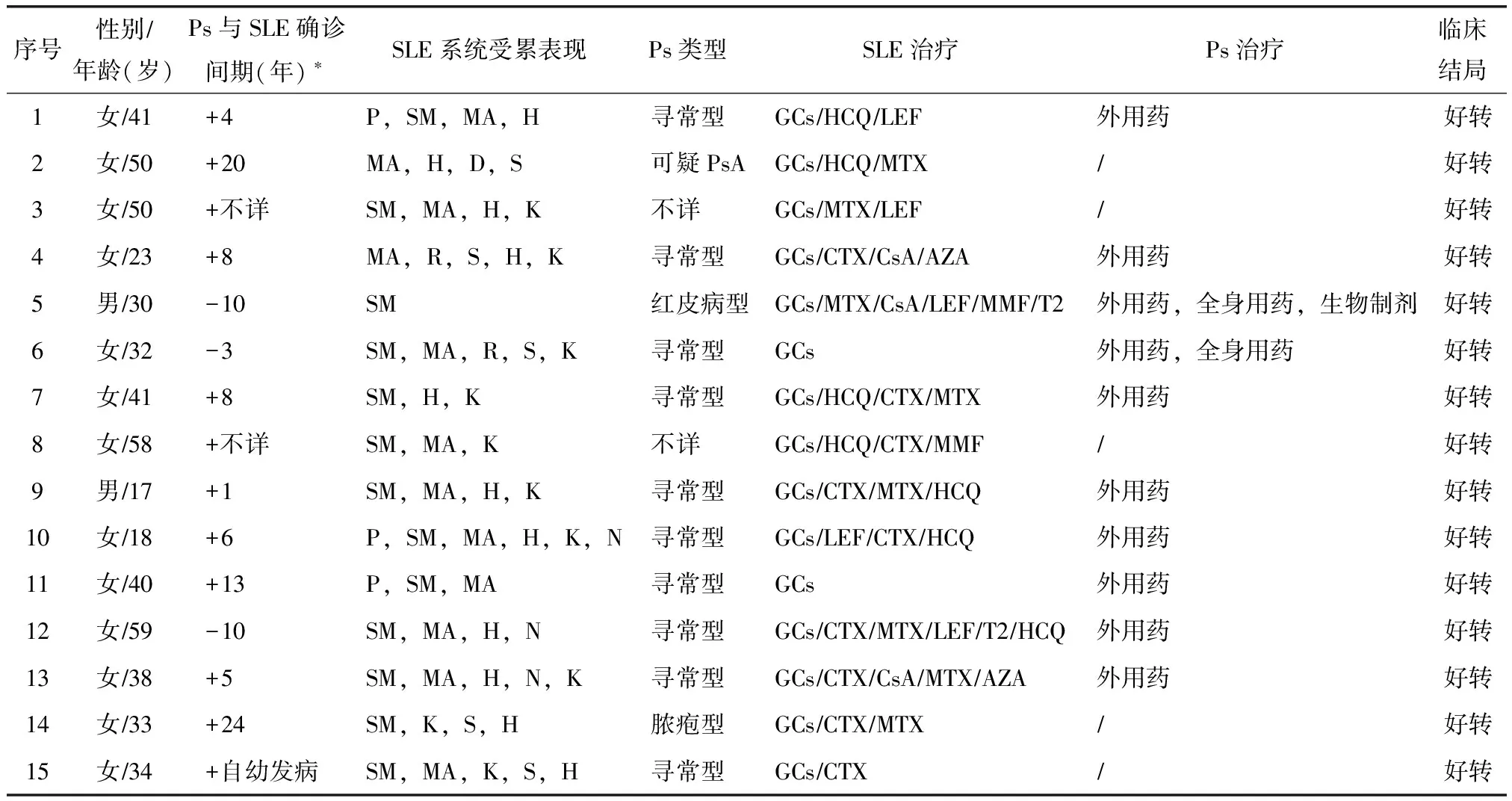
表1 15例SLE并发Ps患者临床特点
*+示Ps先于SLE发病,-示SLE先于Ps发病;SLE:系统性红斑狼疮;Ps:银屑病;P:光过敏;SM:除光过敏外的皮肤和黏膜;MA:肌肉关节;H:血液;R:呼吸;S:浆膜;K:肾脏;D:消化;N:神经;GCs:糖皮质激素;HCQ:羟氯喹;LEF:来氟米特;MTX:甲氨蝶呤;CTX:环磷酰胺;MMF:霉酚酸酯;CsA:环孢素A;T2:雷公藤多甙;AZA:硫唑嘌呤
讨 论
SLE与Ps的病因及发病机制均尚未完全明了,虽然两种疾病均与遗传、免疫、感染及环境等因素有关,但两种疾病共存仍属罕见,目前为止国内外仅有部分个案报道[9-12]。Zalla和Muller[13]10年的回顾性研究中发现,9420例Ps患者中有42例患SLE,流行病学评估显示,Ps患者中0.69%患有LE或其他光敏性皮肤病,且女性较男性发生率高。本研究纳入的15例SLE并发Ps患者中,女13例,男2例,这也与SLE性别分布特点一致;而报道显示,SLE患者仅1.1%患Ps,这与Ps在总体人群中的发病率无明显区别[14]。
在多数报道中,Ps先发于SLE[10],但也有两种病同时发病或SLE先发病的病例报道。本研究15例患者中12例为Ps先发于SLE,3例SLE先发于Ps,与文献报道类似,但无明确同时发病者。据推测,Ps先发于SLE发病很可能是由于治疗Ps过程中所用紫外光照射引发的免疫应答所引发,Ps使用中波紫外线或补骨脂素长波紫外线疗法可以诱发红斑狼疮[15]。据报道,接受抗肿瘤坏死因子(anti-tumor necrosis factor alfa,Anti-TNF-α)抑制剂治疗的Ps患者可检测到自身抗体,且部分狼疮样综合征可随着Anti-TNF-α治疗的停止而消失,也有报道英夫利昔单抗治疗Ps可诱发SLE[16],并可能使SLE病情复发,甚至危及生命[17]。研究1例患者曾使用过依那西普和英夫利昔单抗,但其与SLE的相关性尚不清楚。然而,Varada等[18]回顾性分析96例SLE、盘状红斑狼疮(discoid LE,DLE)、亚急性皮肤型狼疮(subacute cutaneous LE,SCLE)并发Ps和(或)PsA患者的生物制剂治疗情况,结果显示两者共患患者应用Anti-TNF-α抗体引起SLE活动并不常见,仅1例出现狼疮复发,发生率是0.92%;同时提示LE和Ps共患患者应用ustekinumab和abatacept也是安全有效的。
目前已证实羟氯喹可使Ps患者皮疹症状加重,故推测SLE患者应用羟氯喹可诱发Ps的发生。国内也有文献报道了羟氯喹诱发Ps发生的病例[19]。本研究有7例患者在确诊两种疾病共存后仍使用了羟氯喹治疗,且临床随诊观察中并未发现Ps皮损加重的现象,二者关联性尚需进一步明确。
SLE与Ps共存于同一患者可能并非偶然,两种疾病在病因及发病机制上都与感染、遗传及免疫有密切关系。两者均有辅助性T细胞17(T helper 17,Th17)的异常,Th17细胞通过产生白介素(interleukin,IL)-17等促炎症因子在SLE、Ps等自身免疫性疾病和炎症性疾病的发病机制中起作用[20]。全基因组相关性研究(Genome-wide association studies,GWASs)揭示,SLE与Ps共有基因易感位点,如主要组织相容复合物(major histocompatibility complex,MHC)、非MHC如PTPN22、STAT4、TNIP1等[21-27]。单核苷酸多态性(single nucleotide polymorphisms,SNPs)研究显示,在中国汉族人群中SLE和Ps两种疾病有共同的易感基因位点NFKBIA和IL28RA,为两者共同通路的揭示和治疗靶点的选择提供了可能[28]。综上,Ps可并发SLE,本研究结果提示可能以Ps先发为主,临床以寻常型Ps多见,但由于单中心数据存在选择性偏差,就目前来说二者共存仍是罕见现象。
总之,尽管SLE和Ps有着共同的可能启动发病的因素,但关于两种疾病在发生发展过程中有无、以及有何种共同病理通路,仍有待更加深入的研究。
[1]Lau CS,Yin G,Mok MY.Ethnic and geographical differences in systemic lupus erythematosus:an overview[J].Lupus,2006,15:715-719.
[2]Bhalerao J,Bowcock AM.The genetics of psoriasis:a complex disorder of the skin and immune system[J].Hum Mol Genet,1998,7:1537-1545.
[3]Cargill M,Schrodi SJ,Chang M,et al.A large-scale genetic association study confirms IL12B and leads to the identification of IL23R as psoriasis-risk genes[J].Am J Hum Genet,2007,80:273-290.
[4]Kurd SK,Gelfand JM.The prevalence of previonsly diagnosed and undiagnosed psoriasis in US adults:results form NHANES 2003-2004[J].J Am Acad Dermatol,2009,60:218-224.
[5]Yip SY.The prevalence of psoriasis in the Mongoloid race[J].J Am Acad Dermatol,1984,10:965-968.
[6]Shao CG,Zhang GW,Wang GC.Distribution of psoriasis in china:a nation-wide screening[J].Proc Chin Acad Med Sci Peking Union Med Coll,1987,2:59-65.
[7]Lorber M,Gershwin ME,Shoenfeld Y.The coexistence of systemic lupus erythematosus with other autoimmune disease:the kaleidoscope of autoimmunity[J].Semin Arthritis Rheum,1994,24:105-113.
[8]Hochberg MC.Updating the American College of Rheumatology revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus[J].Arthritis Rheum,1997,40:1725.
[9]Lynch WS,Roenigk HH Jr.Lupus erythematosus and psoriasis vulgaris[J].Cutis,1978,21:511-516,523-525.
[10] Millns JL,Muller SA.The coexistence of psoriasis and lupus erythematosus.An analysis of 27 cases[J].Arch Dermatol,1980,116:658-663.
[11] Hays SB,Camisa C,Luzar MJ.The coexistence of systemic lupus erythematosus and psoriasis[J].J Am Acad Dermatol,1984,10:619-622.
[12] Kim EJ,Park HS,Yoon HS,et al.A case of psoriasis accompanied by systemic lupus erythematosus[J].Ann Dermatol,2015,27:347-348.
[13] Zalla MJ,Muller SA.The coexistence of psoriasis and lupus erythematosus and other photosensitive disorders[J].Acta Derm Venereol Suppl(Stockh),1996,195:1-15.
[14] Feldman CH,Hiraki LT,Liu J et al.Epidemiology and sociodemographics of systemic lupus erythematosus and lupus nephritis among US adults with Medicaid coverage,2000-2004[J].Arthritis Rheum,2013,65:753-763.
[15] Avriel A,Zeller L,Flusser D,et al.Coexistent of psoriasis arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus[J].Isr Med Assoc J,2007,9:48-49.
[16] Berthelot C,Nash J,Duvic M.Coexistent psoriasis and lupus erythematosus treated with alefacept[J].Am J Clin Dermatol,2007,8:47-50.
[17] Aringer M,Houssiau F,Gordon C,et al.Adverse events and efficacy of TNF-alpha blockade with infliximab in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus:long-term follow-up of 13 patients[J].Rheumatology(Oxford),2009,48:1451-1454.
[18] Varada S,Gottlieb AB,Merola JF,et al.Treatment of coexistent psoriasis and lupus erythematosus[J].J Am Acad Dermatol,2015,72:253-260.
[19] 徐遵芳,梁希举,杨立新,等.羟氯喹诱发银屑病一例[J].中华风湿病学杂志,2002,12:728.
[20] Raychaudhuri SP.Role of IL-17 in psoriasis and psoriasis arthritis[J].Clin Rev Allergy Immunol,2013,44:183-193.
[21] International Consortium for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Genetics(SLEGEN),Harley JB,Alarcon-Riquelme ME,et al.Genome-wide association scan in women with systemic lupus erythematosus identifies susceptibility variants in ITGAM,PXK,KIAA1542 and other loci[J].Nat Genet,2008,40:204-210.
[22] Li Y,Liao W,Chang M,et al.Further genetic evidence for these psoriasis-risk genes:ADAM33,CDKAL1,and PTPN22[J].J Invest Dermatol,2009,129:629-634.
[23] Nair PR,Duffin KC,Helms C,et al.Genome-wide scan reveals association of psoriasis with IL-23 and NF-kappaB pathways[J].Nat Genet,2009,41:199-204.
[24] Zhang XJ,Huang W,Yang S,etal.Psoriasis genome-wide association study identifies susceptibility variants within LCE gene cluster at 1q21[J].Nat Genet,2009,41:205-210.
[25] Han JW,Zheng HF,Cui Y,et al.Genome-wide association study in a Chinese Han population identifies nine new susceptibility loci for systemic lupus erythematosus[J].Nat Genet,2009,41:1234-1237.
[26] Remmers EF,Plenge RM,Lee AT,et al.STAT4 and the risk of rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus[J].N Engl J Med,2007,357:977-986.
[27] Zervou MI,Goulielmos GN,Castor-Giner F,et al.STAT4 gene polymorphism is associated with psoriasis in the genetically homogeneous population of Crete,Greece[J].Hum Immunol,2009,70:738-741.
[28] Li Y,Cheng H,Zuo XB,et al.Association analyses identifying two common susceptibility loci shared by psoriasis and systemic lupus erythematosus in the chinese Han population[J].J Med Genet,2013,50:812-818.

